概要
前面分别通过C和C++实现了二项堆,本章给出二项堆的Java版本。还是那句老话,三种实现的原理一样,择其一了解即可。
目录
1. 二项树的介绍
2. 二项堆的介绍
3. 二项堆的基本操作
4. 二项堆的Java实现(完整源码)
5. 二项堆的Java测试程序
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3656098.html
更多内容:数据结构与算法系列 目录
(01) 二项堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
(02) 二项堆(二)之 C++的实现
(03) 二项堆(二)之 Java的实现
二项树的介绍
二项树的定义
二项堆是二项树的集合。在了解二项堆之前,先对二项树进行介绍。
二项树是一种递归定义的有序树。它的递归定义如下:
(01) 二项树B0只有一个结点;
(02) 二项树Bk由两棵二项树B(k-1)组成的,其中一棵树是另一棵树根的最左孩子。
如下图所示:
上图的B0、B1、B2、B3、B4都是二项树。对比前面提到的二项树的定义:B0只有一个节点,B1由两个B0所组成,B2由两个B1所组成,B3由两个B2所组成,B4由两个B3所组成;而且,当两颗相同的二项树组成另一棵树时,其中一棵树是另一棵树的最左孩子。
二项树的性质
二项树有以下性质:
[性质一] Bk共有2k个节点。
如上图所示,B0有20=1节点,B1有21=2个节点,B2有22=4个节点,...
[性质二] Bk的高度为k。
如上图所示,B0的高度为0,B1的高度为1,B2的高度为2,...
[性质三] Bk在深度i处恰好有C(k,i)个节点,其中i=0,1,2,...,k。
C(k,i)是高中数学中阶乘元素,例如,C(10,3)=(10*9*8) / (3*2*1)=240
B4中深度为0的节点C(4,0)=1
B4中深度为1的节点C(4,1)= 4 / 1 = 4
B4中深度为2的节点C(4,2)= (4*3) / (2*1) = 6
B4中深度为3的节点C(4,3)= (4*3*2) / (3*2*1) = 4
B4中深度为4的节点C(4,4)= (4*3*2*1) / (4*3*2*1) = 1
合计得到B4的节点分布是(1,4,6,4,1)。
[性质四] 根的度数为k,它大于任何其它节点的度数。
节点的度数是该结点拥有的子树的数目。
注意:树的高度和深度是相同的。关于树的高度的概念,《算法导论》中只有一个节点的树的高度是0,而"维基百科"中只有一个节点的树的高度是1。本文使用了《算法导论中》"树的高度和深度"的概念。
二项堆的介绍
二项堆和之前所讲的堆(二叉堆、左倾堆、斜堆)一样,也是用于实现优先队列的。二项堆是指满足以下性质的二项树的集合:
(01) 每棵二项树都满足最小堆性质。即,父节点的关键字 <= 它的孩子的关键字。
(02) 不能有两棵或以上的二项树具有相同的度数(包括度数为0)。换句话说,具有度数k的二项树有0个或1个。
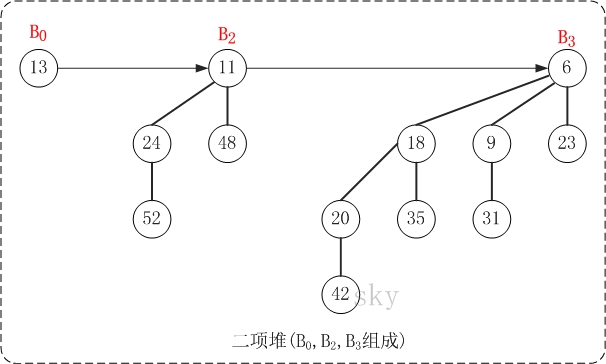
上图就是一棵二项堆,它由二项树B0、B2和B3组成。对比二项堆的定义:(01)二项树B0、B2、B3都是最小堆;(02)二项堆不包含相同度数的二项树。
二项堆的第(01)个性质保证了二项堆的最小节点就是某个二项树的根节点,第(02)个性质则说明结点数为n的二项堆最多只有log{n} + 1棵二项树。实际上,将包含n个节点的二项堆,表示成若干个2的指数和(或者转换成二进制),则每一个2个指数都对应一棵二项树。例如,13(二进制是1101)的2个指数和为13=23 + 22+ 20, 因此具有13个节点的二项堆由度数为3, 2, 0的三棵二项树组成。
二项堆的基本操作
二项堆是可合并堆,它的合并操作的复杂度是O(log n)。
1. 基本定义
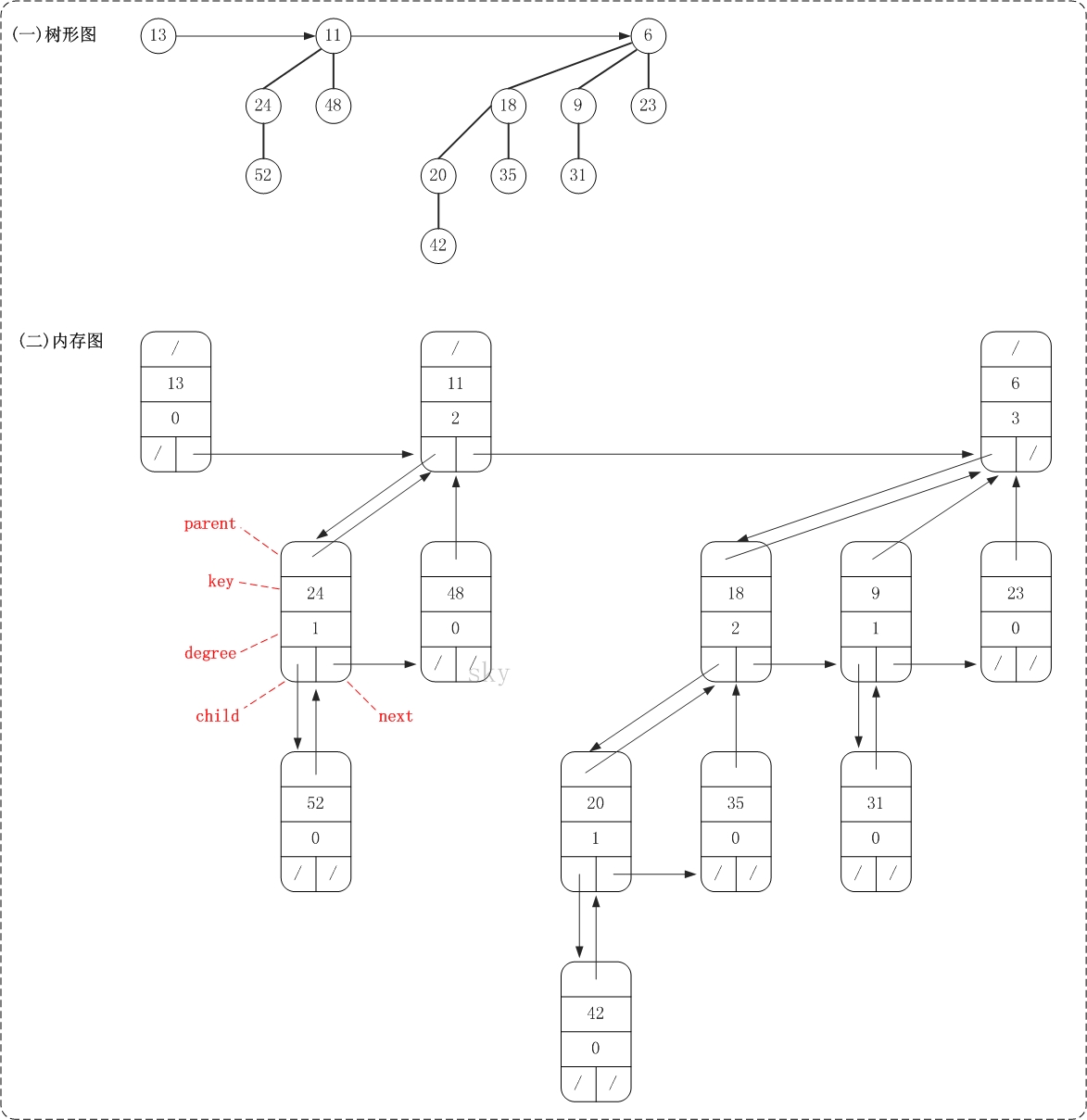
public class BinomialHeap<T extends Comparable<T>> { private BinomialNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点 private class BinomialNode<T extends Comparable<T>> { T key; // 关键字(键值) int degree; // 度数 BinomialNode<T> child; // 左孩子 BinomialNode<T> parent; // 父节点 BinomialNode<T> next; // 兄弟节点 public BinomialNode(T key) { this.key = key; this.degree = 0; this.child = null; this.parent = null; this.next = null; } public String toString() { return "key:"+key; } } ... }
BinomialNode是二项堆的节点。它包括了关键字(key),用于比较节点大小;度数(degree),用来表示当前节点的度数;左孩子(child)、父节点(parent)以及兄弟节点(next)。
BinomialHeap是二项堆对应的类,它包括了二项堆的根节点mRoot以及二项堆的基本操作的定义。
下面是一棵二项堆的树形图和它对应的内存结构关系图。
2. 合并操作
合并操作是二项堆的重点,它的添加操作也是基于合并操作来实现的。合并两个二项堆,需要的步骤概括起来如下:
(01) 将两个二项堆的根链表合并成一个链表。合并后的新链表按照"节点的度数"单调递增排列。
