这里主要涉及到五张表:用户表,角色表(用户所拥有的角色),权限表(角色所涉及到的权限),用户-角色表(用户和角色是多对多的),角色-权限表(角色和权限是多对多的).表结构建立的sql语句如下:

CREATE TABLE `module` ( `mid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `mname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`mid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of module -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `module` VALUES ('1', 'add'); INSERT INTO `module` VALUES ('2', 'delete'); INSERT INTO `module` VALUES ('3', 'query'); INSERT INTO `module` VALUES ('4', 'update'); -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for module_role -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `module_role`; CREATE TABLE `module_role` ( `rid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `mid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, KEY `rid` (`rid`), KEY `mid` (`mid`), CONSTRAINT `mid` FOREIGN KEY (`mid`) REFERENCES `module` (`mid`), CONSTRAINT `rid` FOREIGN KEY (`rid`) REFERENCES `role` (`rid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of module_role -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('1', '1'); INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('1', '2'); INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('1', '3'); INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('1', '4'); INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('2', '1'); INSERT INTO `module_role` VALUES ('2', '3'); -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for role -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`; CREATE TABLE `role` ( `rid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `rname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`rid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of role -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `role` VALUES ('1', 'admin'); INSERT INTO `role` VALUES ('2', 'customer'); -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `uid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`uid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of user -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'wulifu', '123456'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'root', '123456'); -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for user_role -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_role`; CREATE TABLE `user_role` ( `uid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `rid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, KEY `u_fk` (`uid`), KEY `r_fk` (`rid`), CONSTRAINT `r_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`rid`) REFERENCES `role` (`rid`), CONSTRAINT `u_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`uid`) REFERENCES `user` (`uid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of user_role -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES ('1', '1'); INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES ('2', '2');
二、功能要求
admin要求只有具有admin角色的用户才能访问,update需要有update权限的用户才能访问,login、loginUser都不做拦截。
预期目标:
wulifu是有admin角色和所有权限,所以用wulifu登录后,可以访问update和admin,但是不能访问guest;而root是customer角色,只有add和query权限,所以不能访问admin和update。
三、添加依赖,配置文件
1、springboot项目,项目结构如下:
2、添加依赖

<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.0.20</version> </dependency> <!--常用的工具包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> <version>3.4</version> </dependency> <!--spring的上下文工具包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>4.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!--对jsp的处理--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
3、application.yml

server: port: 8010 tomcat.uri-encoding: UTF-8 spring: datasource: type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro?characterEncoding=UTF-8 username: root password: 123456 mvc: view: prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/ suffix: .jsp mybatis: mapper-locations: mappers/*.xml # mapper.xml中的resultType中经常会用到一些自定义POJO,你可以用完全限定名来指定这些POJO的引用,例如 # <select id="getUsers" resultType="com.majing.learning.mybatis.entity.User">, # 又或者你可以通过在application.yml中指定POJO扫描包来让mybatis自动扫描到自定义POJO,如下: # mybatis:type-aliases-package: com.majing.learning.mybatis.entity type-aliases-package: com.example.springbootshiro.pojo
三、项目设计
1、pojo层
User.java
public class User implements Serializable { private Integer uid; private String username; private String password; private Set<Role> roles = new HashSet<>(); }
Role.java
public class Role implements Serializable { private Integer rid; private String rname; private Set<Module> modules = new HashSet<>(); }
Module.java
public class Module implements Serializable { private Integer mid; private String mname; }
2、dao层
UserMapper.java

import com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserMapper { User findByUserName(String username); }
UserMapper.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.example.springbootshiro.dao.UserMapper"> <resultMap id="userMap" type="com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.User"> <id property="uid" column="uid"/> <result property="username" column="username"/> <result property="password" column="password"/> <collection property="roles" ofType="com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.Role"> <id property="rid" column="rid"/> <result property="rname" column="rname"/> <collection property="modules" ofType="com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.Module"> <id property="mid" column="mid"/> <result property="mname" column="mname"/> </collection> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="findByUserName" parameterType="string" resultMap="userMap"> SELECT u.*,r.*,m.* FROM user u inner join user_role ur on ur.uid=u.uid inner join role r on r.rid=ur.rid inner join module_role mr on mr.rid=r.rid inner join module m on mr.mid=m.mid WHERE username=#{username}; </select> </mapper>

