-------------------siwuxie095
Lazy Prim 算法
在介绍 Prim 算法之前,先介绍 Lazy Prim 算法
看如下实例:

这张连通带权无向图中所有边上的权值如下:

求最小生成树的过程,其实就是从这张连通带权无向图
的所有边中选出 V-1 条边,并且这 V-1 条边连接了 V
个顶点
根据切分定理可知,一旦将这个图做一个切分后,相应
的横切边中权值最小的那条边就一定属于最小生成树
将 0 作为起始点,开始切分,逐步将蓝色阵营的顶点
转换到红色阵营中
(1)将 0 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个切分,相应的就有横切边
接下来将最小堆作为辅助数据结构,可以非常快速地找到
横切边中权值最小的那条边
将横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值最小的边
此时,0-7 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.16,且 0、7 分属
不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(2)将 7 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,1-7 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.19,且 1、7
分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(3)将 1 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,0-2 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.26,且 0、2
分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(4)将 2 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,2-3 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.17,且 2、3
分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
注意:此时,1-2 和 2-7 实际上已经不是横切边了,
本来应该从最小堆中剔除,不能再作为最小生成树
的候选边,但这里并不急着剔除,而是依然保留在
最小堆中,当二者上移到最小堆的顶端被拿出来时,
就会发现二者的两端同属红色阵营,直接把二者扔
掉即可。这也正是 Lazy Prim 算法的懒之所在
(5)将 3 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,5-7 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.28,且 5、7
分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(6)将 5 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,1-3 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.29,但 1、3
同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 1-5,权值为 0.32,
但 1、5 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 2-7,权值为 0.34,
但 2、7 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 4-5,权值为 0.35,
且 4、5 分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(7)将 4 加入到红色阵营中

这样一来,就形成了一个新的切分,相应的就有新的
横切边
将新的横切边放入到最小堆中,并拿出最小堆中权值
最小的边
此时,1-2 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.36,但 1、2
同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 4-7,权值为 0.37,
但 4、7 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 0-4,权值为 0.38,
但 0、4 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 2-6,权值为 0.40,
且 2、6 分属不同阵营,一定属于最小生成树
(8)将 6 加入到红色阵营中

至此,所有蓝色阵营的顶点都已经转换到红色阵营中,
此时,Lazy Prim 算法其实就已经可以结束了
但如果是以最小堆中的边为空作为结束依据的话,依
然可以从最小堆中继续拿出权值最小的边,不过,这
之后拿出的边肯定不再是横切边了
此时,3-6 是权值最小的边,权值为 0.52,但 3、6
同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 0-6,权值为 0.58,
但 0、6 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
下一个最小堆中的权值最小的边是 4-6,权值为 0.93,
但 4、6 同属红色阵营,不是横切边,直接扔掉
(9)最后

至此,Lazy Prim 算法就真正结束了,得到了这张图
的最小生成树
程序 1:
Edge.h:
|
#ifndef EDGE_H #define EDGE_H
#include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//边信息:两个顶点和权值 template<typename Weight> class Edge {
private:
int a, b; //边的两个顶点a和b(如果是有向图,就默认从顶点a指向顶点b) Weight weight; //边上的权值
public:
Edge(int a, int b, Weight weight) { this->a = a; this->b = b; this->weight = weight; }
//默认构造函数 Edge(){}
~Edge(){}
int v(){ return a; }
int w(){ return b; }
Weight wt() { return weight; }
//知道边的一个顶点x,返回另一个顶点 int other(int x) { assert(x == a || x == b); return x == a ? b : a; }
//友元函数重载 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Edge &e) { os << e.a << "-" << e.b << ": " << e.weight; return os; }
bool operator<(Edge<Weight> &e) { return weight < e.wt(); }
bool operator<=(Edge<Weight> &e) { return weight <= e.wt(); }
