一、命名空间与作用域
命名空间是名字和对象的映射,就像是字典,key是变量名,value是变量的值
1.命名空间的定义
name='egon' #定义变量
def func(): #定义函数
pass
class Foo: #定义类
pass
2.命名空间的分类
- 1.内置名称空间: 随着python解释器的启动而产生,包括异常类型、内建函数和特殊方法,可以代码中任意地方调用
print(sum)
print(max)
print(min)
print(max([1,2,3]))
import builtins
for i in dir(builtins): #打印所有的内置函数
print(i)
输出

<built-in function sum>
<built-in function max>
<built-in function min>
3
ArithmeticError
AssertionError
AttributeError
BaseException
BlockingIOError
BrokenPipeError
BufferError
BytesWarning
ChildProcessError
ConnectionAbortedError
ConnectionError
ConnectionRefusedError
ConnectionResetError
DeprecationWarning
EOFError
Ellipsis
EnvironmentError
Exception
False
FileExistsError
FileNotFoundError
FloatingPointError
FutureWarning
GeneratorExit
IOError
ImportError
ImportWarning
IndentationError
IndexError
InterruptedError
IsADirectoryError
KeyError
KeyboardInterrupt
LookupError
MemoryError
NameError
None
NotADirectoryError
NotImplemented
NotImplementedError
OSError
OverflowError
PendingDeprecationWarning
PermissionError
ProcessLookupError
RecursionError
ReferenceError
ResourceWarning
RuntimeError
RuntimeWarning
StopAsyncIteration
StopIteration
SyntaxError
SyntaxWarning
SystemError
SystemExit
TabError
TimeoutError
True
TypeError
UnboundLocalError
UnicodeDecodeError
UnicodeEncodeError
UnicodeError
UnicodeTranslateError
UnicodeWarning
UserWarning
ValueError
Warning
ZeroDivisionError
__build_class__
__debug__
__doc__
__import__
__loader__
__name__
__package__
__spec__
abs
all
any
ascii
bin
bool
bytearray
bytes
callable
chr
classmethod
compile
complex
copyright
credits
delattr
dict
dir
divmod
enumerate
eval
exec
exit
filter
float
format
frozenset
getattr
globals
hasattr
hash
help
hex
id
input
int
isinstance
issubclass
iter
len
license
list
locals
map
max
memoryview
min
next
object
oct
open
ord
pow
print
property
quit
range
repr
reversed
round
set
setattr
slice
sorted
staticmethod
str
sum
super
tuple
type
vars
zip
- 2.全局名称空间:文件的执行会产生全局名称空间,指的是文件级别定义的名字都会放入该空间
x=1 #全局命名空间
def func():
money=2000 #非全局
x=2
print('func')
print(x)
print(func)
func()
- 3.局部名称空间:调用函数时会产生局部名称空间,只在函数调用时临时绑定,调用结束解绑定
x=10000 #全局
def func():
x=1 #局部
def f1():
pass
3.作用域
命名空间的可见性就是作用域
- 1. 全局作用域:内置名称空间,全局名称空间
- 2. 局部作用域:局部名称空间
名字的查找顺序:局部名称空间---》全局名层空间---》内置名称空间
查看全局作用域内的名字:gloabls()
查看局部作用域内的名字:locals()
全局作用域的名字:全局有效,在任何位置都能被访问到,除非del删掉,否则会一直存活到文件执行完毕
局部作用域的名字:局部有效,只能在局部范围调用,只在函数调用时才有效,调用结束就失效
x=1000
def func(y):
x=2
print(locals())
print(globals())
func(1)
输出
{'y': 1, 'x': 2}
{'__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x10c436c88>, '__package__': None, '__cached__': None, '__file__': '/Users/hexin/PycharmProjects/py3/day4/2.py', 'func': <function func at 0x10c3c9f28>, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__spec__': None, '__doc__': None, 'time': <module 'time' (built-in)>, '__name__': '__main__', 'x': 1000}
二、闭包函数
简单来说,一个闭包就是你调用了一个函数A,这个函数A返回了一个函数B给你。这个返回的函数B就叫做闭包。
闭包函数须满足以下条件:
1. 定义在内部函数;
2. 包含对外部作用域而非全局作用域的引用;
例
def f1():
x = 1
def f2():
print(x)
return f2
f=f1()
print(f)
x=100
f()
print(x)
输出
<function f1.<locals>.f2 at 0x107714400>
1
100
闭包应用
from urllib.request import urlopen
def index(url):
def get():
return urlopen(url).read()
return get
oldboy=index('http://crm.oldboyedu.com')
print(oldboy().decode('utf-8'))
输出

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>OldboyCRM</title>
<!--Bootstrap Stylesheet [ REQUIRED ]-->
<link href="/static/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="/static/css/custom.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Nifty Stylesheet [ REQUIRED ]-->
<link href="/static/css/nifty.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Font Awesome [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<link href="/static/plugins/font-awesome/css/font-awesome.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Bootstrap Validator [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<link href="/static/plugins/bootstrap-validator/bootstrapValidator.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Demo [ DEMONSTRATION ]-->