图中红框内可能会报错,但是依然可以正常运行。
3、service层
IUserService.Interface

public interface IUserService { User findByUserName(String username); }
UserServiceImpl.java

@Service("iUserService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User findByUserName(String username) {
return userMapper.findByUserName(username);
}
}
4、controller层
TestController.java

@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/login") public String login(){ return "login"; } @RequestMapping("/index") public String index(){ return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/unauthorized") public String unauthorized() { return "unauthorized"; } /** * 拥有admin角色的人才能访问 * @return */ @RequestMapping("/admin") public String admin(){ return "admin"; } /** * 拥有update权限的人才能访问 * @return */ @RequestMapping("/update") public String update(){ return "update"; } @RequestMapping("/logout") public String logout(){ Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();//取出当前验证主体 if(subject != null){ subject.logout(); //执行一次logout的操作,将session全部清空 } return "login"; } /** * 整个form表单的验证流程: * 将登陆的用户/密码传入UsernamePasswordToken,当调用subject.login(token)开始, * 调用Relam的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法,开始密码验证 * 此时这个时候执行我们自己编写的CredentialMatcher(密码匹配器), * 执行doCredentialsMatch方法,具体的密码比较实现在这实现 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/loginUser") public String loginUser(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password, HttpSession session) { UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password); Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); try { subject.login(token); //登陆成功的话,放到session中 User user = (User) subject.getPrincipal(); session.setAttribute("user", user); return "index"; }catch (Exception e) { return "login"; } } }
5、jsp页面
login.jsp(登录页面)

<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>login</title> </head> <body> <form action="/loginUser" method="post"> <input type="text" name="username"> <br> <input type="password" name="password"> <br> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
index.jsp(登录成功后跳转的页面)

<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <h1> 欢迎登录, ${user.username} </h1> </body> </html>
unauthorized.jsp (无权访问跳转的页面)

<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> Unauthorized! </body> </html>
admin.jsp

<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>admin</title> </head> <body> admin! </body> </html>
update.jsp

<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>update</title> </head> <body> update! </body> </html>
四、配置Shiro
1、核心配置类:ShiroConfiguration.java