bool operator>(Edge<Weight> &e) { return weight > e.wt(); }
bool operator>=(Edge<Weight> &e) { return weight >= e.wt(); }
bool operator==(Edge<Weight> &e) { return weight == e.wt(); } };
#endif |
SparseGraph.h:
|
#ifndef SPARSEGRAPH_H #define SPARSEGRAPH_H
#include "Edge.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
// 稀疏图 - 邻接表 template<typename Weight> class SparseGraph {
private:
int n, m; //n 和 m 分别表示顶点数和边数 bool directed; //directed表示是有向图还是无向图 vector<vector<Edge<Weight> *>> g; //g[i]里存储的就是和顶点i相邻的所有边指针
public:
SparseGraph(int n, bool directed) { this->n = n; this->m = 0; this->directed = directed; //g[i]初始化为空的vector for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { g.push_back(vector<Edge<Weight> *>()); } }
~SparseGraph() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < g[i].size(); j++) { delete g[i][j]; } } }
int V(){ return n; } int E(){ return m; }
void addEdge(int v, int w, Weight weight) { assert(v >= 0 && v < n); assert(w >= 0 && w < n);
g[v].push_back(new Edge<Weight>(v, w, weight)); //(1)顶点v不等于顶点w,即不是自环边 //(2)且不是有向图,即是无向图 if (v != w && !directed) { g[w].push_back(new Edge<Weight>(w, v, weight)); }
m++; }
//hasEdge()判断顶点v和顶点w之间是否有边 //hasEdge()的时间复杂度:O(n) bool hasEdge(int v, int w) { assert(v >= 0 && v < n); assert(w >= 0 && w < n);
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++) { if (g[v][i]->other(v) == w) { return true; } }
return false; }
void show() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << "vertex " << i << ": "; for (int j = 0; j < g[i].size(); j++) { cout << "{to:" << g[i][j]->w() << ",wt:" << g[i][j]->wt() << "} "; } cout << endl; } }
//邻边迭代器(相邻,即 adjacent) // //使用迭代器可以隐藏迭代的过程,按照一定的 //顺序访问一个容器中的所有元素 class adjIterator { private:
SparseGraph &G; //图的引用,即要迭代的图 int v; //顶点v int index; //相邻顶点的索引
public:
adjIterator(SparseGraph &graph, int v) : G(graph) { this->v = v; this->index = 0; }
//要迭代的第一个元素 Edge<Weight> *begin() { //因为有可能多次调用begin(), //所以显式的将index设置为0 index = 0; //如果g[v]的size()不为0 if (G.g[v].size()) { return G.g[v][index]; }
return NULL; }
//要迭代的下一个元素 Edge<Weight> *next() { index++; if (index < G.g[v].size()) { return G.g[v][index]; }
return NULL; }
//判断迭代是否终止 bool end() { return index >= G.g[v].size(); } }; };
#endif |
DenseGraph.h:
|
#ifndef DENSEGRAPH_H #define DENSEGRAPH_H
#include "Edge.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
// 稠密图 - 邻接矩阵 template<typename Weight> class DenseGraph {
private:
int n, m; //n 和 m 分别表示顶点数和边数 bool directed; //directed表示是有向图还是无向图 vector<vector<Edge<Weight> *>> g; //二维矩阵,存储边指针
public:
DenseGraph(int n, bool directed) { this->n = n; this->m = 0; this->directed = directed; //二维矩阵:n行n列,全部初始化为NULL for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { g.push_back(vector<Edge<Weight> *>(n, NULL)); } }
~DenseGraph() { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (g[i][j] != NULL) { delete g[i][j]; } } } }
int V(){ return n; } int E(){ return m; }
//在顶点v和顶点w之间建立一条边 void addEdge(int v, int w, Weight weight) { assert(v >= 0 && v < n); assert(w >= 0 && w < n);
//如果顶点v和顶点w之间已经存在一条边,就删掉, //之后按照传入权值重建一条边,即直接覆盖 if (hasEdge(v, w)) { delete g[v][w];
//如果是无向图,还要删除和主对角线对称的值 if (!directed) { delete g[w][v]; }
m--; }
g[v][w] = new Edge<Weight>(v, w, weight);
//如果是无向图,还要在和主对角线对称处添加值 if (!directed) { g[w][v] = new Edge<Weight>(w, v, weight); }
m++; }
