如下图表示一颗二叉树,对它进行先序遍历操作,采用两种方法,递归和非递归操作。。
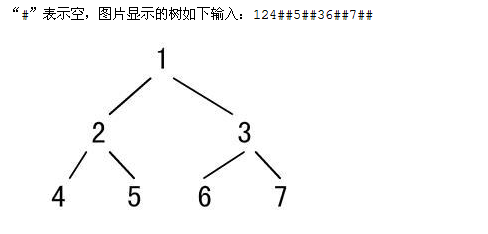
遍历结果为:1245367。
1、递归操作:
思想:若二叉树为空,返回。否则
1)遍历根节点;2)先序遍历左子树;3)先序遍历右子树
代码:
void PreOrder(BiTree root) { if(root==NULL) return ; printf("%c ", root->data); //输出数据 PreOrder(root->lchild); //递归调用,先序遍历左子树 PreOrder(root->rchild); //递归调用,先序遍历右子树 }
2、非递归操作
思想:二叉树的非递归先序遍历,先序遍历思想:先让根进栈,只要栈不为空,就可以做弹出操作, 每次弹出一个结点,记得把它的左右结点都进栈,记得右子树先进栈,这样可以保证右子树在栈中总处于左子树的下面。
代码:
void PreOrder_Nonrecursive(BiTree T) //先序遍历的非递归 { if(!T) return ; stack<BiTree> s; s.push(T); while(!s.empty()) { BiTree temp = s.top(); cout<<temp->data<<" "; s.pop(); if(temp->rchild) s.push(temp->rchild); if(temp->lchild) s.push(temp->lchild); } }
或者:
void PreOrder_Nonrecursive(BiTree T) //先序遍历的非递归 { if(!T) return ; stack<BiTree> s; while(T) // 左子树上的节点全部压入到栈中 { s.push(T); cout<<T->data<<" "; T = T->lchild; } while(!s.empty()) { BiTree temp = s.top()->rchild; // 栈顶元素的右子树 s.pop(); // 弹出栈顶元素 while(temp) // 栈顶元素存在右子树,则对右子树同样遍历到最下方 { cout<<temp->data<<" "; s.push(temp); temp = temp->lchild; } } }