import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; @Configuration public class ShiroConfiguration { /** * @Qualifier("XXX") Spring的Bean注入配置注解,该注解指定注入的Bean的名称, * Spring框架使用byName方式寻找合格的bean,这样就消除了byType方式产生的歧义。 */ @Bean("shiroFilter") public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilter(@Qualifier("securityManager") SecurityManager manager) { ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); System.out.println(bean); bean.setSecurityManager(manager); bean.setLoginUrl("/login"); //提供登录到url bean.setSuccessUrl("/index"); //提供登陆成功的url bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauthorized"); /** * 可以看DefaultFilter,这是一个枚举类,定义了很多的拦截器authc,anon等分别有对应的拦截器 */ //配置访问权限 LinkedHashMap<String, String> filterChainDefinitionMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/index", "authc"); //代表着前面的url路径,用后面指定的拦截器进行拦截 filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/login", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/loginUser", "anon"); filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/admin", "roles[admin]"); //admin的url,要用角色是admin的才可以登录,对应的拦截器是RolesAuthorizationFilter filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/update", "perms[update]"); //拥有update权限的用户才有资格去访问 //filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/druid/**", "anon"); //所有的druid请求,不需要拦截,anon对应的拦截器不会进行拦截 filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/**", "user"); //所有的路径都拦截,被UserFilter拦截,这里会判断用户有没有登陆 bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterChainDefinitionMap);//设置一个拦截器链 return bean; } /** * 定义安全管理器securityManager,注入自定义的realm * @param authRealm * @return */ @Bean("securityManager") public SecurityManager securityManager(@Qualifier("authRealm") AuthRealm authRealm) { //这个DefaultWebSecurityManager构造函数,会对Subject,realm等进行基本的参数注入 DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); manager.setRealm(authRealm);//往SecurityManager中注入Realm,代替原本的默认配置 return manager; } //自定义的Realm @Bean("authRealm") //@DependsOn("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor") //可选 public AuthRealm authRealm(@Qualifier("credentialsMatcher") CredentialMatcher matcher) { AuthRealm authRealm = new AuthRealm(); //这边可以选择是否将认证的缓存到内存中,现在有了这句代码就将认证信息缓存的内存中了 //authRealm.setCacheManager(new MemoryConstrainedCacheManager()); //最简单的情况就是明文直接匹配,然后就是加密匹配,这里的匹配工作则就是交给CredentialsMatcher来完成 authRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(matcher); return authRealm; } /** * Realm在验证用户身份的时候,要进行密码匹配 * 最简单的情况就是明文直接匹配,然后就是加密匹配,这里的匹配工作则就是交给CredentialsMatcher来完成 * 支持任意数量的方案,包括纯文本比较、散列比较和其他方法。除非该方法重写,否则默认值为 * @return */ @Bean("credentialsMatcher") public CredentialMatcher credentialsMatcher() { CredentialMatcher credentialsMatcher = new CredentialMatcher(); return credentialsMatcher; } /** * 配置shiro跟spring的关联 * 以下AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor,DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator两个类是为了支持shiro注解 * @param securityManager * @return */ @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(@Qualifier("securityManager") SecurityManager securityManager) { AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); advisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return advisor; } /** * Spring的一个bean , 由Advisor决定对哪些类的方法进行AOP代理 * @return */ @Bean public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() { DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator creator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(); creator.setProxyTargetClass(true); return creator; } /** * lifecycleBeanPostProcessor是负责生命周期的 , 初始化和销毁的类 * (可选) * @return */ @Bean("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor") public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor lifecycleBeanPostProcessor() { return new LifecycleBeanPostProcessor(); } }

这个SecurityManager的导包是org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager,不要导了java的包。
2、自定义域:AuthRealm.java
编写AuthRealm完成根据用户名去数据库的查询,并且将用户信息放入shiro中,供核心配置类:ShiroConfiguration调用。有认证与授权的方法。

import com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.Module; import com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.Role; import com.example.springbootshiro.pojo.User; import com.example.springbootshiro.service.IUserService; import org.apache.shiro.authc.*; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import java.util.*; //AuthenticatingRealm是抽象类,用于认证授权 public class AuthRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Autowired private IUserService iUserService; /** * 用户授权 * @param principals * @return */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { //获取前端输入的用户信息,封装为User对象 User userweb = (User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); //获取前端输入的用户名 String username = userweb.getUsername(); //根据前端输入的用户名查询数据库中对应的记录 User user = iUserService.findByUserName(username); if(user != null){ SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); //因为addRoles和addStringPermissions方法需要的参数类型是Collection //所以先创建两个collection集合 Collection<String> rolesCollection = new HashSet<String>(); Collection<String> perStringCollection = new HashSet<String>(); //获取user的Role的set集合 Set<Role> roles = user.getRoles(); //遍历集合 for (Role role : roles){ //将每一个role的name装进collection集合 rolesCollection.add(role.getRname()); //获取每一个Role的permission的set集合 Set<Module> permissionSet = role.getModules(); //遍历集合 for (Module permission : permissionSet){ //将每一个permission的name装进collection集合 perStringCollection.add(permission.getMname()); System.out.println(permission.getMname()); } //为用户授权 info.addStringPermissions(perStringCollection); } //为用户授予角色 info.addRoles(rolesCollection); return info; } return null; } /** * 用于认证登录,认证接口实现方法,该方法的回调一般是通过subject.login(token)方法来实现的 * AuthenticationToken 用于收集用户提交的身份(如用户名)及凭据(如密码): * AuthenticationInfo是包含了用户根据username返回的数据信息,用于在匹马比较的时候进行相互比较 * * shiro的核心是java servlet规范中的filter,通过配置拦截器,使用拦截器链来拦截请求,如果允许访问,则通过。 * 通常情况下,系统的登录、退出会配置拦截器。登录的时候,调用subject.login(token),token是用户验证信息, * 这个时候会在Realm中doGetAuthenticationInfo方法中进行认证。这个时候会把用户提交的验证信息与数据库中存储的认证信息,将所有的数据拿到,在匹配器中进行比较 * 这边是我们自己实现的CredentialMatcher类的doCredentialsMatch方法,返回true则一致,false则登陆失败 * 退出的时候,调用subject.logout(),会清除回话信息 * @param token * @return * @throws AuthenticationException */ @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //token携带了用户信息 UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; //获取前端输入的用户名 String username = usernamePasswordToken.getUsername(); //根据用户名查询数据库中对应的记录 User user = iUserService.findByUserName(username); /*//当前realm对象的name String realmName = getName(); //盐值 ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getUsername()); //封装用户信息,构建AuthenticationInfo对象并返回 AuthenticationInfo authcInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), credentialsSalt, realmName);*/ return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPassword(),this.getClass().getName()); } }
3、数据库密码为明文时密码匹配类:CredentialMatcher.java