(02) 将新链表中"根节点度数相同的二项树"连接起来,直到所有根节点度数都不相同。
下面,先看看合并操作的代码;然后再通过示意图对合并操作进行说明。
merge()代码(Java)

1 /* 2 * 将h1, h2中的根表合并成一个按度数递增的链表,返回合并后的根节点 3 */ 4 private BinomialNode<T> merge(BinomialNode<T> h1, BinomialNode<T> h2) { 5 if (h1 == null) return h2; 6 if (h2 == null) return h1; 7 8 // root是新堆的根,h3用来遍历h1和h3的。 9 BinomialNode<T> pre_h3, h3, root=null; 10 11 pre_h3 = null; 12 //整个while,h1, h2, pre_h3, h3都在往后顺移 13 while ((h1!=null) && (h2!=null)) { 14 15 if (h1.degree <= h2.degree) { 16 h3 = h1; 17 h1 = h1.next; 18 } else { 19 h3 = h2; 20 h2 = h2.next; 21 } 22 23 if (pre_h3 == null) { 24 pre_h3 = h3; 25 root = h3; 26 } else { 27 pre_h3.next = h3; 28 pre_h3 = h3; 29 } 30 31 if (h1 != null) { 32 h3.next = h1; 33 } else { 34 h3.next = h2; 35 } 36 } 37 return root; 38 }
link()代码(Java)

1 /* 2 * 合并两个二项堆:将child合并到root中 3 */ 4 private void link(BinomialNode<T> child, BinomialNode<T> root) { 5 child.parent = root; 6 child.next = root.child; 7 root.child = child; 8 root.degree++; 9 }
合并操作代码(Java)
1 /* 2 * 合并二项堆:将h1, h2合并成一个堆,并返回合并后的堆 3 */ 4 private BinomialNode<T> union(BinomialNode<T> h1, BinomialNode<T> h2) { 5 BinomialNode<T> root; 6 7 // 将h1, h2中的根表合并成一个按度数递增的链表root 8 root = merge(h1, h2); 9 if (root == null) 10 return null; 11 12 BinomialNode<T> prev_x = null; 13 BinomialNode<T> x = root; 14 BinomialNode<T> next_x = x.next; 15 while (next_x != null) { 16 17 if ( (x.degree != next_x.degree) 18 || ((next_x.next != null) && (next_x.degree == next_x.next.degree))) { 19 // Case 1: x.degree != next_x.degree 20 // Case 2: x.degree == next_x.degree == next_x.next.degree 21 prev_x = x; 22 x = next_x; 23 } else if (x.key.compareTo(next_x.key) <= 0) { 24 // Case 3: x.degree == next_x.degree != next_x.next.degree 25 // && x.key <= next_x.key 26 x.next = next_x.next; 27 link(next_x, x); 28 } else { 29 // Case 4: x.degree == next_x.degree != next_x.next.degree 30 // && x.key > next_x.key 31 if (prev_x == null) { 32 root = next_x; 33 } else { 34 prev_x.next = next_x; 35 } 36 link(x, next_x); 37 x = next_x; 38 } 39 next_x = x.next; 40 } 41 42 return root; 43 } 44 45 /* 46 * 将二项堆other合并到当前堆中 47 */ 48 public void union(BinomialHeap<T> other) { 49 if (other!=null && other.mRoot!=null) 50 mRoot = union(mRoot, other.mRoot); 51 }
合并函数combine(h1, h2)的作用是将h1和h2合并,并返回合并后的二项堆。在combine(h1, h2)中,涉及到了两个函数merge(h1, h2)和link(child, root)。
merge(h1, h2)就是我们前面所说的"两个二项堆的根链表合并成一个链表,合并后的新链表按照'节点的度数'单调递增排序"。
link(child, root)则是为了合并操作的辅助函数,它的作用是将"二项堆child的根节点"设为"二项堆root的左孩子",从而将child整合到root中去。