//hasEdge()判断顶点v和顶点w之间是否有边 //hasEdge()的时间复杂度:O(1) bool hasEdge(int v, int w) { assert(v >= 0 && v < n); assert(w >= 0 && w < n); return g[v][w] != NULL; }
void show() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (g[i][j]) { cout << g[i][j]->wt() << " "; } else { cout << "NULL "; } } cout << endl; } }
//邻边迭代器(相邻,即 adjacent) class adjIterator { private:
DenseGraph &G; //图引用,即要迭代的图 int v; //顶点v int index; //相邻顶点的索引
public:
adjIterator(DenseGraph &graph, int v) : G(graph) { this->v = v; this->index = -1; }
//要迭代的第一个元素 Edge<Weight> *begin() { //找第一个权值不为NULL的元素,即为要迭代的第一个元素 index = -1; return next(); }
//要迭代的下一个元素 Edge<Weight> *next() { for (index += 1; index < G.V(); index++) { if (G.g[v][index]) { return index; } }
return NULL; }
//判断迭代是否终止 bool end() { return index >= G.V(); } }; };
#endif |
ReadGraph.h:
|
#ifndef READGRAPH_H #define READGRAPH_H
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//从文件中读取图的测试用例 template <typename Graph, typename Weight> class ReadGraph {
public: ReadGraph(Graph &graph, const string &filename) {
ifstream file(filename); string line; //一行一行的读取 int V, E;
assert(file.is_open());
//读取file中的第一行到line中 assert(getline(file, line)); //将字符串line放在stringstream中 stringstream ss(line); //通过stringstream解析出整型变量:顶点数和边数 ss >> V >> E;
//确保文件里的顶点数和图的构造函数中传入的顶点数一致 assert(V == graph.V());
//读取file中的其它行 for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
assert(getline(file, line)); stringstream ss(line);
int a, b; Weight w; ss >> a >> b >> w; assert(a >= 0 && a < V); assert(b >= 0 && b < V); graph.addEdge(a, b, w); } } };
#endif |
MinHeap.h:
|
#ifndef MINHEAP_H #define MINHEAP_H
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//最小堆:索引从0开始 template<typename Item> class MinHeap {
private: Item *data; int count; int capacity;
//私有函数,用户不能调用 void shiftUp(int k) { //如果新添加的元素小于父节点的元素,则进行交换 while (k > 0 && data[(k - 1) / 2] > data[k]) { swap(data[(k - 1) / 2], data[k]); k = (k - 1) / 2; } }
//也是私有函数,用户不能调用 void shiftDown(int k) { //只要当前节点有孩子就进行循环 while (2 * k + 1 < count) { // 在此轮循环中,data[k]和data[j]交换位置 int j = 2 * k + 1;
// data[j]是data[2*k]和data[2*k+1]中的最小值 if (j + 1 < count && data[j + 1] < data[j]) { j++; }
if (data[k] <= data[j]) { break; }
swap(data[k], data[j]); k = j; } }
public:
MinHeap(int capacity) { data = new Item[capacity]; //计数器,即序列号,这里索引等于序列号减一 count = 0; this->capacity = capacity; }
~MinHeap() { delete []data; }
int size() { return count; }
bool isEmpty() { return count == 0; }
//向最小堆中添加新元素,新元素放在数组末尾 void insert(Item item) { //防止越界 assert(count <= capacity);
//索引从0开始 data[count] = item; count++;
//新加入的元素有可能破坏最小堆的定义,需要通过 //Shift Up操作,把索引为count-1的元素尝试着向上 //移动来保持最小堆的定义 shiftUp(count - 1); }
//取出最小堆中根节点的元素(最小值) Item extractMin() { //首先要保证堆不为空 assert(count > 0);
//取出根节点的元素(最小值) Item ret = data[0];
//将第一个元素(最小值)和最后一个元素进行交换 swap(data[0], data[count - 1]);
//count--后,被取出的根节点就不用再考虑了 count--;
//调用Shift Down操作,想办法将此时的根节点(索引为0) //向下移动,来保持最小堆的定义 shiftDown(0);
return ret; }
public:
//在控制台打印测试用例 void testPrint() {
//限制:只能打印100个元素以内的堆,因为控制台一行的字符数量有限 if (size() >= 100) { cout << "Fancy print can only work for less than 100 int"; return; }
//限制:只能打印类型是int的堆 if (typeid(Item) != typeid(int)) { cout << "Fancy print can only work for int item"; return; }
cout << "The Heap size is: " << size() << endl; cout << "data in heap: "; for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) { cout << data[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << endl;