<link href="/static/css/demo/nifty-demo.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Bootstrap Datepicker [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<link href="/static/plugins/bootstrap-datepicker/bootstrap-datepicker.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="container" class="effect mainnav-lg">
<div id="page-title">
<h1 class="page-header text-overflow">老男孩IT教育 | 只培养技术精英</h1>
</div>
<div id="page-content">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3 class="panel-title">学员平台</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body" style="">
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/grade/single/">成绩查询</a></h4>
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/scholarship/">奖学金政策</a></h4>
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/training_contract/">培训协议查询</a></h4>
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/compliant/">投诉建议</a></h4>
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/stu_faq/">学员常见问题汇总</a></h4>
<h4><a class="btn-link" href="/stu/">学员登录</a></h4>
</div> <!--end panel-body-->
</div> <!--end panel-->
</div> <!--end col-lg-12-->
</div><!--end row-->
</div><!--end page-content-->
</div>
<!--jQuery [ REQUIRED ]-->
<script src="/static/js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<!--BootstrapJS [ RECOMMENDED ]-->
<script src="/static/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<!--Nifty Admin [ RECOMMENDED ]-->
<script src="/static/js/nifty.min.js"></script>
<!--jquery-cookie-->
<script src="/static/js/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script src="/static/js/ajax_comm.js"></script>
<!--Bootstrap Wizard [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<script src="/static/plugins/bootstrap-wizard/jquery.bootstrap.wizard.min.js"></script>
<!--Bootstrap Validator [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<script src="/static/plugins/bootstrap-validator/bootstrapValidator.min.js"></script>
<!--Demo script [ DEMONSTRATION ]-->
<script src="/static/js/demo/nifty-demo.min.js"></script>
<!--Form Wizard [ SAMPLE ]-->
<script src="/static/js/demo/form-wizard.js"></script>
<!--Bootstrap Datepicker [ OPTIONAL ]-->
<script src="/static/plugins/bootstrap-datepicker/bootstrap-datepicker.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
三、装饰器
1.定义
装饰器:修饰别人的工具,修饰添加功能,工具指的是函数
装饰器本身可以是任何可调用对象,被装饰的对象也可以是任意可调用对象
2.为什么要用装饰器?
开放封闭原则:对修改是封闭的,对扩展是开放的
装饰器就是为了在不修改被装饰对象的源代码以及调用方式的前提下,为其添加新功能
3.装饰器的实现
装饰器的功能是将被装饰的函数当作参数传递给与装饰器对应的函数(名称相同的函数),并返回包装后的被装饰的函数”
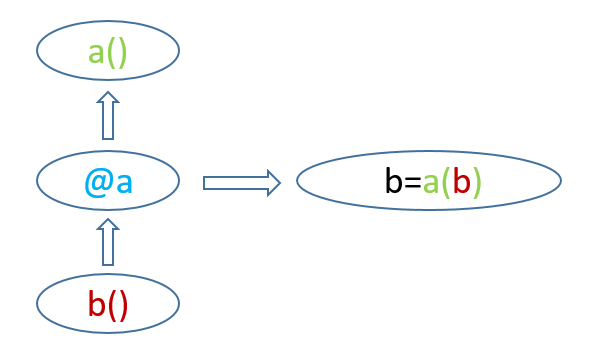
直接看示意图,其中 a 为与装饰器 @a 对应的函数, b 为装饰器修饰的函数,装饰器@a的作用是:
简而言之:@a 就是将 b 传递给 a(),并返回新的 b = a(b)
例如
def a(name): #与装饰器对应的函数
return name()
@a #装饰器 b = a(b)
def b(): #被装饰函数
print('hexin')
输出
hexin
解析过程是这样子的:
1.python 解释器发现@a,就去调用与其对应的函数( a 函数)
2.a 函数调用前要指定一个参数,传入的就是@a下面修饰的函数,也就是 b()
3.a() 函数执行,调用 b(),b() 打印“hexin”
5.装饰器的应用
import time
def timmer(func):
def wrapper():
start_time=time.time()
func() #index()
stop_time=time.time()
print('run time is %s' %(stop_time-start_time))
return wrapper
@timmer #index=timmer(index)
def index():
time.sleep(1)
print('welcome to index')
index()
输出
welcome to index
run time is 1.005241870880127
例子
login_user={'user':None,'status':False}
def auth(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
if login_user['user'] and login_user['status']:
res=func(*args,**kwargs)
return res
else:
name=input('请输入用户名: ')
password=input('请输入密码: ')
if name == 'hexin' and password == '123':
login_user['user']='hexin'
login_user['status']=True
print('�33[45mlogin successful�33[0m')
res=func(*args,**kwargs)
return res
else:
print('�33[45mlogin err�33[0m')
return wrapper
@auth #index=auth(index)
def index():
print('welcome to index page')
@auth #home=auth(home)
def home(name):
print('%s welcome to home page' %name)
index()
home('hexin')
输出
请输入用户名: heixn
请输入密码: 123
login err
请输入用户名: hexin
请输入密码: 123
login successful
hexin welcome to home page
补充:
装饰器的基本框架:
def timer(func):
def wrapper():
func()
return wrapper
带参数
def timer(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
func(*args,**kwargs)
return wrapper