在combine(h1, h2)中对h1和h2进行合并时;首先通过 merge(h1, h2) 将h1和h2的根链表合并成一个"按节点的度数单调递增"的链表;然后进入while循环,对合并得到的新链表进行遍历,将新链表中"根节点度数相同的二项树"连接起来,直到所有根节点度数都不相同为止。在将新联表中"根节点度数相同的二项树"连接起来时,可以将被连接的情况概括为4种。
x是根链表的当前节点,next_x是x的下一个(兄弟)节点。
Case 1: x->degree != next_x->degree
即,"当前节点的度数"与"下一个节点的度数"相等时。此时,不需要执行任何操作,继续查看后面的节点。
Case 2: x->degree == next_x->degree == next_x->next->degree
即,"当前节点的度数"、"下一个节点的度数"和"下下一个节点的度数"都相等时。此时,暂时不执行任何操作,还是继续查看后面的节点。实际上,这里是将"下一个节点"和"下下一个节点"等到后面再进行整合连接。
Case 3: x->degree == next_x->degree != next_x->next->degree
&& x->key <= next_x->key
即,"当前节点的度数"与"下一个节点的度数"相等,并且"当前节点的键值"<="下一个节点的度数"。此时,将"下一个节点(对应的二项树)"作为"当前节点(对应的二项树)的左孩子"。
Case 4: x->degree == next_x->degree != next_x->next->degree
&& x->key > next_x->key
即,"当前节点的度数"与"下一个节点的度数"相等,并且"当前节点的键值">"下一个节点的度数"。此时,将"当前节点(对应的二项树)"作为"下一个节点(对应的二项树)的左孩子"。
下面通过示意图来对合并操作进行说明。
第1步:将两个二项堆的根链表合并成一个链表
执行完第1步之后,得到的新链表中有许多度数相同的二项树。实际上,此时得到的是对应"Case 4"的情况,"树41"(根节点为41的二项树)和"树13"的度数相同,且"树41"的键值 > "树13"的键值。此时,将"树41"作为"树13"的左孩子。
第2步:合并"树41"和"树13"
执行完第2步之后,得到的是对应"Case 3"的情况,"树13"和"树28"的度数相同,且"树13"的键值 < "树28"的键值。此时,将"树28"作为"树13"的左孩子。
第3步:合并"树13"和"树28"
执行完第3步之后,得到的是对应"Case 2"的情况,"树13"、"树28"和"树7"这3棵树的度数都相同。此时,将x设为下一个节点。
第4步:将x和next_x往后移
执行完第4步之后,得到的是对应"Case 3"的情况,"树7"和"树11"的度数相同,且"树7"的键值 < "树11"的键值。此时,将"树11"作为"树7"的左孩子。
第5步:合并"树7"和"树11"
执行完第5步之后,得到的是对应"Case 4"的情况,"树7"和"树6"的度数相同,且"树7"的键值 > "树6"的键值。此时,将"树7"作为"树6"的左孩子。
第6步:合并"树7"和"树6"
此时,合并操作完成!
PS. 合并操作的图文解析过程与"测试程序(Main.java)中的testUnion()函数"是对应的!
3. 插入操作
理解了"合并"操作之后,插入操作就相当简单了。插入操作可以看作是将"要插入的节点"和当前已有的堆进行合并。
插入操作代码(Java)
1 /* 2 * 新建key对应的节点,并将其插入到二项堆中。 3 */ 4 public void insert(T key) { 5 BinomialNode<T> node; 6 7 // 禁止插入相同的键值 8 if (contains(key)==true) { 9 System.out.printf("insert failed: the key(%s) is existed already! ", key); 10 return ; 11 } 12 13 node = new BinomialNode<T>(key); 14 if (node==null) 15 return ; 16 17 mRoot = union(mRoot, node); 18 }
在插入时,首先通过contains(key)查找键值为key的节点。存在的话,则直接返回;不存在的话,则新建BinomialNode对象node,然后将node和heap进行合并。
注意:我这里实现的二项堆是"进制插入相同节点的"!若你想允许插入相同键值的节点,则屏蔽掉插入操作中的contains(key)部分代码即可。
4. 删除操作
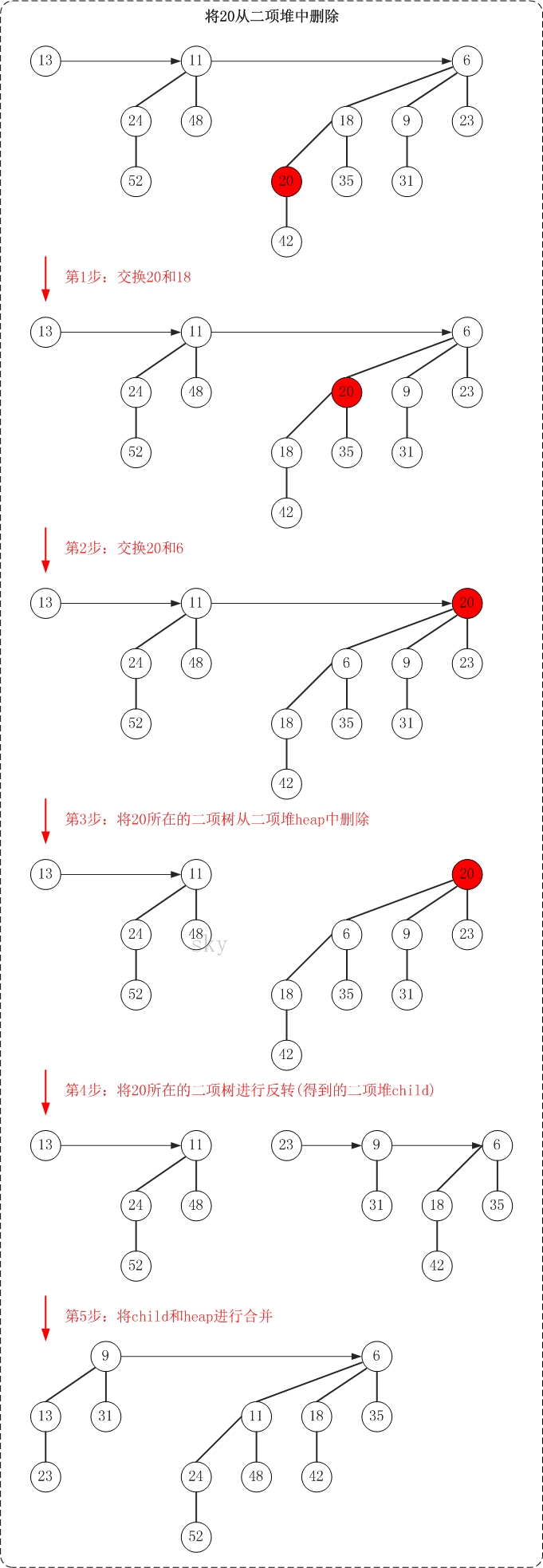
删除二项堆中的某个节点,需要的步骤概括起来如下:
(01) 将"该节点"交换到"它所在二项树"的根节点位置。方法是,从"该节点"不断向上(即向树根方向)"遍历,不断交换父节点和子节点的数据,直到被删除的键值到达树根位置。
(02) 将"该节点所在的二项树"从二项堆中移除;将该二项堆记为heap。
(03) 将"该节点所在的二项树"进行反转。反转的意思,就是将根的所有孩子独立出来,并将这些孩子整合成二项堆,将该二项堆记为child。
(04) 将child和heap进行合并操作。
下面,先看看删除操作的代码;再进行图文说明。
删除操作代码(Java)
