觉得还是先从简单例子程序着手,先了解各个算法的基本思想。
目录:
算法是指对特定问题求解步骤 的一种描述
算法的评价标准:时间复杂度与空间复杂度。
时间复杂度:考虑给定的数据数目n,关于算法的执行次数。渐进上界用O()表示,最坏情况对衡量算法的好坏具有实际的意义。
空间复杂度:算法占用的空间大小。一般将算法的辅助空间作为衡量标准。
算法思想:一个贪心算法总是做出当前最好的选择,也就是说,它期望通过局部最优选择从而得到全局最优的解决方案。
小插曲:c++中有排序函数sort,可以直接利用
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<algorithm> int main() { int a[4] = { 4,7,3,5 }; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << a[i] << " "; cout << endl << "排序后::::" << endl; sort(a, a + 3); //可以只对某几项进行排列 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << a[i] << " "; cin.ignore(); return 0; }
4 7 3 5
排序后::::
3 4 7 5
举列1:最优装载问题
描述:海盗们截获一批财宝,海盗船载重有限,如何尽可能多的获取宝贝??
算法设计:每次选择重量最小的,直到不能再装为止。
代码:

#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<algorithm> const int N = 100; double w[N]; //古董 的重量数组 int main() { double c; int n; cout << "请输入载重量c以及古董个数n:" << endl; cin >> c >> n; cout << "请输入每个古董的重量" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> w[i]; } sort(w, w + n); double temp = 0; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { temp += w[i]; if (temp <= c) ans++; else break; } cout << "最大装载数目:" << ans << endl; cin.ignore(); cin.ignore(); cin.ignore(); return 0; }
请输入载重量c以及古董个数n:
30 8
请输入每个古董的重量
4 10 7 11 3 5 14 2
最大装载数目:5
扩展:如何知道装入了那些宝贝呢??
引入结构体数组,增加宝贝的编号属性,具体程序如下

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<algorithm> 4 5 const int N = 100; 6 struct two { 7 int n; //宝物标号 8 double w; //宝物重量 9 }s[N]; 10 //double w[N]; //古董 的重量数组 11 bool cmp(two a, two b) 12 { 13 return a.w < b.w; 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 double c; 19 int n; 20 cout << "请输入载重量c以及古董个数n:" << endl; 21 cin >> c >> n; 22 23 cout << "请输入每个古董的重量" << endl; 24 25 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 26 { 27 cin >> s[i].w; 28 s[i].n = i + 1; 29 } 30 sort(s, s + n, cmp); 31 32 double temp = 0; 33 int ans = 0; 34 35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 36 { 37 temp += s[i].w; 38 if (temp <= c) 39 { 40 ans++; 41 cout << "选择第" << s[i].n << "个宝贝" << endl; 42 } 43 else 44 break; 45 } 46 cout << "最大装载数目:" << ans << endl; 47 48 49 cin.ignore(); 50 cin.ignore(); 51 cin.ignore(); 52 return 0; 53 }
请输入载重量c以及古董个数n:
30 8
请输入每个古董的重量
4 10 7 11 3 5 14 2
选择第8个宝贝
选择第5个宝贝
选择第1个宝贝
选择第6个宝贝
选择第3个宝贝
最大装载数目:5
算法思想:本质是将一个大规模的问题分解为若干个规模较小 的相同子问题,分而治之
在分治算法中,各个子问题形式相同,解决的方法也一样,因此可以使用递归算法快速解决,递归是彰显分治法优势的利器
举列1:猜数游戏
描述:n个数,给定一个数x,从中找出特定的元素x
算法设计:每次从中间元素开始 查找,与x进行比较,这样每次就可以将问题的规模减半,直到查到x
code:

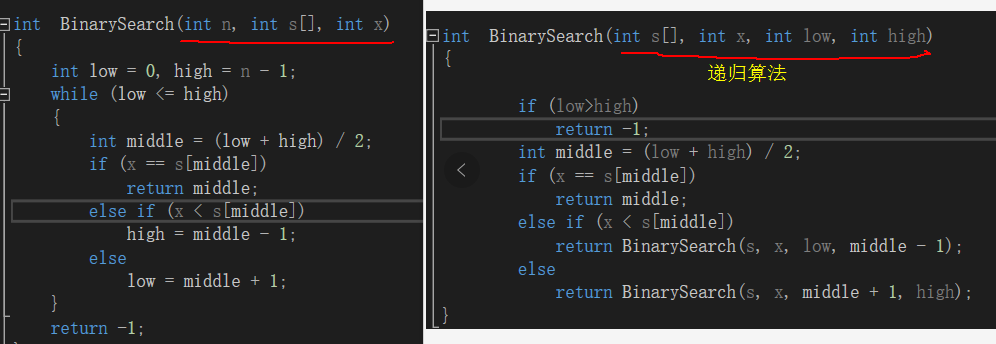
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int M = 10000; 7 int s[M]; 8 9 int BinarySearch(int n, int s[], int x) 10 { 11 int low = 0, high = n - 1; 12 while (low <= high) 13 { 14 int middle = (low + high) / 2; 15 if (x == s[middle]) 16 return middle; 17 else if (x < s[middle]) 18 high = middle - 1; 19 else 20 low = middle + 1; 21 } 22 return -1; 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 int n,x,i; 28 29 cout << "请输入数列中的元素个数n为: "; 30 while (cin >> n) 31 { 32 cout << "请依次输入:"; 33 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 34 cin >> s[i]; 35 sort(s, s + n); 36 cout << "排序后的数组为:"; 37 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 38 cout << s[i]<<" "; 39 cout << endl; 40 cout << "输入要查找的元素:"; 41 cin >> x; 42 i = BinarySearch(n, s, x); 43 if (i == -1) 44 cout << "no found"; 45 else 46 cout << "the element found is" << i + 1 << "位" << endl; 47 48 49 } 50 51 cin.ignore(); 52 return 0; 53 }
请输入数列中的元素个数n为: 11
请依次输入:2 6 3 7 99 33 45 82 14 32 5
排序后的数组为:2 3 5 6 7 14 32 33 45 82 99
输入要查找的元素:3
the element found is2位
扩展:使用递归算法实现:

1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int M = 10000; 7 int s[M]; 8 9 int BinarySearch(int s[], int x, int low, int high) 10 { 11 12 if (low>high) 13 return -1; 14 int middle = (low + high) / 2; 15 if (x == s[middle]) 16 return middle; 17 else if (x < s[middle]) 18 return BinarySearch(s, x, low, middle - 1); 19 else 20 return BinarySearch(s, x, middle + 1, high); 21 } 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 int n,x,i; 26 27 cout << "请输入数列中的元素个数n为: "; 28 while (cin >> n) 29 { 30 cout << "请依次输入:"; 31 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 32 cin >> s[i]; 33 sort(s, s + n); 34 cout << "排序后的数组为:"; 35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 36 cout << s[i]<<" "; 37 cout << endl; 38 cout << "输入要查找的元素:"; 39 cin >> x; 40 i = BinarySearch(s,x,0,n-1); 41 if (i == -1) 42 cout << "no found"; 43 else 44 cout << "the element found is" << i + 1 << "位" << endl; 45 46 47 } 48 49 cin.ignore(); 50 return 0; 51 }
算法思想:
