题目: 5 替换空格
描述
请实现一个函数, 把字符串中的每个空格替换成
"%20".
- 示例
输入: "We are happy!"
输出: "We%20are%20happy!"
- 注意
应该判断是否有
空间限制
此处限制为只能在原字符数组进行替换, 假设数组给定足够的空余内存
思路
因为是在原数组上进行操作, 主要需要考虑如何移动有效数据
-
从前往后移动, 每次遇到空格, 就将空格以后的字符向后移动2个位置
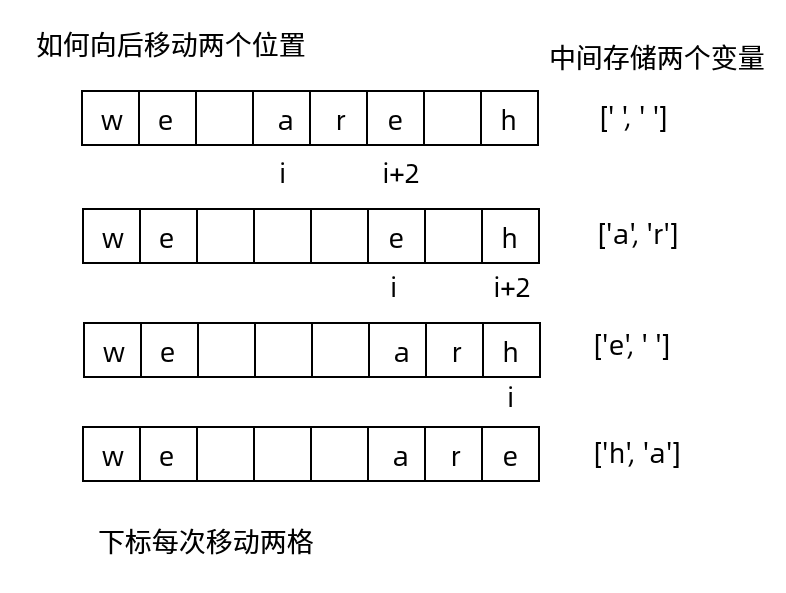
-
从后往前移动, 因为有足够的空余位置, 所以直接从结果(成功替换后)的最后位置出发
逐个替换原有效字符, 遇到空格就相当于加速前进
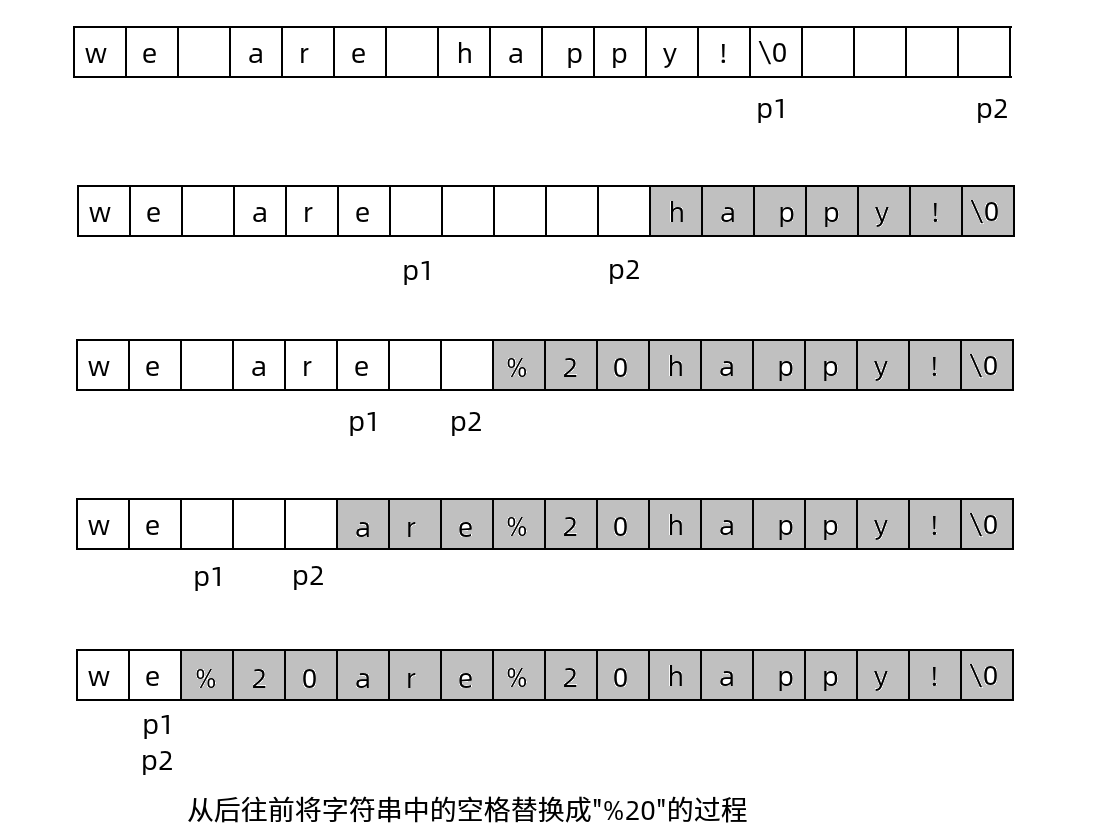
代码实现
class Solution {
/********
* 暴力破解
* 从头到尾遍历
* 每次遇到空格先将数组从该位置向后移动两格
* 并在此填充"%20"
*
* 注意:
* 假设没有足够的空间创建新的字符数组
* 只能在原数组上替换, 原数组后面提供足够的空余
*
* @param chs 需要进行转换的字符数组
*/
public void bruteReplaceBlank(char[] chs) {
if (null == chs) return;
int len = chs.length;
if (len == 0) return;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (chs[i] == '�') {
break;
} else if (chs[i] == ' ') {
pushBack(chs, i+1);
chs[i] = '%'; chs[i+1] = '2'; chs[i+2] = '0';
}
}
}
/******
* 将字符串数组从指定位置向后移动两格
*/
void pushBack(char[] chs, int start) {
char front1 = ' ';
char front2 = ' ';
for (int i = start; i < chs.length-1; i=i+2) {
char t1 = chs[i];
char t2 = chs[i+1];
chs[i] = front1;
chs[i+1] = front2;
front1 = t1;
front2 = t2;
}
}
/************************************************
* 方法二:从后往前处理字符
*/
public void fromEndReplaceBlank(char[] chs) {
if (null == chs) return;
int len = chs.length;
if (len == 0) return;
// realLen 字符串有效长度
int realLen = 0;
// blankCount 字符串中空格数 需要替换的空格
int blankCount = 0;
int i = 0;
while (chs[i] != '�') {
if (chs[i] == ' ') {
blankCount++;
}
realLen++;
i++;
}
// 只有一个空格字符的情况
if (blankCount == realLen) {
chs[0] = '%'; chs[1] = '2'; chs[2] = '0';
return;
}
// p 表示替换空格后, 有效字符数组最后一位下标
// q 表示当前有效字符数组最后一位下标
int p = realLen + 2*blankCount, q = realLen;
// 需要替换的字符过多 超出原字符数组的边界
if (p > len) return;
while (q >= 0 && p > q) {
if (chs[q] != ' ') {
chs[p--] = chs[q];
} else {
chs[p--] = '0';
chs[p--] = '2';
chs[p--] = '%';
}
q--;
}
}
}
- 测试
public class ReplaceBlank {
static Solution s = new Solution();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试用例包含空格
// 空格在前面 " we are happy!"
unitTest(generateTestChars(" we are happy!"));
// 空格在中间 "we are happy!"
unitTest(generateTestChars("we are happy!"));
// 空格在后面 "we are happy! "
unitTest(generateTestChars("we are happy! "));
// 测试用例没有包含空格
// 没空格字符数组 "wearehappy!"
unitTest(generateTestChars("wearehappy!"));
// 特殊测试用例
