每段代码都是在牛客网在线编程通过后,然后拷过来的,准确性可以保证。
1、二维数组中的查找
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
(1)
1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean Find(int[][] array, int target) { 3 int len = array.length - 1; 4 int i = 0; 5 while ((len >= 0) && (i < array[0].length)) { 6 if (array[len][i] > target) { 7 len--; 8 } else if (array[len][i] < target) { 9 i++; 10 } else { 11 return true; 12 } 13 } 14 return false; 15 } 16 }
(2)
1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean Find(int[][] array, int target) { 3 int len = array.length - 1; 4 int i = 0; 5 while ((len >= 0) && (i < array[0].length)) { 6 if (array[len][i] > target) { 7 len–; 8 } else if (array[len][i] < target) { 9 i++; 10 } else { 11 return true; 12 } 13 } 14 return false; 15 } 16 }
2、替换空格
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
(1)
1 public class Solution { 2 public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) { 3 int spaceNum = 0; 4 for(int i=0; i<str.length(); i++){ 5 if(str.charAt(i)==' '){ 6 spaceNum++; 7 } 8 } 9 10 int indexOld = str.length() - 1; 11 int newLength = str.length() + 2*spaceNum; 12 int indexNew = newLength - 1; 13 str.setLength(newLength); 14 for(; indexOld>=0 && indexOld<newLength; indexOld--){ 15 if(str.charAt(indexOld)==' '){ 16 str.setCharAt(indexNew--,'0'); 17 str.setCharAt(indexNew--,'2'); 18 str.setCharAt(indexNew--,'%'); 19 }else{ 20 str.setCharAt(indexNew--, str.charAt(indexOld)); 21 } 22 } 23 return str.toString(); 24 } 25 }
(2)
1 public class Solution { 2 public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) { 3 if(str==null) { 4 return null; 5 } 6 7 8 int spaceNum = 0; 9 int length = str.length(); 10 int newLength = 0; 11 for(int i=0; i<length; i++) { 12 if(str.charAt(i)==' ') { 13 spaceNum++; 14 } 15 } 16 17 newLength = length + 2*spaceNum; 18 char[] newChars = new char[newLength]; 19 int index = newLength - 1; 20 for(int i=length-1; i>=0; i--) { 21 if(str.charAt(i)==' ') { 22 newChars[index--] = '0'; 23 newChars[index--] = '2'; 24 newChars[index--] = '%'; 25 }else { 26 newChars[index--] = str.charAt(i); 27 } 28 } 29 return new String(newChars); 30 } 31 }
(3)
1 public class Solution { 2 public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) { 3 if(str == null){ 4 return null; 5 } 6 7 int spaceNum = 0; 8 int length = str.length(); 9 int newLength = 0; 10 for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ 11 if(str.charAt(i)==' '){ 12 spaceNum++; 13 } 14 } 15 16 newLength = length + 2*spaceNum; 17 char[] newChars = new char[newLength]; 18 int index = newLength - 1; 19 for(int i=length-1; i>=0; i--){ 20 if(str.charAt(i)==' '){ 21 newChars[index--] = '0'; 22 newChars[index--] = '2'; 23 newChars[index--] = '%'; 24 }else{ 25 newChars[index--] = str.charAt(i); 26 } 27 } 28 return new String(newChars); 29 } 30 }
(4)
