一、概念
朴素贝叶斯模型(Naive Bayesian Model,NBM)是以条件概率为基础的分类器,是一种监督算法,常被用于文本分类和垃圾邮件过滤。
贝叶斯理论解决的是逆向概率问题,即通过已经发生的已知的概率来推测未发生的事将会发生的概率。
二、计算
朴素贝叶斯各个事件发生的概率是彼此独立的,即m事件概率P(m)和n事件概率P(n)同时发生的概率为P(mn)=P(m)*P(n)。
条件概率的含义,B发生时A发生的概率为:
![]()
A发生时B发生的概率为:
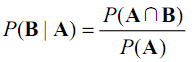
所以:
![]()
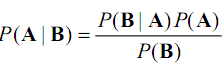
即,通过已知结果算出概率,然后根据一些条件推测即将发生的结果。
三、实现
features = ['looks', 'credit', 'education', 'height'] samples = [['nice', 'bad', 'S', 'low', 'no'], ['ugly', 'good', 'S', 'high', 'no'], ['nice', 'good', 'S', 'high', 'yes'], ['ugly', 'good', 'H', 'high', 'yes'], ['nice', 'bad', 'S', 'high', 'no'], ['nice', 'bad', 'S', 'high', 'no'], ['nice', 'good', 'H', 'low', 'yes'], ['ugly', 'good', 'M', 'high', 'yes'], ['nice', 'good', 'M', 'high', 'yes'], ['ugly', 'bad', 'H', 'high', 'yes'], ['nice', 'good', 'S', 'low', 'no'], ['nice', 'good', 'S', 'low', 'no'], ['nice', 'bad', 'H', 'low', 'no']] def train(): data = {} results = {} for sample in samples: for index in range(len(sample) - 1): element = sample[index] relation = '%s_%s' % (element, sample[-1]) if element in data: data[element] += 1 else: data[element] = 1 if relation in data: data[relation] += 1 else: data[relation] = 1 if sample[-1] in results: results[sample[-1]] += 1 else: results[sample[-1]] = 1 return data, results def classify(new_data): data, results = train() classify_result = [] for ret_key, ret_value in results.items(): dividend_probabilities = [] divisor_probabilities = [] for element in new_data: divisor_probabilities.append(data[element] / len(samples)) relation = '%s_%s' % (element, ret_key) dividend_probabilities.append(data.get(relation, 0) / ret_value) value_probability = ret_value / len(samples) final_probability = reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, dividend_probabilities) * value_probability / reduce( lambda x, y: x * y, divisor_probabilities) classify_result.append((ret_key, final_probability)) return classify_result print(classify(['nice', 'bad', 'S', 'low']))
有一款开源的贝叶斯分类器也很好用,叫做naive-bayes-classifier,因为该分类传入的为字符串,在传入样本前需要先进行转换。
from naiveBayesClassifier import tokenizer from naiveBayesClassifier.trainer import Trainer from naiveBayesClassifier.classifier import Classifier def third_part_method(test_data): news_trainer = Trainer(tokenizer) for sample in samples: news_trainer.train(' '.join(sample[0:-1]), sample[-1]) news_classifier = Classifier(news_trainer.data, tokenizer) a = ' '.join(test_data) classification = news_classifier.classify(a) return classification print(third_part_method(['nice', 'good', 'H', 'high']))
对于同一个测试数据,两种方法概率不相等,但是分类结果是一致的。
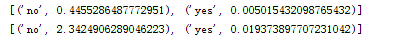
第一行是第三方包的结果,第二行是自己写的分类器的结果。