// 空指针 null
s.bruteReplaceBlank(null);
s.fromEndReplaceBlank(null);
// 空字符串 ""
unitTest(new char[]{});
// 只有一个空格字符 " "
unitTest(generateTestChars(" "));
// 有连续多个空格 "we are happy!"
unitTest(generateTestChars("we are happy!"));
}
static void unitTest(char[] chs) {
char[] test = Arrays.copyOf(chs, chs.length);
s.bruteReplaceBlank(test);
System.out.println("By Brute: " + Arrays.toString(test));
test = Arrays.copyOf(chs, chs.length);
s.fromEndReplaceBlank(test);
System.out.println("From Back: " + Arrays.toString(test));
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------");
}
/***
* 生成测试字符数组
*
* @param str 被包含的字符串
* @return 有足够空余空间且包含str内容的字符数组
*/
static char[] generateTestChars(String str) {
int len = str.length();
char[] chs = Arrays.copyOf(str.toCharArray(), 3 * len);
return chs;
}
}
相关题目: 合并两个排序数组到其中一个数组中
描述
有两个排序的数组A1和A2, 内存在A1的末尾有足够多的空余空间容纳A2.
请实现一个函数, 把A2中的所以数字插入A1中, 并且所有数字是排序的.
- 示例
输入: A1 = [1, 3, 5, 7, , , , ,] A2 = [2, 4, 6, 8]
输出: A1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
思路
采用本例题的思想, 从尾到头比较A1和A2中的数字, 并把较大的数字复制到A1中的合适位置.
代码实现
class Solution {
/*********
* 合并两个排序数组到第一个数组内
* 使用从后往前合并的方式
*
* @param A1 被合并数组
* @param A2 合并数组
* @param len1 A1的有效数字长度
* @param len2 A2的有效数字长度
*/
public void mergeSortedArrays(int[] A1, int[] A2, int len1, int len2) {
if (A1 == null || A2 == null) return;
// 当A1为空数组时, 直接复制A2到A1
if (len1 == 0) {
A1 = Arrays.copyOf(A2, A2.length);
return;
}
// 合并后数组最尾部的下标
int endOfMergeIndex = len1+len2-1;
// p表示A1尾部 q表示A2尾部
int p = len1-1, q = len2-1;
while (p >= 0 && q >= 0) {
if (A1[p] > A2[q]) {
A1[endOfMergeIndex--] = A1[p--];
} else {
A1[endOfMergeIndex--] = A2[q--];
}
}
// 当A2没合并完
while (q > 0) {
A1[endOfMergeIndex--] = A2[q--];
}
}
}
- 测试
public class MergeSortedArrays {
static Solution s = new Solution();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试用例 准备
int[] A11 = {1,3,5,6};
int[] A2 = {2,4,6,8};
// 有足够的空间合并A2
int[] A1 = Arrays.copyOf(A11, A11.length+A2.length);
System.out.println("before: " + Arrays.toString(A1));
// before: [1, 3, 5, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0]
s.mergeSortedArrays(A1, A2, A11.length, A2.length);
System.out.println("after: " + Arrays.toString(A1));
// after: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 8]
}
}