1 /* 2 * 删除节点:删除键值为key的节点 3 */ 4 private BinomialNode<T> remove(BinomialNode<T> root, T key) { 5 if (root==null) 6 return root; 7 8 BinomialNode<T> node; 9 10 // 查找键值为key的节点 11 if ((node = search(root, key)) == null) 12 return root; 13 14 // 将被删除的节点的数据数据上移到它所在的二项树的根节点 15 BinomialNode<T> parent = node.parent; 16 while (parent != null) { 17 // 交换数据 18 T tmp = node.key; 19 node.key = parent.key; 20 parent.key = tmp; 21 22 // 下一个父节点 23 node = parent; 24 parent = node.parent; 25 } 26 27 // 找到node的前一个根节点(prev) 28 BinomialNode<T> prev = null; 29 BinomialNode<T> pos = root; 30 while (pos != node) { 31 prev = pos; 32 pos = pos.next; 33 } 34 // 移除node节点 35 if (prev!=null) 36 prev.next = node.next; 37 else 38 root = node.next; 39 40 root = union(root, reverse(node.child)); 41 42 // help GC 43 node = null; 44 45 return root; 46 } 47 48 public void remove(T key) { 49 mRoot = remove(mRoot, key); 50 }
remove(key)的作用是删除二项堆中键值为key的节点,并返回删除节点后的二项堆。
下面通过示意图来对删除操作进行说明(删除二项堆中的节点20)。
总的思想,就是将被"删除节点"从它所在的二项树中孤立出来,然后再对二项树进行相应的处理。
PS. 删除操作的图文解析过程与"测试程序(Main.java)中的testDelete()函数"是对应的!
5. 更新操作
更新二项堆中的某个节点,就是修改节点的值,它包括两部分分:"减少节点的值" 和 "增加节点的值" 。
更新操作代码(Java)
/* * 更新二项堆的节点node的键值为key */ private void updateKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { if (node == null) return ; int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key); if(cmp < 0) // key < node.key decreaseKey(node, key); else if(cmp > 0) // key > node.key increaseKey(node, key); else System.out.println("No need to update!!!"); } /* * 将二项堆中键值oldkey更新为newkey */ public void update(T oldkey, T newkey) { BinomialNode<T> node; node = search(mRoot, oldkey); if (node != null) updateKey(node, newkey); }
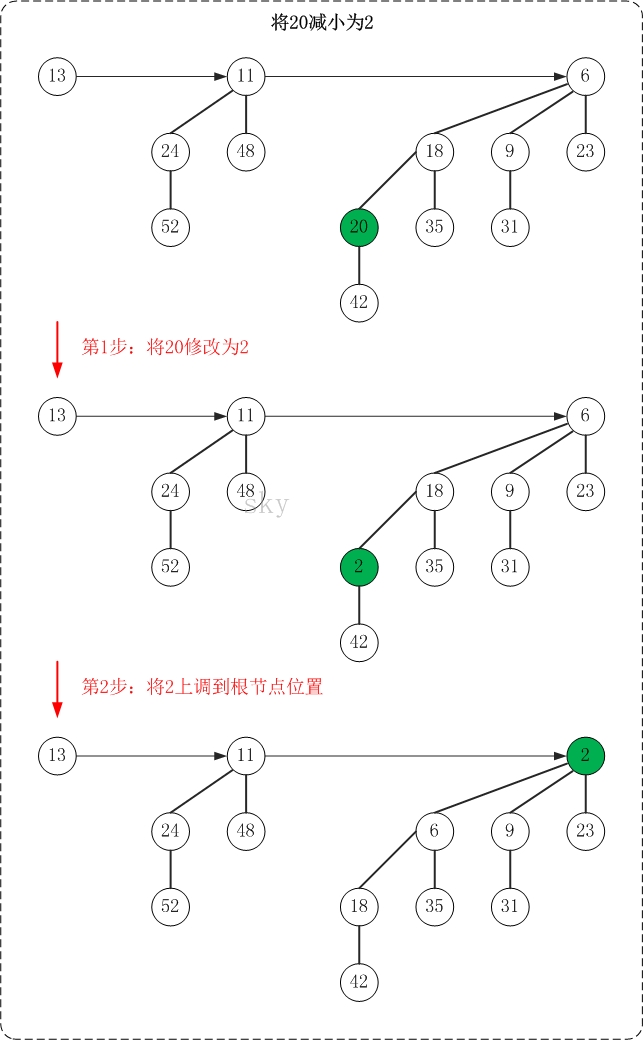
5.1 减少节点的值
减少节点值的操作很简单:该节点一定位于一棵二项树中,减小"二项树"中某个节点的值后要保证"该二项树仍然是一个最小堆";因此,就需要我们不断的将该节点上调。
减少操作代码(Java)
1 /* 2 * 减少关键字的值:将二项堆中的节点node的键值减小为key。 3 */ 4 private void decreaseKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { 5 if(key.compareTo(node.key)>=0 || contains(key)==true) { 6 System.out.println("decrease failed: the new key("+key+") is existed already, or is no smaller than current key("+node.key+")"); 7 return ; 8 } 9 node.key = key; 10 11 BinomialNode<T> child, parent; 12 child = node; 13 parent = node.parent; 14 while(parent != null && child.key.compareTo(parent.key)<0) { 15 // 交换parent和child的数据 16 T tmp = parent.key; 17 parent.key = child.key; 18 child.key = tmp; 19 20 child = parent; 21 parent = child.parent; 22 } 23 }
下面是减少操作的示意图(20->2)
减少操作的思想很简单,就是"保持被减节点所在二项树的最小堆性质"。
PS. 减少操作的图文解析过程与"测试程序(Main.java)中的testDecrease()函数"是对应的!