1 public class Solution { 2 public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) { 3 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 4 for(int i=0; i<str.length(); i++){ 5 if(str.charAt(i)==' '){ 6 sb.append("%20"); 7 }else{ 8 sb.append(str.charAt(i)); 9 } 10 } 11 return sb.toString(); 12 } 13 }
3、从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表,从尾到头打印链表每个节点的值。
链表结点定义:
/** * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next = null; * * ListNode(int val) { * this.val = val; * } * }
(1)常规栈实现
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Stack; 3 public class Solution { 4 public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { 5 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); 6 while(listNode != null){ 7 stack.push(listNode.val); 8 listNode = listNode.next; 9 } 10 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 11 while(!stack.isEmpty()){ 12 list.add(stack.pop()); 13 } 14 return list; 15 } 16 }
(2)使用递归实现
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 public class Solution { 3 ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 4 public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { 5 if(listNode != null){ 6 printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next); 7 arrayList.add(listNode.val); 8 } 9 return arrayList; 10 } 11 }
4、重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
二叉树结构是这样的:
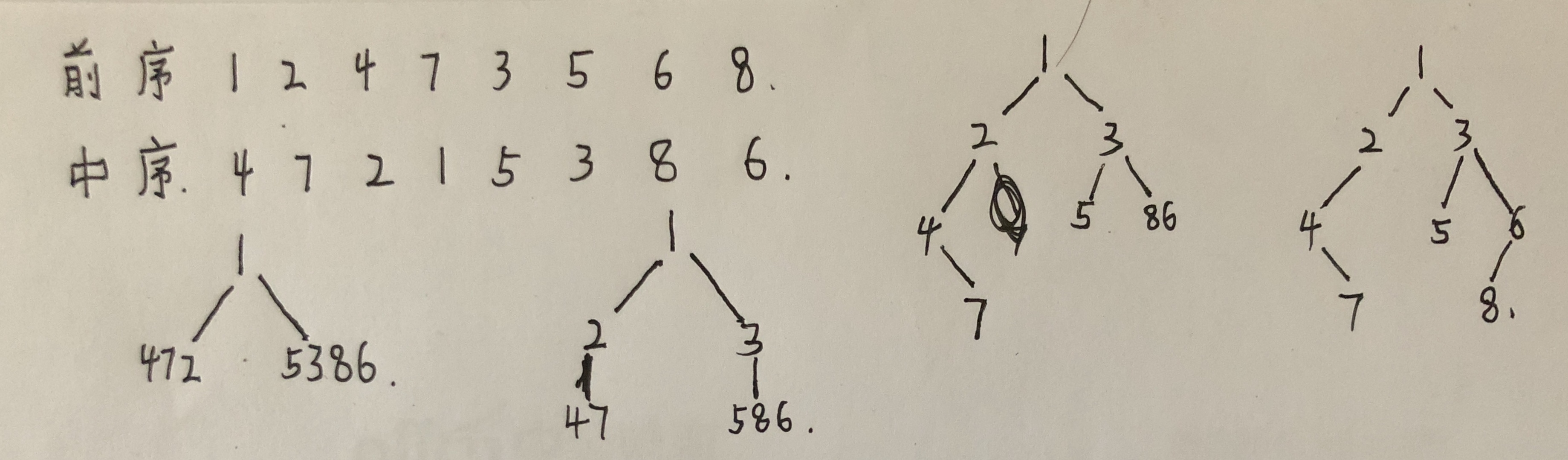
二叉树结点定义:
/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */
(1)
1 public class Solution { 2 public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre,int[] in) { 3 TreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, 0, pre.length-1, 4 in, 0, in.length-1); 5 //返回根节点 6 return root; 7 } 8 9 private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int startPre, int endPre, 10 int[] in, int startIn, int endIn){ 11 //该节点没有左子树或右子树 12 if(startPre > endPre||startIn > endIn) 13 return null; 14 //新建一个二叉树节点,并将值存进去 15 TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre[startPre]); 16 //对该node结点的左右结点赋值 17 for(int i=startIn; i<=endIn; i++){ 18 //从中序遍历中得到根节点在数组中的下标,下标左边是左子树的数,下标右边是右子树的,对左右子树进行递归,感觉有点像二分查找。 19 if(pre[startPre]==in[i]){ 20 //父节点的左子树, i-startIn是节点pre[startPer]的左子树节点共有多少个,然后加上startPre就是pre数组中pre[startPre]的左子树所有结点在先序遍历序列中最后一个下标。 21 node.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, startPre+1, startPre+i-startIn, 22 in, startIn, i-1); 23 //父节点的右子树 24 node.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, i-startIn+startPre+1, endPre, 25 in, i+1, endIn); 26 } 27 } 28 return node; 29 } 30 }
5、用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
(1)
1 import java.util.Stack; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); 5 Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); 6 7 public void push(int node) { 8 stack1.push(node); 9 } 10 //这里用栈stack1表示队尾,用来入队,栈stack2表队首,用来出队 11 public int pop() { 12 if(stack1.empty() && stack2.empty()) 13 throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!"); 14 if(stack2.empty()) 15 while(!stack1.empty()) 16 stack2.push(stack1.pop()); 17 return stack2.pop(); 18 } 19 }