int n = size(); int max_level = 0; int number_per_level = 1; while (n > 0) { max_level += 1; n -= number_per_level; number_per_level *= 2; }
int max_level_number = int(pow(2, max_level - 1)); int cur_tree_max_level_number = max_level_number; int index = 0; for (int level = 0; level < max_level; level++) { string line1 = string(max_level_number * 3 - 1, ' ');
int cur_level_number = min(count - int(pow(2, level)) + 1, int(pow(2, level)));
bool isLeft = true;
for (int index_cur_level = 0; index_cur_level < cur_level_number; index++, index_cur_level++) { putNumberInLine(data[index], line1, index_cur_level, cur_tree_max_level_number * 3 - 1, isLeft);
isLeft = !isLeft; } cout << line1 << endl;
if (level == max_level - 1) { break; }
string line2 = string(max_level_number * 3 - 1, ' '); for (int index_cur_level = 0; index_cur_level < cur_level_number; index_cur_level++) { putBranchInLine(line2, index_cur_level, cur_tree_max_level_number * 3 - 1); }
cout << line2 << endl;
cur_tree_max_level_number /= 2; } }
private:
void putNumberInLine(int num, string &line, int index_cur_level, int cur_tree_width, bool isLeft) {
int sub_tree_width = (cur_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int offset = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_tree_width;
assert(offset + 1 < line.size());
if (num >= 10) { line[offset + 0] = '0' + num / 10; line[offset + 1] = '0' + num % 10; } else { if (isLeft) line[offset + 0] = '0' + num; else line[offset + 1] = '0' + num; } }
void putBranchInLine(string &line, int index_cur_level, int cur_tree_width) {
int sub_tree_width = (cur_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int sub_sub_tree_width = (sub_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int offset_left = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_sub_tree_width;
assert(offset_left + 1 < line.size());
int offset_right = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_tree_width + 1 + sub_sub_tree_width;
assert(offset_right < line.size());
line[offset_left + 1] = '/'; line[offset_right + 0] = '\'; } };
#endif |
LazyPrimMST.h:
|
#ifndef LAZYPRIMMST_H #define LAZYPRIMMST_H
#include "Edge.h" #include "MinHeap.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//Lazy Prim 算法实现最小生成树 template<typename Graph, typename Weight> class LazyPrimMST {
private:
Graph &G; //图的引用,即要切分的图 MinHeap<Edge<Weight>> pq; //pq 充当一个优先队列,pq 即 priority queue bool *marked; //切分后的顶点分到另一阵营时,需要进行标记 vector<Edge<Weight>> mst; //属于最小生成树的 V-1 条边存储到向量 mst 中 Weight mstWeight; //最后最小生成树的总权值 mstWeight
void visit(int v) { //保证顶点 v 属于蓝色阵营,即 false assert(!marked[v]); //访问过顶点 v 后转为红色阵营,即 true marked[v] = true;
//注意:声明迭代器时,前面还要加 typename,表明 adjIterator //是 Graph 中的类型,而不是成员变量 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); //遍历顶点 v 所有的邻边 for (Edge<Weight> *e = adj.begin(); !adj.end(); e = adj.next()) { //如果顶点 v 的邻边 e 对应的另一端的顶点没有被访问过, //即分属不同阵营,即为横切边,放入优先队列中 if (!marked[e->other(v)]) { pq.insert(*e); } } }
public:
LazyPrimMST(Graph &graph) :G(graph), pq(MinHeap<Edge<Weight>>(graph.E())) {
marked = new bool[G.V()]; for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) { marked[i] = false; } //保证向量 mst 在初始化时为空 mst.clear();
// Lazy Prim visit(0); //如果优先队列不为空 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { Edge<Weight> e = pq.extractMin(); //如果取出来权值最小的边的两个端点同属 //红色阵营,就直接把这条边扔掉 if (marked[e.v()] == marked[e.w()]) { continue; }