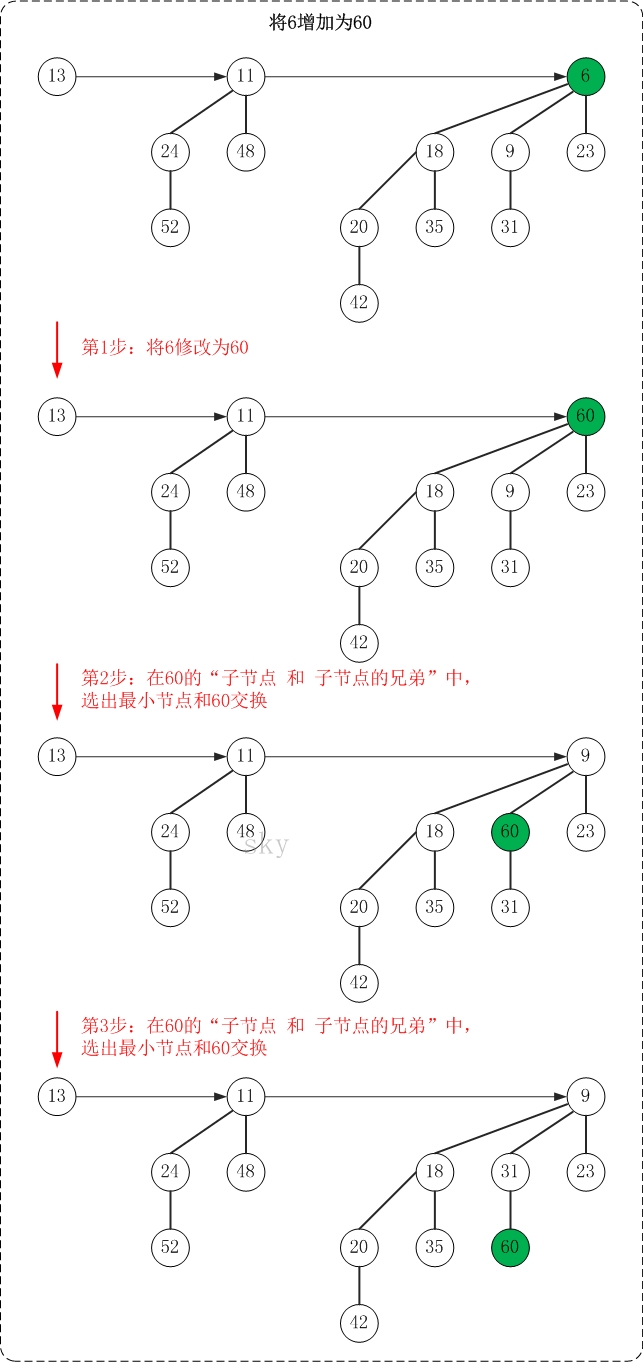
5.2 增加节点的值
增加节点值的操作也很简单。上面说过减少要将被减少的节点不断上调,从而保证"被减少节点所在的二项树"的最小堆性质;而增加操作则是将被增加节点不断的下调,从而保证"被增加节点所在的二项树"的最小堆性质。
增加操作代码(Java)
1 /* 2 * 增加关键字的值:将二项堆中的节点node的键值增加为key。 3 */ 4 private void increaseKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { 5 if(key.compareTo(node.key)<=0 || contains(key)==true) { 6 System.out.println("increase failed: the new key("+key+") is existed already, or is no greater than current key("+node.key+")"); 7 return ; 8 } 9 node.key = key; 10 11 BinomialNode<T> cur = node; 12 BinomialNode<T> child = cur.child; 13 while (child != null) { 14 15 if(cur.key.compareTo(child.key) > 0) { 16 // 如果"当前节点" < "它的左孩子", 17 // 则在"它的孩子中(左孩子 和 左孩子的兄弟)"中,找出最小的节点; 18 // 然后将"最小节点的值" 和 "当前节点的值"进行互换 19 BinomialNode<T> least = child; // least是child和它的兄弟中的最小节点 20 while(child.next != null) { 21 if (least.key.compareTo(child.next.key) > 0) 22 least = child.next; 23 child = child.next; 24 } 25 // 交换最小节点和当前节点的值 26 T tmp = least.key; 27 least.key = cur.key; 28 cur.key = tmp; 29 30 // 交换数据之后,再对"原最小节点"进行调整,使它满足最小堆的性质:父节点 <= 子节点 31 cur = least; 32 child = cur.child; 33 } else { 34 child = child.next; 35 } 36 } 37 }
下面是增加操作的示意图(6->60)
增加操作的思想很简单,"保持被增加点所在二项树的最小堆性质"。
PS. 增加操作的图文解析过程与"测试程序(Main.java)中的testIncrease()函数"是对应的!
