1⃣️普通库函数排序:
class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { Arrays.sort(nums); return nums[nums.length-k]; } }
2⃣️堆排序:
时间复杂度 O(nlogk),空间复杂度 O(k)
三种函数poll,peek,element,add
共同点:
- 都是返回队列中的首个元素
不同点:
- poll:将首个元素从队列中弹出,如果队列是空的,就返回null
- peek:查看首个元素,不会移除首个元素,如果队列是空的就返回null
- element:查看首个元素,不会移除首个元素,如果队列是空的就抛出异常NoSuchElementException
- add:添加新元素在堆内
- size:表示求堆的大小
- 首先先整理一下本题的思路,要求的是数组中第K个最大元素,也就是说要求排序之后的倒数第K个;
- 再考虑应该是用大顶堆还是小顶堆呢?只有使用小顶堆才能每次都poll(更新)出去不是候选的数值,也就是每次都poll出去最小的第K+1个,来始终保持堆顶的元素是K个最大的元素中最小的一个;
- 注意大顶堆和小顶堆两者的建立,之前我的博文中有提到:
Java 使用 PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (y - x)) 可方便实现大顶堆。
Java 使用 PriorityQueue<>() 可方便实现小顶堆。
实际上小顶堆内部默认的完整格式是:PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (x - y)),尤其注意全部参数的设置都是括号里面的写法;
class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { PriorityQueue<Integer> q=new PriorityQueue<>(); for(int n:nums){ q.add(n); if(q.size()>k){ q.poll(); } } return q.peek(); } }
3⃣️快速选择
一般用于求解 Kth Element 问题,可以在 O(n) 时间复杂度,O(1) 空间复杂度完成求解工作。与快速排序一样,快速选择一般需要先打乱数组,否则最坏情况下时间复杂度为 O(n2)。也就是说对于每一个选定的对比数都要比较N次。
快速排序较为详细介绍:https://xiaozhuanlan.com/topic/6854379012
import java.lang.*; class Solution { //为什么要用this指针呢?如果不用this指针函数参数就要一直传递nums数组。 int[] nums; int size; public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k){ this.nums = nums; size = nums.length; // kth largest is (N - k)th smallest return quickselect(0, size - 1, size - k); } public int quickselect(int l,int r,int index){ //注意这里既可以用递归的方法也可以用循环的方法 //递归的方法 if(l==r) return this.nums[l]; Random rd=new Random(); int pivot=l+rd.nextInt(r-l);//产生一定范围的随机数 int j=partition(l,r,pivot); if(j==index) return this.nums[j]; if(j>index){ return quickselect(l,j-1,index);//注意不是j } else { return quickselect(j+1,r,index); } //循环的方法 // k = nums.length - k; // int lo = 0; // int hi = nums.length - 1; // while (lo < hi) { // final