//否则,把 e 加入到向量 mst 中 mst.push_back(e); //继续访问 e 的蓝色一端的顶点 if (!marked[e.v()]) { visit(e.v()); } else { visit(e.w()); } }
mstWeight = mst[0].wt(); for (int i = 1; i < mst.size(); i++) { mstWeight += mst[i].wt(); } }
~LazyPrimMST() { delete []marked; }
vector<Edge<Weight>> mstEdges() { return mst; };
Weight result() { return mstWeight; }; };
#endif |
main.cpp:
|
#include "SparseGraph.h" #include "DenseGraph.h" #include "ReadGraph.h" #include "LazyPrimMST.h" #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std;
int main() {
string filename = "testG1.txt"; int V = 8;
//稀疏图 SparseGraph<double> g = SparseGraph<double>(V, false); ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>, double> readGraph(g, filename);
// Test Lazy Prim MST cout << "Test Lazy Prim MST:" << endl; LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST(g); vector<Edge<double>> mst = lazyPrimMST.mstEdges(); for (int i = 0; i < mst.size(); i++) { cout << mst[i] << endl; } cout << "The MST weight is: " << lazyPrimMST.result() << endl;
cout << endl;
system("pause"); return 0; }
//Lazy Prim 的时间复杂度: // //主要循环都是在 Priority Queue 不为空的情况下,所有的边都会进入一次 //Priority Queue,所以共循环了 E 次 // //每次循环有两个主要的操作: //(1)extractMin(),时间复杂度是 O(logE) //(2)visit(),其中:(a)遍历的部分:如果是邻接表,就是 O(E),如果是 //邻接矩阵,就是 O(V^2),但在邻接矩阵中,通常表达的是稠密图,对于稠密 //图来说,V^2 近乎和 E 是一个级别的;(b)insert()部分也是 logE 级别的 // // //综上,Lazy Prim 的时间复杂度是 O(E*logE) |
运行一览:

testG1.txt 的内容如下:

该文件可以分成两个部分:
(1)第一行:两个数字分别代表顶点数和边数
(2)其它行:每一行的前两个数字表示一条边,第三个数字表示权值
Prim 算法
Prim 算法是 Lazy Prim 算法的优化,Lazy Prim 的主要问题:
(1)图中所有的边都要进入最小堆,虽然随着切分的改变,红色
阵营中的顶点越来越多,但很多已经在最小堆中的边,其实已经不
再是横切边了
(2)虽然横切边有很多,但通常只关注权值最小的横切边,尤其
是和每个顶点相连的横切边中权值最小的那条边
基于此,Prim 算法的实现如下:
将最小索引堆作为辅助数据结构,用来存储和每个顶点相连的横切
边中权值最小的那条边
随着切分改变,只要不断更新和每个顶点相连的横切边中权值最小
的那条边即可
程序 2:(在程序 1 的基础上,用 MinIndexHeap.h、PrimMST.h
分别替换 MinHeap.h、LazyPrimMST.h,修改 main.cpp 即可)
MinIndexHeap.h:
|
#ifndef MININDEXHEAP_H #define MININDEXHEAP_H
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;
//最小索引堆:索引从0开始 template<typename Item> class MinIndexHeap {
private: Item *data; //指向存储元素的数组 int *indexes; //指向存储索引的数组 int *reverse; //指向存储反向索引的数组 int count; int capacity;
//私有函数,用户不能调用 void shiftUp(int k) { //如果新添加的元素小于父节点的元素,则进行交换 while (k > 0 && data[indexes[(k - 1) / 2]] > data[indexes[k]]) { swap(indexes[(k - 1) / 2], indexes[k]); reverse[indexes[(k - 1) / 2]] = (k - 1) / 2; reverse[indexes[k]] = k; k = (k - 1) / 2; } }
//也是私有函数,用户不能调用 void shiftDown(int k) { //只要当前节点有孩子就进行循环 while (2 * k + 1 < count) { // 在此轮循环中,data[indexes[k]]和data[indexes[j]]交换位置 int j = 2 * k + 1;
// data[indexes[j]]是data[indexes[j]]和data[indexes[j+1]]中的最小值 if (j + 1 < count && data[indexes[j + 1]] < data[indexes[j]]) { j += 1; }
if (data[indexes[k]] <= data[indexes[j]]) { break; }
swap(indexes[k], indexes[j]); reverse[indexes[k]] = k; reverse[indexes[j]] = j; k = j; } }
public:
MinIndexHeap(int capacity) { data = new Item[capacity]; indexes = new int[capacity]; reverse = new int[capacity]; //初始化reverse数组 for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) { reverse[i] = -1; } //计数器,这里索引等于计数器减一 count = 0; this->capacity = capacity;
}
~MinIndexHeap() { delete []data; delete []indexes; delete []reverse; }
int size() { return count; }
bool isEmpty() { return count == 0; }
void insert(int i, Item item) { //防止越界 assert(count <= capacity); assert(i >= 0 && i <= capacity);
data[i] = item; indexes[count] = i; reverse[i] = count; count++;