import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.SimpleCredentialsMatcher; public class CredentialMatcher extends SimpleCredentialsMatcher { @Override public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { UsernamePasswordToken utoken=(UsernamePasswordToken) token; //获得用户输入的密码:(可以采用加盐(salt)的方式去检验) String inPassword = new String(utoken.getPassword()); //获得数据库中的密码 String dbPassword=(String) info.getCredentials(); //进行密码的比对 return this.equals(inPassword, dbPassword); } }
4、数据库为加密加盐时
authRealm引用的密码匹配需要更换。
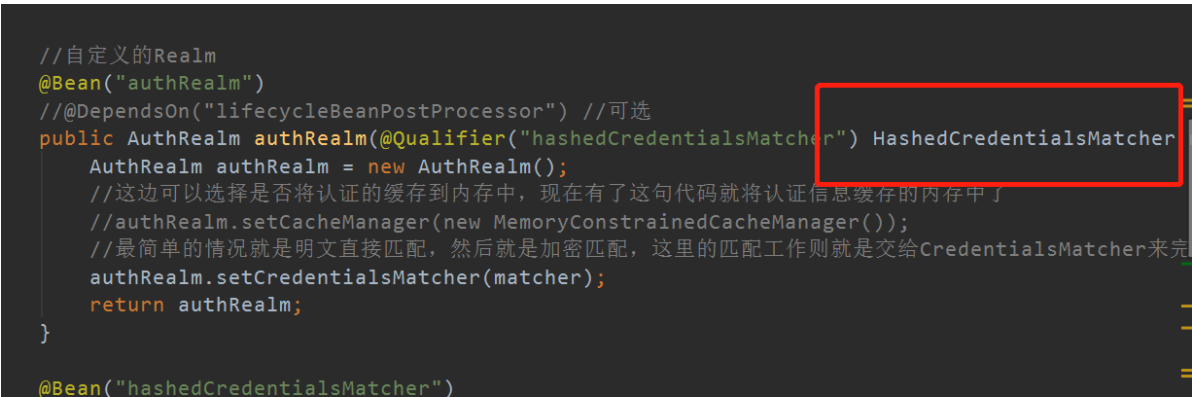
以下密码匹配直接写在核心配置类:ShiroConfiguration.java中

/** * 密码校验规则HashedCredentialsMatcher * 这个类是为了对密码进行编码的 , * 防止密码在数据库里明码保存 , 当然在登陆认证的时候 , * 这个类也负责对form里输入的密码进行编码 * 处理认证匹配处理器:如果自定义需要实现继承HashedCredentialsMatcher */ @Bean("hashedCredentialsMatcher") public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher() { HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher(); //指定加密方式为MD5 credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5"); //加密次数 credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024); credentialsMatcher.setStoredCredentialsHexEncoded(true); return credentialsMatcher; }
附上明文转密文的代码:

public static void main(String[] args) { String hashAlgorithName = "MD5"; String password = "登录时输入的密码"; int hashIterations = 1;//加密次数 ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes("登录时输入的用户名"); Object obj = new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithName, password, credentialsSalt, hashIterations); System.out.println(obj); }
