Hough Transform 霍夫变换检测直线
从理论到代码,再从代码到理论
(1)理论之通俗理解:
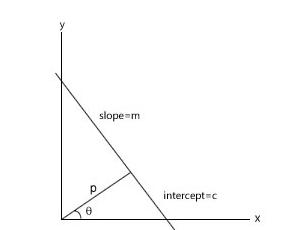
1.在图像中检测直线的问题,其实质是找到构成直线的所有的像素点。那么问题就是从找到直线,变成找到符合y=mx+c的所有(x,y)的点的问题。
2.进行坐标系变化y=mx+c,变成c=-xm+b。直线上的点(x1,y1),在转换坐标系后为一条直线。这个原理应该是高中的。
3.直线上每一个点在MC坐标系中都表现为直线,而且,这些直线都相交于一个点,(m,c)。找到所有点的问题,转变为寻找直线的问题。
4.对于图像中的每一个点,在MC坐标系中对应着很多的直线。找到直线的交点,就对应着找到图像中的直线。

如何实现:
1. 将θ角在-90度到90度的范围里,划分为很多区间,对所有的像素点(x,y)在所有θ角的时候,求出ρ.从而累加ρ值出现的次数。高于某个阈值的ρ就是一个直线。
2. 这个过程就类似于如下一个二维的表格,横坐标就是θ角,ρ就是到直线的最短距离。
横坐标θ不断变换,对于所有的不为0的像素点,计算出ρ,找到ρ在坐标(θ,ρ)的位置累加1.
3. 上图中局部最大的就是找到的直线的θ和ρ的值。
(2) 具体代码片段
for( ang = 0, n = 0; n < numangle; ang += theta, n++ )
{
tabSin[n] = (float)(sin(ang) * irho);
tabCos[n] = (float)(cos(ang) * irho);
}
// stage 1. fill accumulator
for( i = 0; i < height; i++ )
for( j = 0; j < width; j++ )
{
if( image[i * step + j] != 0 )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
r = cvRound( j * tabCos[n] + i * tabSin[n] );
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
accum[(n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1]++;
}
}
// stage 2. find local maximums
for( r = 0; r < numrho; r++ )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int base = (n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1;
if( accum[base] > threshold &&
accum[base] > accum[base - 1] && accum[base] >= accum[base + 1] &&
accum[base] > accum[base - numrho - 2] && accum[base] >= accum[base + numrho + 2] )
sort_buf[total++] = base;
}
// stage 3. sort the detected lines by accumulator value
icvHoughSortDescent32s( sort_buf, total, accum );
// stage 4. store the first min(total,linesMax) lines to the output buffer
linesMax = MIN(linesMax, total);
scale = 1./(numrho+2);
for( i = 0; i < linesMax; i++ )
{
CvLinePolar line;
int idx = sort_buf[i];
int n = cvFloor(idx*scale) - 1;
int r = idx - (n+1)*(numrho+2) - 1;
line.rho = (r - (numrho - 1)*0.5f) * rho;
line.angle = n * theta;
cvSeqPush( lines, &line );
}
{
tabSin[n] = (float)(sin(ang) * irho);
tabCos[n] = (float)(cos(ang) * irho);
}
// stage 1. fill accumulator
for( i = 0; i < height; i++ )
for( j = 0; j < width; j++ )
{
if( image[i * step + j] != 0 )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
r = cvRound( j * tabCos[n] + i * tabSin[n] );
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
accum[(n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1]++;
}
}
// stage 2. find local maximums
for( r = 0; r < numrho; r++ )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int base = (n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1;
if( accum[base] > threshold &&
accum[base] > accum[base - 1] && accum[base] >= accum[base + 1] &&
accum[base] > accum[base - numrho - 2] && accum[base] >= accum[base + numrho + 2] )
sort_buf[total++] = base;
}
// stage 3. sort the detected lines by accumulator value
icvHoughSortDescent32s( sort_buf, total, accum );
// stage 4. store the first min(total,linesMax) lines to the output buffer
linesMax = MIN(linesMax, total);
scale = 1./(numrho+2);
for( i = 0; i < linesMax; i++ )
{
CvLinePolar line;
int idx = sort_buf[i];
int n = cvFloor(idx*scale) - 1;
int r = idx - (n+1)*(numrho+2) - 1;
line.rho = (r - (numrho - 1)*0.5f) * rho;
line.angle = n * theta;
cvSeqPush( lines, &line );
}