组件注册-自定义TypeFilter指定过滤规则
4.1 FilterType.ANNOTATION 按照注解方式
4.2 FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE 按照给定的类型
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {BookService.class})4.3 FilterType.ASPECTJ 按照ASPECTJ表达式
4.4 FilterType.REGEX 按照正则表达
4.5 FilterType.CUSTOM 按照自定义规则
@ComponentScan(value = "com.hw.springannotation", useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class}),
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {BookService.class}),
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {MyTypeFilter.class})
}
) // 指定只扫描
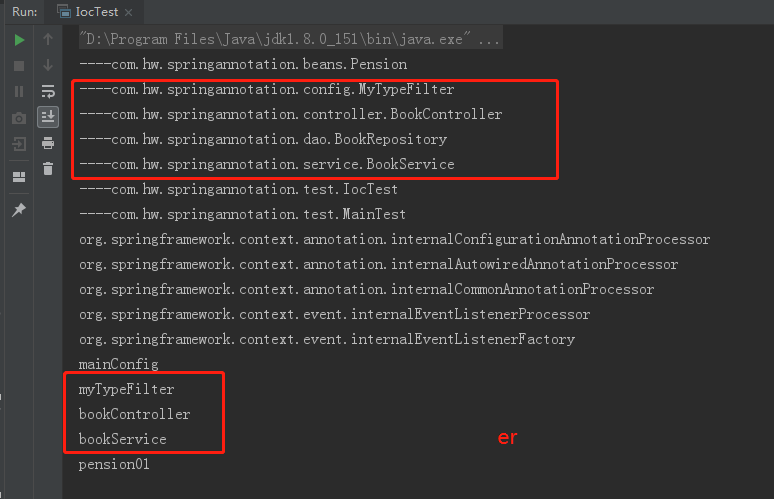
- 创建MyTypeFilter类,需要实现TypeFilter 接口,重写match()方法
package com.hw.springannotation.config;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.ClassMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Description TODO
* @Author hw
* @Date 2018/11/27 18:49
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {
/**
* Determine whether this filter matches for the class described by
* the given metadata.
*
* @param metadataReader the metadata reader for the target class 读取到得当前正在扫描的类的信息
* @param metadataReaderFactory a factory for obtaining metadata readers 一个可以探索其他类信息的工厂类
* for other classes (such as superclasses and interfaces)
* @return whether this filter matches
* @throws IOException in case of I/O failure when reading metadata
*/
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
// 获取当前类的注解信息
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
// 获取当前类信息
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
// 获取当前类的资源(类的路径)
Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource();
String className = classMetadata.getClassName();
System.out.println("----" + className);
if (className.contains("er")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
HashMap按键排序和按值排序
对map集合进行排序
今天做统计时需要对X轴的地区按照地区代码(areaCode)进行排序,由于在构建XMLData使用的map来进行数据统计的,所以在统计过程中就需要对map进行排序。
一、简单介绍Map
在讲解Map排序之前,我们先来稍微了解下map。map是键值对的集合接口,它的实现类主要包括:HashMap,TreeMap,Hashtable以及LinkedHashMap等。其中这四者的区别如下(简单介绍):
HashMap:我们最常用的Map,它根据key的HashCode 值来存储数据,根据key可以直接获取它的Value,同时它具有很快的访问速度。HashMap最多只允许一条记录的key值为Null(多条会覆盖);允许多条记录的Value为 Null。非同步的。
TreeMap: 能够把它保存的记录根据key排序,默认是按升序排序,也可以指定排序的比较器,当用Iterator 遍历TreeMap时,得到的记录是排过序的。TreeMap不允许key的值为null。非同步的。
Hashtable: 与 HashMap类似,不同的是:key和value的值均不允许为null;它支持线程的同步,即任一时刻只有一个线程能写Hashtable,因此也导致了Hashtale在写入时会比较慢。
LinkedHashMap: 保存了记录的插入顺序,在用Iterator遍历LinkedHashMap时,先得到的记录肯定是先插入的.在遍历的时候会比HashMap慢。key和value均允许为空,非同步的。
二、Map排序
TreeMap
TreeMap默认是升序的,如果我们需要改变排序方式,则需要使用比较器:Comparator。
Comparator可以对集合对象或者数组进行排序的比较器接口,实现该接口的public compare(T o1,To2)方法即可实现排序,该方法主要是根据第一个参数o1,小于、等于或者大于o2分别返回负整数、0或者正整数。如下:
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new TreeMap<String, String>(
new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String obj1, String obj2) {
// 降序排序
return obj2.compareTo(obj1);
}
});
map.put("c", "ccccc");
map.put("a", "aaaaa");
map.put("b", "bbbbb");
map.put("d", "ddddd");
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> iter = keySet.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
String key = iter.next();
System.out.println(key + ":" + map.get(key));
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
d:ddddd
c:ccccc
b:bbbbb
a:aaaaa
上面例子是对根据TreeMap的key值来进行排序的,但是有时我们需要根据TreeMap的value来进行排序。对value排序我们就需要借助于Collections的sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)方法,该方法根据指定比较器产生的顺序对指定列表进行排序。但是有一个前提条件,那就是所有的元素都必须能够根据所提供的比较器来进行比较。如下:
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new TreeMap<String, String>();
map.put("d", "ddddd");
map.put("b", "bbbbb");
map.put("a", "aaaaa");
map.put("c", "ccccc");
//这里将map.entrySet()转换成list
List<Map.Entry<String,String>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String,String>>(map.entrySet());
//然后通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,String>>() {
//升序排序
public int compare(Entry<String, String> o1,
Entry<String, String> o2) {
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for(Map.Entry<String,String> mapping:list){
System.out.println(mapping.getKey()+":"+mapping.getValue());
}
}
}
运行结果
a:aaaaa
b:bbbbb
c:ccccc
d:ddddd
HashMap
我们都是HashMap的值是没有顺序的,他是按照key的HashCode来实现的。对于这个无序的HashMap我们要怎么来实现排序呢?参照TreeMap的value排序,我们一样的也可以实现HashMap的排序。
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("c", "ccccc");
map.put("a", "aaaaa");
map.put("b", "bbbbb");
map.put("d", "ddddd");
List<Map.Entry<String,String>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String,String>>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,String>>() {
//升序排序
public int compare(Entry<String, String> o1,
Entry<String, String> o2) {
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for(Map.Entry<String,String> mapping:list){
System.out.println(mapping.getKey()+":"+mapping.getValue());
}
}
}
运行结果
a:aaaaa
b:bbbbb
c:ccccc
d:ddddd
https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhong/p/6113183.html