shiftUp(count - 1); }
//取出最小的data Item extractMin() { //首先要保证堆不为空 assert(count > 0);
Item ret = data[indexes[0]]; swap(indexes[0], indexes[count - 1]); reverse[indexes[count - 1]] = -1; reverse[indexes[0]] = 0; count--; shiftDown(0); return ret; }
//取出最小的data对应的index int extractMinIndex() { assert(count > 0);
//对于外部来说,索引从0开始,所以要减一 int ret = indexes[0]; swap(indexes[0], indexes[count - 1]); reverse[indexes[count - 1]] = -1; reverse[indexes[0]] = 0; count--; shiftDown(0); return ret; }
Item getMin() { assert(count > 0); return data[indexes[0]]; }
int getMinIndex() { assert(count > 0); return indexes[0]; }
bool contain(int i){ assert(i >= 0 && i <= capacity); //reverse数组在构造函数中都初始化为-1, //所以拿-1做比较 return reverse[i] != -1; }
Item getItem(int i) { assert(contain(i)); //对于外部来说,索引从0开始, //对于内部来说,索引从1开始, //所以要加一 return data[i]; }
//修改 index 对应的 data void change(int i, Item newItem) { //防止越界和检查i是否在堆中, //因为有可能已经取出去了 assert(contain(i));
data[i] = newItem;
// 找到indexes[j] = i, j表示data[i]在堆中的位置 // 之后尝试着shiftUp(j)一下, 再shiftDown(j)一下 //即看看能不能向上或向下移动以保持堆的性质 int j = reverse[i]; shiftUp(j); shiftDown(j);
//先用O(1)的时间找到位置,再用O(lgn)的时间完成 //Shift Up和Shift Down,此时,该函数的时间复杂 //度就是O(lgn)级别的,如果有n个堆操作,总时间 //就是O(n*lgn) // //加入了反向查找后,性能得到了巨大的提升 }
public:
//在控制台打印测试用例 void testPrint() {
//限制:只能打印100个元素以内的堆,因为控制台一行的字符数量有限 if (size() >= 100) { cout << "Fancy print can only work for less than 100 int"; return; }
//限制:只能打印类型是int的堆 if (typeid(Item) != typeid(int)) { cout << "Fancy print can only work for int item"; return; }
cout << "The Heap size is: " << size() << endl; cout << "data in heap: "; for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) { cout << data[i] << " "; } cout << endl; cout << endl;
int n = size(); int max_level = 0; int number_per_level = 1; while (n > 0) { max_level += 1; n -= number_per_level; number_per_level *= 2; }
int max_level_number = int(pow(2, max_level - 1)); int cur_tree_max_level_number = max_level_number; int index = 0; for (int level = 0; level < max_level; level++) { string line1 = string(max_level_number * 3 - 1, ' ');
int cur_level_number = min(count - int(pow(2, level)) + 1, int(pow(2, level)));
bool isLeft = true;
for (int index_cur_level = 0; index_cur_level < cur_level_number; index++, index_cur_level++) { putNumberInLine(indexes[index], line1, index_cur_level, cur_tree_max_level_number * 3 - 1, isLeft);
isLeft = !isLeft; } cout << line1 << endl;
if (level == max_level - 1) { break; }
string line2 = string(max_level_number * 3 - 1, ' '); for (int index_cur_level = 0; index_cur_level < cur_level_number; index_cur_level++) { putBranchInLine(line2, index_cur_level, cur_tree_max_level_number * 3 - 1); }
cout << line2 << endl;
cur_tree_max_level_number /= 2; } }
private:
void putNumberInLine(int num, string &line, int index_cur_level, int cur_tree_width, bool isLeft) {
int sub_tree_width = (cur_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int offset = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_tree_width;
assert(offset + 1 < line.size());
if (num >= 10) { line[offset + 0] = '0' + num / 10; line[offset + 1] = '0' + num % 10; } else { if (isLeft) line[offset + 0] = '0' + num; else line[offset + 1] = '0' + num; } }
void putBranchInLine(string &line, int index_cur_level, int cur_tree_width) {
int sub_tree_width = (cur_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int sub_sub_tree_width = (sub_tree_width - 1) / 2;