int j = partition(nums, lo, hi); // if(j < k) { // lo = j + 1; // } else if (j > k) { // hi = j - 1; // } else { // break; // } // } // return nums[k]; } public int partition(int l,int r,int pivot){ //这里写的比较晦涩,把最右边的数值选作为pivot对比数 int cp=this.nums[pivot]; swap(pivot,r); int zl=l; //从头开始遍历,用一个滞留指针指向最靠前的大于对比数的值,也就是把小于对比数的值移动到前面 for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){ if(this.nums[i]<cp){ swap(i,zl); zl++; } } swap(zl,r); return zl; } public void swap(int l,int r){ int tmp=this.nums[l]; this.nums[l]=this.nums[r]; this.nums[r]=tmp; } }
leetcode 347
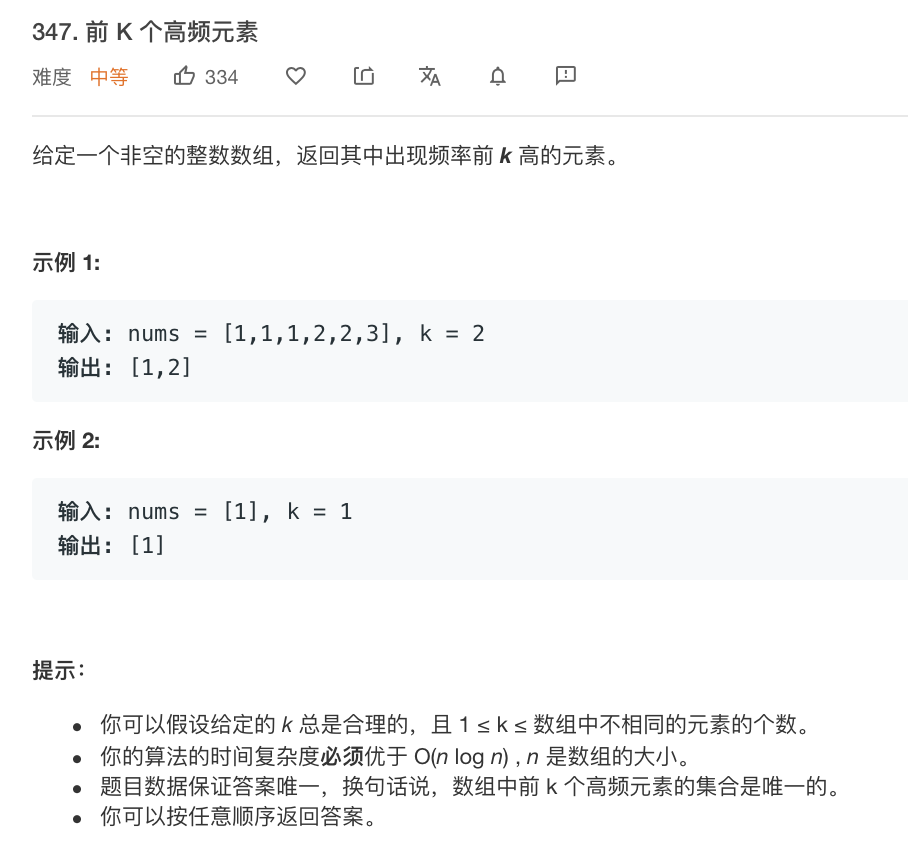
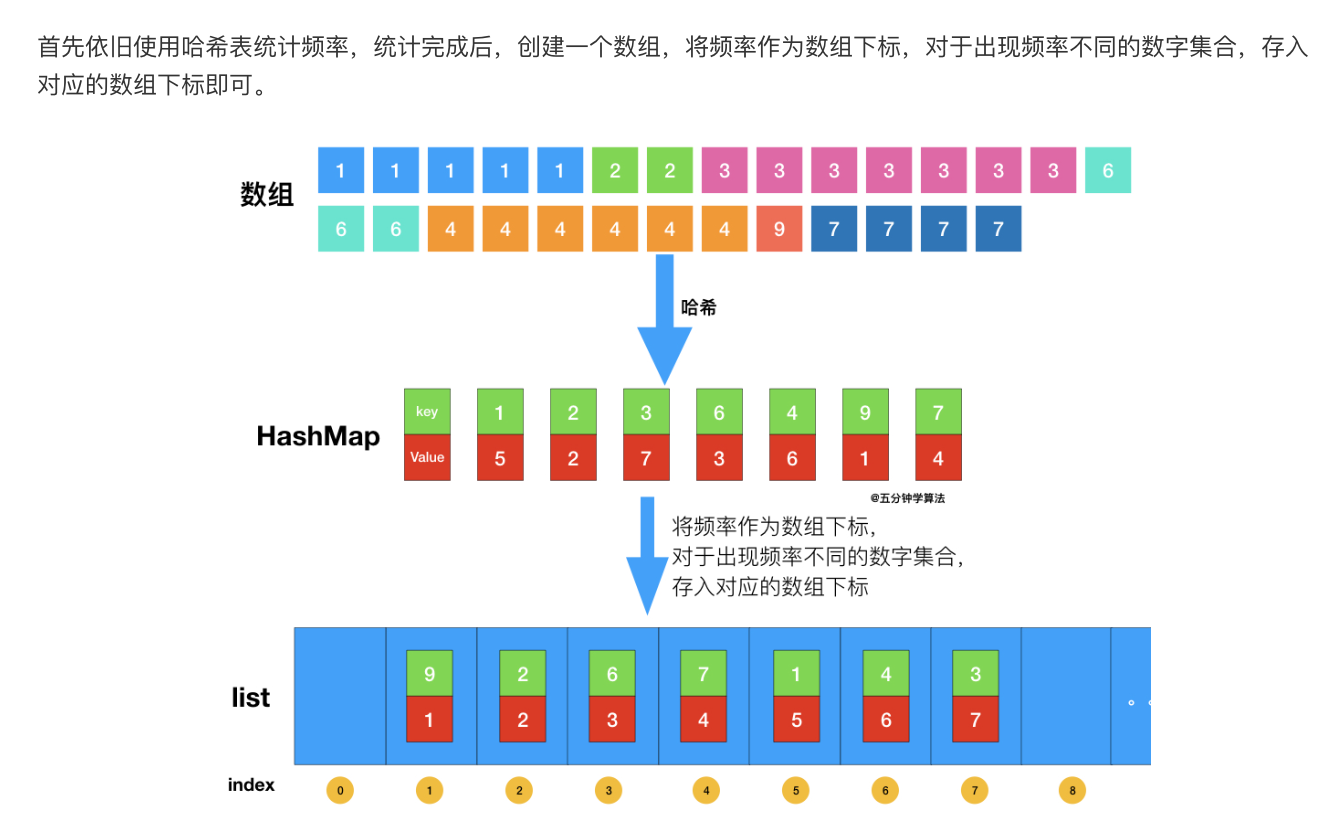

//基于桶排序求解「前 K 个高频元素」 class Solution { public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList(); // 使用字典,统计每个元素出现的次数,元素为键,元素出现的次数为值 HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); for(int num : nums){ if (map.containsKey(num)) { map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1); } else { map.put(num, 1); } } //桶排序 //将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标 List<Integer>[] list = new List[nums.length+1]; for(int key : map.keySet()){ // 获取出现的次数作为下标 int i = map.get(key); if(list[i] == null){ list[i] = new ArrayList(); } list[i].add(key); } // 倒序遍历数组获取出现顺序从大到小的排列 for(int i = list.length - 1;i >= 0 && res.size() < k;i--){ if(list[i] == null) continue; res.addAll(list[i]); } return res; } }
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>(); Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } List<Integer>[] bucket = new List[nums.length + 1]; for(int key : map.keySet()) { int frequency = map.get(key); if(bucket[frequency] == null) { bucket[frequency] = new ArrayList<>(); } bucket[frequency].add(key); } for(int i = bucket.length - 1; i >= 0 && ret.size() < k; i--) { if(bucket[i] != null) { ret.addAll(bucket[i]); } } return ret; }