一、题目
1、审题
2、分析
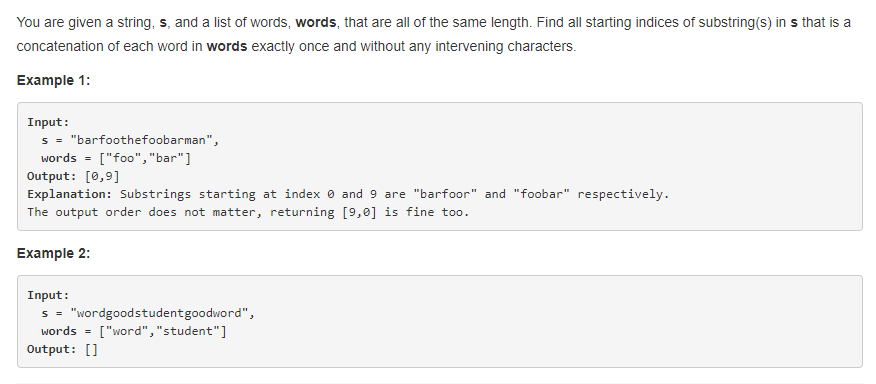
给出一个字符串 S, 一个字符串单词数组 words(所有单词均等长),在S中找到包含words中所有单词且只包含一次的子字符串,返回符合该要求的所有子串的首位置,word中的字符串可能会有重复。
二、解答
1、思路:
实现一: 通过暴力的方法依次截取 S 中的字符串进行判断是否包含了 words 中的所有元素。借助 Map 进行存放 words 中元素,从而判断是否包含所有元素。
class Solution { public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) { Map<String, Integer> mapOfWords = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); int wordsLen = words.length; // 字符串个数 int slen = s.length(); int i, j, count = wordsLen; boolean countChanged = false; // 判断是否改变了 map 中的值,如果没改变则无需初始化 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if(wordsLen == 0 || slen == 0) return result; int singleWordLen = words[0].length(); // 单个字符串长度 initializeMap(mapOfWords, words); for (i = 0; i <= slen - wordsLen*singleWordLen; i++) { String subStr = s.substring(i, i + singleWordLen); // 取出一个子串 j = i; if(mapOfWords.containsKey(subStr) ) while (mapOfWords.get(subStr) != 0) { mapOfWords.put(subStr, mapOfWords.get(subStr) - 1); // 值 - 1 count--; countChanged = true; j += singleWordLen; if(j + singleWordLen > slen) break; subStr = s.substring(j, j + singleWordLen); // 下一个字符串 if (!mapOfWords.containsKey(subStr)) break; } if(count == 0) //找齐所有字符串数组中的字串后把该索引压入; result.add(i); if(countChanged) { //若改变了map的值需要重新初始化map和count mapOfWords.clear(); initializeMap(mapOfWords, words); count = wordsLen; countChanged = false; } } return result; } public void initializeMap(Map<String, Integer> mapOfWords, String[] words) { for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) { //初始化map if(mapOfWords.containsKey(words[i])) { mapOfWords.put(words[i], mapOfWords.get(words[i]) + 1); } else { mapOfWords.put(words[i], 1); } } } }
实现二: 通过两个 Map 来实现代码的简化,一个 Map 存放数组的字符串及其出现个数,另一个存放遍历的字符串中出现的数组元素的情况。每次遍历一个 S 的子串只需将 两个Map 进行对比,即可判断该字符串是否符合要求。
public class Solution { public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); Map<String, Integer> tmp = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); int sLength = s.length(); int wordsNum = words.length; int wordslength = words[0].length(); int j; if(sLength < wordsNum || wordsNum == 0) return list; for(int i = 0; i < wordsNum; i++) { if(map.containsKey(words[i])) map.put(words[i], map.get(words[i]) + 1); else map.put(words[i], 1); } for (int i = 0; i <= sLength-wordsNum*wordslength; i++) { tmp.clear(); for(j = 0; j < wordsNum; j++) { String word = s.substring(i+j*wordslength, i + j*wordslength+wordslength); if(!map.containsKey(word)) break; // 可能有重复 if(tmp.containsKey(word)) tmp.put(word, tmp.get(word)+1); else tmp.put(word, 1); if(tmp.get(word) > map.get(word)) break; } if(j == wordsNum) list.add(i); } return list; } }