int offset_left = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_sub_tree_width;
assert(offset_left + 1 < line.size());
int offset_right = index_cur_level * (cur_tree_width + 1) + sub_tree_width + 1 + sub_sub_tree_width;
assert(offset_right < line.size());
line[offset_left + 1] = '/'; line[offset_right + 0] = '\'; } };
#endif |
PrimMST.h:
|
#ifndef PRIMMST_H #define PRIMMST_H
#include "Edge.h" #include "MinIndexHeap.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//Prim 算法实现最小生成树 template<typename Graph, typename Weight> class PrimMST {
private:
Graph &G; //图的引用,即要切分的图 MinIndexHeap<Weight> ipq; //ipq 充当一个索引优先队列,ipq 即 index priority queue bool* marked; //切分后的顶点分到另一阵营时,需要进行标记 vector<Edge<Weight>> mst; //属于最小生成树的 V-1 条边存储到向量 mst 中 Weight mstWeight; //最后最小生成树的总权值 mstWeight vector<Edge<Weight>*> edgeTo; //向量 edgeTo 用于存储和每个顶点相连的权值最小的横切边指针
void visit(int v) { //保证顶点 v 属于蓝色阵营,即 false assert(!marked[v]); //访问过顶点 v 后转为红色阵营,即 true marked[v] = true;
//注意:声明迭代器时,前面还要加 typename,表明 adjIterator //是 Graph 中的类型,而不是成员变量 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); //遍历顶点 v 所有的邻边 for (Edge<Weight> *e = adj.begin(); !adj.end(); e = adj.next()) { int w = e->other(v); //如果顶点 v 的邻边 e 对应的另一端的顶点 w 没有被访问过, //即分属不同阵营,即 e 为横切边 if (!marked[w]) { //如果和顶点 w 相连的横切边为空,即之前没有找到过和 //顶点 w 相连的横切边,则对edge[w]进行赋值并插入到 //索引优先队列中 if (!edgeTo[w]) { edgeTo[w] = e; ipq.insert(w, e->wt()); } //如果和顶点 w 相连的横切边不为空,即之前找到过和 //顶点 w 相连的横切边。此时就要判断新的横切边的权 //值和之前找到的横切边的权值的大小,如果小于,就进 //行一次更新 else if (e->wt() < edgeTo[w]->wt()) { edgeTo[w] = e; ipq.change(w, e->wt()); } } }
}
public:
// assume graph is connected PrimMST(Graph &graph) :G(graph), ipq(MinIndexHeap<double>(graph.V())) {
assert(graph.E() >= 1);
marked = new bool[G.V()]; for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) { marked[i] = false; edgeTo.push_back(NULL); }
//保证向量 mst 在初始化时为空 mst.clear();
//Prim visit(0); //如果索引优先队列不为空 while (!ipq.isEmpty()) { int v = ipq.extractMinIndex();
//确认该横切边确实是存在的 assert(edgeTo[v]);
mst.push_back(*edgeTo[v]);
visit(v); }
mstWeight = mst[0].wt(); for (int i = 1; i < mst.size(); i++) { mstWeight += mst[i].wt(); } }
~PrimMST() { delete []marked; }
vector<Edge<Weight>> mstEdges() { return mst; };
Weight result() { return mstWeight; }; };
#endif |
main.cpp:
|
#include "SparseGraph.h" #include "DenseGraph.h" #include "ReadGraph.h" #include "PrimMST.h" #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std;
int main() {
string filename = "testG1.txt"; int V = 8;
//稀疏图 SparseGraph<double> g = SparseGraph<double>(V, false); ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>, double> readGraph(g, filename);
// Test Prim MST cout << "Test Prim MST:" << endl; PrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> primMST(g); vector<Edge<double>> mst = primMST.mstEdges(); for (int i = 0; i < mst.size(); i++) { cout << mst[i] << endl; } cout << "The MST weight is: " << primMST.result() << endl;
cout << endl;
system("pause"); return 0; }
//整个过程,其实对图中所有的边都考虑了一遍,不过因为最小索引堆 //的元素个数和图中的顶点数一致,所以,基于堆的操作,变快了一些 // //与此同时,每次访问到一个顶点时,考察这个顶点的邻边,对于那些 //不是横切边的边,一旦判断出来,也会马上扔掉,所以其实对于Prim //算法来说,虽然它的时间复杂度是 O(E*logV),好像只是将 logE 改 //进到了 logV,但其实除了对于堆的改进之外,遍历边的次数其实也更 //小了 // //因此,整体而言,使用这个最小索引堆以后,整个 Prim 算法的时间 //复杂度的改进还是非常可观的 // //PS:Lazy Prim 的时间复杂度:O(E*logE) |
运行一览:
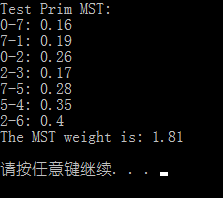
其中,testG1.txt 的内容同程序 1
【made by siwuxie095】