注意:关于二项堆的"查找"、"更新"、"打印"等接口就不再单独介绍了,后文的源码中有给出它们的实现代码。有兴趣的话,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
二项堆的Java实现(完整源码)
二项堆的实现文件(BinomialHeap.java)

1 /** 2 * Java 语言: 二项堆 3 * 4 * @author skywang 5 * @date 2014/04/03 6 */ 7 8 public class BinomialHeap<T extends Comparable<T>> { 9 10 private BinomialNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点 11 12 private class BinomialNode<T extends Comparable<T>> { 13 T key; // 关键字(键值) 14 int degree; // 度数 15 BinomialNode<T> child; // 左孩子 16 BinomialNode<T> parent; // 父节点 17 BinomialNode<T> next; // 兄弟节点 18 19 public BinomialNode(T key) { 20 this.key = key; 21 this.degree = 0; 22 this.child = null; 23 this.parent = null; 24 this.next = null; 25 } 26 27 public String toString() { 28 return "key:"+key; 29 } 30 } 31 32 public BinomialHeap() { 33 mRoot = null; 34 } 35 36 /* 37 * 获取二项堆中的最小节点的键值 38 */ 39 public T minimum() { 40 if (mRoot==null) 41 return null; 42 43 BinomialNode<T> x, prev_x; // x是用来遍历的当前节点 44 BinomialNode<T> y, prev_y; // y是最小节点 45 46 prev_x = mRoot; 47 x = mRoot.next; 48 prev_y = null; 49 y = mRoot; 50 // 找到最小节点 51 while (x != null) { 52 if (x.key.compareTo(y.key) < 0) { 53 y = x; 54 prev_y = prev_x; 55 } 56 prev_x = x; 57 x = x.next; 58 } 59 60 return y.key; 61 } 62 63 64 /* 65 * 合并两个二项堆:将child合并到root中 66 */ 67 private void link(BinomialNode<T> child, BinomialNode<T> root) { 68 child.parent = root; 69 child.next = root.child; 70 root.child = child; 71 root.degree++; 72 } 73 74 /* 75 * 将h1, h2中的根表合并成一个按度数递增的链表,返回合并后的根节点 76 */ 77 private BinomialNode<T> merge(BinomialNode<T> h1, BinomialNode<T> h2) { 78 if (h1 == null) return h2; 79 if (h2 == null) return h1; 80 81 // root是新堆的根,h3用来遍历h1和h3的。 82 BinomialNode<T> pre_h3, h3, root=null; 83 84 pre_h3 = null; 85 //整个while,h1, h2, pre_h3, h3都在往后顺移 86 while ((h1!=null) && (h2!=null)) { 87 88 if (h1.degree <= h2.degree) { 89 h3 = h1; 90 h1 = h1.next; 91 } else { 92 h3 = h2; 93 h2 = h2.next; 94 } 95 96 if (pre_h3 == null) { 97 pre_h3 = h3; 98 root = h3; 99 } else { 100 pre_h3.next = h3; 101 pre_h3 = h3; 102 } 103 104 if (h1 != null) { 105 h3.next = h1; 106 } else { 107 h3.next = h2; 108 } 109 } 110 return root; 111 } 112 113 /* 114 * 合并二项堆:将h1, h2合并成一个堆,并返回合并后的堆 115 */ 116 private BinomialNode<T> union(BinomialNode<T> h1, BinomialNode<T> h2) { 117 BinomialNode<T> root; 118 119 // 将h1, h2中的根表合并成一个按度数递增的链表root 120 root = merge(h1, h2); 121 if (root == null) 122 return null; 123 124 BinomialNode<T> prev_x = null; 125 BinomialNode<T> x = root; 126 BinomialNode<T> next_x = x.next; 127 while (next_x != null) { 128 129 if ( (x.degree != next_x.degree) 130 || ((next_x.next != null) && (next_x.degree == next_x.next.degree))) { 131 // Case 1: x.degree != next_x.degree 132 // Case 2: x.degree == next_x.degree == next_x.next.degree 133 prev_x = x; 134 x = next_x; 135 } else if (x.key.compareTo(next_x.key) <= 0) { 136 // Case 3: x.degree == next_x.degree != next_x.next.degree 137 // && x.key <= next_x.key 138 x.next = next_x.next; 139 link(next_x, x); 140 } else { 141 // Case 4: x.degree == next_x.degree != next_x.next.degree 142 // && x.key > next_x.key 143 if (prev_x == null) { 144 root = next_x; 145 } else { 146 prev_x.next = next_x; 147 } 148 link(x, next_x); 149 x = next_x; 150 } 151 next_x = x.next; 152 } 153 154 return root; 155 } 156 157 /* 158 * 将二项堆other合并到当前堆中 159 */ 160 public void union(BinomialHeap<T> other) { 161 if (other!=null && other.mRoot!=null) 162 mRoot = union(mRoot, other.mRoot); 163 } 164 165 /* 166 * 新建key对应的节点,并将其插入到二项堆中。 167 */ 168 public void insert(T key) { 169 BinomialNode<T> node; 170 171 // 禁止插入相同的键值 172 if (contains(key)==true) { 173 System.out.printf("insert failed: the key(%s) is existed already! ", key); 174 return ; 175 } 176 177 node = new BinomialNode<T>(key); 178 if (node==null) 179 return ; 180 181 mRoot = union(mRoot, node); 182 } 183 184 /* 185 * 反转二项堆root,并返回反转后的根节点 186 */ 187 private BinomialNode<T> reverse(BinomialNode<T> root) { 188 BinomialNode<T> next; 189 BinomialNode<T> tail = null; 190 191 if (root==null) 192 return root; 193 194 root.parent = null; 195 while (root.next!=null) { 196 next = root.next; 197 root.next = tail; 198 tail = root; 199 root = next; 200 root.parent = null; 201 } 202 root.next = tail; 203 204 return root; 205 } 206 207 /* 208 * 移除二项堆root中的最小节点,并返回删除节点后的二项树 209 */ 210 private BinomialNode<T> extractMinimum(BinomialNode<T> root) { 211 if (root==null) 212 return root; 213 214 BinomialNode<T> x, prev_x; // x是用来遍历的当前节点 215 BinomialNode<T> y, prev_y; // y是最小节点 216 217 prev_x = root; 218 x = root.next; 219 prev_y = null; 220 y = root; 221 // 找到最小节点 222 while (x != null) { 223 if (x.key.compareTo(y.key) < 0) { 224 y = x; 225 prev_y = prev_x; 226 } 227 prev_x = x; 228 x = x.next; 229 } 230 231 if (prev_y == null) // root的根节点就是最小根节点 232 root = root.next; 233 else // root的根节点不是最小根节点 234 prev_y.next = y.next; 235 236 // 反转最小节点的左孩子,得到最小堆child; 237 // 这样,就使得最小节点所在二项树的孩子们都脱离出来成为一棵独立的二项树(不包括最小节点) 238 BinomialNode<T> child = reverse(y.child); 239 // 将"删除最小节点的二项堆child"和"root"进行合并。 