6、旋转数组的最小数字
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 public class Solution { 3 public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) { 4 if(array.length==0) 5 return 0; 6 for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) 7 if(array[i]>array[i+1]) 8 return array[i+1]; 9 //数组长度为0 10 return 0; 11 } 12 }
(2)基于二分法实现
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 public class Solution { 3 public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) { 4 if(array==null || array.length==0) 5 return 0; 6 int low = 0; 7 int high = array.length-1; 8 while(low<high){ 9 int mid = low+(high-low)/2; 10 if(array[mid]>array[high]){ 11 low = mid+1; 12 }else if(array[mid] == array[high]){ 13 high = high-1; 14 }else{ 15 high = mid; 16 } 17 } 18 return array[low]; 19 } 20 }
7、斐波那契数列
大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项。n<=39
(补充:斐波那契数列指的是这样一个数列 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21等,从第三项开始,每项都是前两项的和)
(1)
1 public class Solution { 2 public int Fibonacci(int n) { 3 int value = 1; 4 int pre = 1; 5 int next = 1; 6 int num = 3; 7 if(n<=0) return 0; 8 if(n==1 || n==2) return value; 9 while(n >= num){ 10 value = pre+next; 11 pre = next; 12 next = value; 13 num++; 14 } 15 return value; 16 } 17 }
8、跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
(1)递归实现
1 public class Solution { 2 public int JumpFloor(int target) { 3 int result = 0; 4 if(target > 0){ 5 if(target <= 2){ 6 return target; 7 }else{ 8 return result = JumpFloor(target-1)+ 9 JumpFloor(target-2); 10 } 11 } 12 return result; 13 } 14 }
(2)
1 public class Solution { 2 public int JumpFloor(int target) { 3 int fir = 1; 4 int sec = 2; 5 int race = 0; 6 if(target <= 0) 7 return 0; 8 if(target == 1) 9 return 1; 10 if(target == 2) 11 return 2; 12 for(int i=3; i<=target; i++){ 13 race = fir+sec; 14 fir = sec; 15 sec = race; 16 } 17 return race; 18 } 19 }
9、变态跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
(1)2^(n-1)使用左移运算符计算
1 public class Solution { 2 public int JumpFloorII(int target) { 3 return 1<<--target; 4 } 5 }
(2)递归方式
1 public class Solution { 2 public int JumpFloorII(int target) { 3 if(target<0){ 4 return 0; 5 }else if(target==1){ 6 return 1; 7 }else{ 8 return 2*JumpFloorII(target-1); 9 } 10 } 11 }
(3)循环方式
1 public class Solution { 2 public int JumpFloorII(int target) { 3 int jumpFloor = 1; 4 while(--target>0){ 5 jumpFloor *=2; 6 } 7 return jumpFloor; 8 } 9 }
10、矩形覆盖
我们可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
(1)
1 public class Solution { 2 public int RectCover(int target) { 3 if(target<=0) return 0; 4 if(target==1) return 1; 5 if(target==2) return 2; 6 else 7 return RectCover(target-1)+RectCover(target-2); 8 } 9 }