240 root = union(root, child); 241 242 // help GC 243 y = null; 244 245 return root; 246 } 247 248 public void extractMinimum() { 249 mRoot = extractMinimum(mRoot); 250 } 251 252 /* 253 * 减少关键字的值:将二项堆中的节点node的键值减小为key。 254 */ 255 private void decreaseKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { 256 if(key.compareTo(node.key)>=0 || contains(key)==true) { 257 System.out.println("decrease failed: the new key("+key+") is existed already, or is no smaller than current key("+node.key+")"); 258 return ; 259 } 260 node.key = key; 261 262 BinomialNode<T> child, parent; 263 child = node; 264 parent = node.parent; 265 while(parent != null && child.key.compareTo(parent.key)<0) { 266 // 交换parent和child的数据 267 T tmp = parent.key; 268 parent.key = child.key; 269 child.key = tmp; 270 271 child = parent; 272 parent = child.parent; 273 } 274 } 275 276 /* 277 * 增加关键字的值:将二项堆中的节点node的键值增加为key。 278 */ 279 private void increaseKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { 280 if(key.compareTo(node.key)<=0 || contains(key)==true) { 281 System.out.println("increase failed: the new key("+key+") is existed already, or is no greater than current key("+node.key+")"); 282 return ; 283 } 284 node.key = key; 285 286 BinomialNode<T> cur = node; 287 BinomialNode<T> child = cur.child; 288 while (child != null) { 289 290 if(cur.key.compareTo(child.key) > 0) { 291 // 如果"当前节点" < "它的左孩子", 292 // 则在"它的孩子中(左孩子 和 左孩子的兄弟)"中,找出最小的节点; 293 // 然后将"最小节点的值" 和 "当前节点的值"进行互换 294 BinomialNode<T> least = child; // least是child和它的兄弟中的最小节点 295 while(child.next != null) { 296 if (least.key.compareTo(child.next.key) > 0) 297 least = child.next; 298 child = child.next; 299 } 300 // 交换最小节点和当前节点的值 301 T tmp = least.key; 302 least.key = cur.key; 303 cur.key = tmp; 304 305 // 交换数据之后,再对"原最小节点"进行调整,使它满足最小堆的性质:父节点 <= 子节点 306 cur = least; 307 child = cur.child; 308 } else { 309 child = child.next; 310 } 311 } 312 } 313 314 /* 315 * 更新二项堆的节点node的键值为key 316 */ 317 private void updateKey(BinomialNode<T> node, T key) { 318 if (node == null) 319 return ; 320 321 int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key); 322 if(cmp < 0) // key < node.key 323 decreaseKey(node, key); 324 else if(cmp > 0) // key > node.key 325 increaseKey(node, key); 326 else 327 System.out.println("No need to update!!!"); 328 } 329 330 /* 331 * 将二项堆中键值oldkey更新为newkey 332 */ 333 public void update(T oldkey, T newkey) { 334 BinomialNode<T> node; 335 336 node = search(mRoot, oldkey); 337 if (node != null) 338 updateKey(node, newkey); 339 } 340 341 /* 342 * 查找:在二项堆中查找键值为key的节点 343 */ 344 private BinomialNode<T> search(BinomialNode<T> root, T key) { 345 BinomialNode<T> child; 346 BinomialNode<T> parent = root; 347 348 parent = root; 349 while (parent != null) { 350 if (parent.key.compareTo(key) == 0) 351 return parent; 352 else { 353 if((child = search(parent.child, key)) != null) 354 return child; 355 parent = parent.next; 356 } 357 } 358 359 return null; 360 } 361 362 /* 363 * 二项堆中是否包含键值key 364 */ 365 public boolean contains(T key) { 366 return search(mRoot, key)!=null ? true : false; 367 } 368 369 /* 370 * 删除节点:删除键值为key的节点 371 */ 372 private BinomialNode<T> remove(BinomialNode<T> root, T key) { 373 if (root==null) 374 return root; 375 376 BinomialNode<T> node; 377 378 // 查找键值为key的节点 379 if ((node = search(root, key)) == null) 380 return root; 381 382 // 将被删除的节点的数据数据上移到它所在的二项树的根节点 383 BinomialNode<T> parent = node.parent; 384 while (parent != null) { 385 // 交换数据 386 T tmp = node.key; 387 node.key = parent.key; 388 parent.key = tmp; 389 390 // 下一个父节点 391 node = parent; 392 parent = node.parent; 393 } 394 395 // 找到node的前一个根节点(prev) 396 BinomialNode<T> prev = null; 397 BinomialNode<T> pos = root; 398 while (pos != node) { 399 prev = pos; 400 pos = pos.next; 401 } 402 // 移除node节点 403 if (prev!=null) 404 prev.next = node.next; 405 else 406 root = node.next; 407 408 root = union(root, reverse(node.child)); 409 410 // help GC 411 node = null; 412 413 return root; 414 } 415 416 public void remove(T key) { 417 mRoot = remove(mRoot, key); 418 } 419 420 /* 421 * 打印"二项堆" 422 * 423 * 参数说明: 424 * node -- 当前节点 425 * prev -- 当前节点的前一个节点(父节点or兄弟节点) 426 * direction -- 1,表示当前节点是一个左孩子; 427 * 2,表示当前节点是一个兄弟节点。 428 */ 429 private void print(BinomialNode<T> node, BinomialNode<T> prev, int direction) { 430 while(node != null) 431 { 432 if(direction==1) // node是根节点 433 System.out.printf(" %2d(%d) is %2d's child ", node.key, node.degree, prev.key); 434 else // node是分支节点 435 System.out.printf(" %2d(%d) is %2d's next ", node.key, node.degree, prev.key); 436 437 if (node.child != null) 438 print(node.child, node, 1); 439 440 // 兄弟节点 441 prev = node; 442 node = node.next; 443 direction = 2; 444 } 445 } 446 447 public void print() { 448 if (mRoot == null) 449 return ; 450 451 BinomialNode<T> p = mRoot; 452 System.out.printf("== 二项堆( "); 453 while (p != null) { 454 System.out.printf("B%d ", p.degree); 455 p = p.next; 456 } 457 System.out.printf(")的详细信息: "); 458 459 int i=0; 460 p = mRoot; 461 while (p != null) { 462 i++; 463 System.out.printf("%d. 二项树B%d: ", i, p.degree); 464 System.out.printf(" %2d(%d) is root ", p.key, p.degree); 465 466 print(p.child, p, 1); 467 p = p.next; 468 } 469 System.out.printf(" "); 470 } 471 }
二项堆的测试程序(Main.java)

1 /** 2 * Java 语言: 二项堆 3 * 4 * @author skywang 5 * @date 2014/03/31 6 */ 7 8 public class Main { 9 10 private static final boolean DEBUG = false; 11 12 // 共7个 = 1+2+4 13 private static int a[] = {12, 7, 25, 15, 28, 33, 41}; 14 // 共13个 = 1+4+8 15 private static int b[] = {18, 35, 20, 42, 9, 16 31, 23, 6, 48, 11, 17 24, 52, 13 }; 18 19 20 // 验证"二项堆的插入操作" 21 public static void testInsert() { 22 BinomialHeap<Integer> ha=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 23 24 // 二项堆ha 25 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(ha)中依次添加: "); 26 for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) { 27 System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]); 28 ha.insert(a[i]); 29 } 30 System.out.printf(" "); 31 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(ha)的详细信息: "); 32 ha.print(); 33 } 34 35 // 验证"二项堆的合并操作" 36 public static void testUnion() { 37 BinomialHeap<Integer> ha=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 38 BinomialHeap<Integer> hb=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 39 40 // 二项堆ha 41 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(ha)中依次添加: "); 42 for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) { 43 System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]); 44 ha.insert(a[i]); 45 } 46 System.out.printf(" "); 47 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(ha)的详细信息: "); 48 ha.print(); 49 50 // 二项堆hb 51 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)中依次添加: "); 52 for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { 53 System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]); 54 hb.insert(b[i]); 55 } 56 System.out.printf(" "); 57 // 打印二项堆hb 58 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)的详细信息: "); 59 hb.print(); 60 61 // 将"二项堆hb"合并到"二项堆ha"中。 62 ha.union(hb); 63 // 打印二项堆ha的详细信息 64 System.out.printf("== 合并ha和hb后的详细信息: "); 65 ha.print(); 66 } 67 68 // 验证"二项堆的删除操作" 69 public static void testDelete() { 70 BinomialHeap<Integer> hb=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 71 72 // 二项堆hb 73 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)中依次添加: "); 74 for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { 75 System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]); 76 hb.insert(b[i]); 77 } 78 System.out.printf(" "); 79 // 打印二项堆hb 80 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)的详细信息: "); 81 hb.print(); 82 83 // 将"二项堆hb"合并到"二项堆ha"中。 84 hb.remove(20); 85 System.out.printf("== 删除节点20后的详细信息: "); 86 hb.print(); 87 } 88 89 // 验证"二项堆的更新(减少)操作" 90 public static void testDecrease() { 91 BinomialHeap<Integer> hb=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 92 93 // 二项堆hb 94 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)中依次添加: "); 95 for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { 96 System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]); 97 hb.insert(b[i]); 98 } 99 System.out.printf(" "); 100 // 打印二项堆hb 101 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)的详细信息: "); 102 hb.print(); 103 104 // 将节点20更新为2 105 hb.update(20, 2); 106 System.out.printf("== 更新节点20->2后的详细信息: "); 107 hb.print(); 108 } 109 110 // 验证"二项堆的更新(减少)操作" 111 public static void testIncrease() { 112 BinomialHeap<Integer> hb=new BinomialHeap<Integer>(); 113 114 // 二项堆hb 115 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)中依次添加: "); 116 for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { 117 System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]); 118 hb.insert(b[i]); 119 } 120 System.out.printf(" "); 121 // 打印二项堆hb 122 System.out.printf("== 二项堆(hb)的详细信息: "); 123 hb.print(); 124 125 // 将节点6更新为60 126 hb.update(6, 60); 127 System.out.printf("== 更新节点6->60后的详细信息: "); 128 hb.print(); 129 } 130 131 public static void main(String[] args) { 132 // 1. 验证"二项堆的插入操作" 133 testInsert(); 134 // 2. 验证"二项堆的合并操作" 135 //testUnion(); 136 // 3. 验证"二项堆的删除操作" 137 //testDelete(); 138 // 4. 验证"二项堆的更新(减少)操作" 139 //testDecrease(); 140 // 5. 验证"二项堆的更新(增加)操作" 141 //testIncrease(); 142 } 143 }
二项堆的Java测试程序
二项堆的测试程序包括了五部分,分别是"插入"、"删除"、"增加"、"减少"、"合并"这5种功能的测试代码。默认是运行的"插入"功能代码,你可以根据自己的需要来对相应的功能进行验证!
下面是插入功能运行结果:
== 二项堆(ha)中依次添加: 12 7 25 15 28 33 41 == 二项堆(ha)的详细信息: == 二项堆( B0 B1 B2 )的详细信息: 1. 二项树B0: 41(0) is root 2. 二项树B1: 28(1) is root 33(0) is 28's child 3. 二项树B2: 7(2) is root 15(1) is 7's child 25(0) is 15's child 12(0) is 15's next