CS61A Spring 2018
原文地址:http://composingprograms.com/pages/24-mutable-data.html
视频地址 :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dd2AxpOiHGg&list=PL6BsET-8jgYUqH93Ik4w5Rk-A3qGMhhq0&index=4
One powerful technique for creating modular programs is to incorporate data that may change state over time. Adding state to data is a central ingredient of a paradigm called object-oriented programming.
The Object Metaphor
The difference between functions and data: functions performed operations and data were operated upon.
Objects combine data values with behavior.
Objects are both information and processes, bundled together to represent the properties, interactions, and behaviors of complex things.
Object behavior is implemented in Python through specialized object syntax and associated terminology。

like many other programming languages, we use dot notation to designated an attribute of an object.
Sequence Objects
introduce the operation by a story.
the develop of the chinese cards to Playing cards:
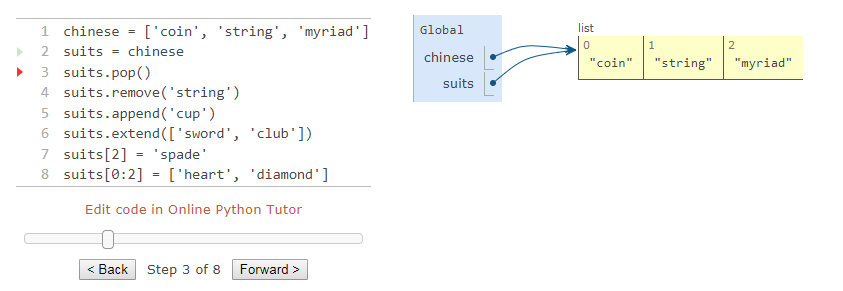
>>> chinese = ['coin', 'string', 'myriad'] # A list literal
>>> suits = chinese # Two names refer to the same listAs cards migrated to Europe (perhaps through Egypt), only the suit of coins remained in Spanish decks (oro).
>>> suits.pop() # Remove and return the final element
'myriad'
>>> suits.remove('string') # Remove the first element that equals the arguments Three more suits were added (they evolved in name and design over time),
>>> suits.append('cup') # Add an element to the end
>>> suits.extend(['sword', 'club']) # Add all elements of a sequence to the endand Italians called swords spades.
>>> suits[2] = 'spade' # Replace an elementgiving the suits of a traditional Italian deck of cards.
>>> suits
['coin', 'cup', 'spade', 'club']The French variant used today in the U.S. changes the first two suits:
>>> suits[0:2] = ['heart', 'diamond'] # Replace a slice
>>> suits
['heart', 'diamond', 'spade', 'club']Methods also exist for inserting, sorting, and reversing lists. All of these mutation operations change the value of the list; they do not create new list objects.
comparison operators : is and is not
Sameness and Change
evaluate to the identical object
Identity is a stronger condition than equality.
>>> suits is nest[0]
True
>>> suits is ['heart', 'diamond', 'spade', 'club']
False
>>> suits == ['heart', 'diamond', 'spade', 'club']
TrueThe former checks for identity, while the latter checks for the equality of contents.
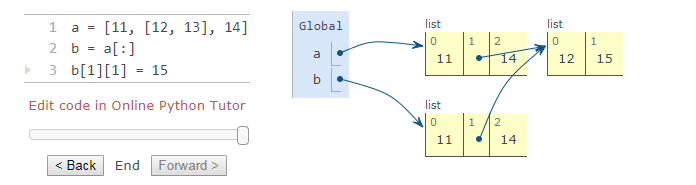
slice
Slicing a list creates a new list and leaves the original list unchanged.
a new list is constructed that contains a subset of the same values as the sliced list.
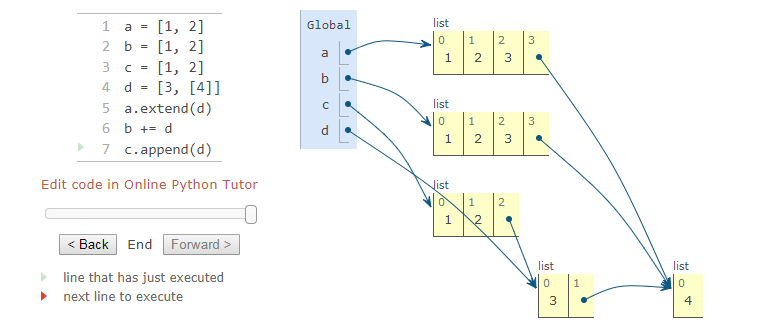
the different between extend and append:
the pop and remove
pop - it removes and returns the element at index i of the list.
remove - It removes the first item in the list that is equal to its argument.
the argument is difference, one is index, the other is element.
etc
Tuples
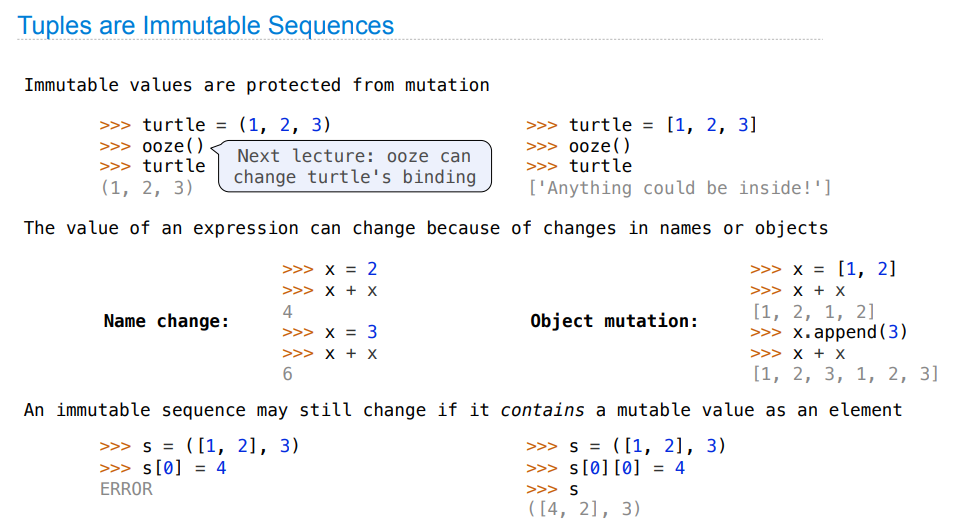
A tuple, an instance of the built-in tuple type, is an immutable sequence.
Any objects can be placed within tuples.
>>> () # 0 elements
()
>>> (10,) # 1 element
(10,)While it is not possible to change which elements are in a tuple, it is possible to change the value of a mutable element contained within a tuple.
Dictionaries
for storing and manipulating correspondence relationships
A dictionary contains key-value pairs, where both the keys and values are objects.
Adding new key-value pairs and changing the existing value for a key can both be achieved with assignment statements.
>>> numerals = {'I': 1.0, 'V': 5, 'X': 10}
>>> numerals['I'] = 1
>>> numerals['L'] = 50
>>> numerals
{'I': 1, 'X': 10, 'L': 50, 'V': 5}
Notice that ‘L’ was not added to the end of the output above. Dictionaries are unordered collections of key-value pairs.
restrictions:
A key of a dictionary cannot be or contain a mutable value.
There can be at most one value for a given key.
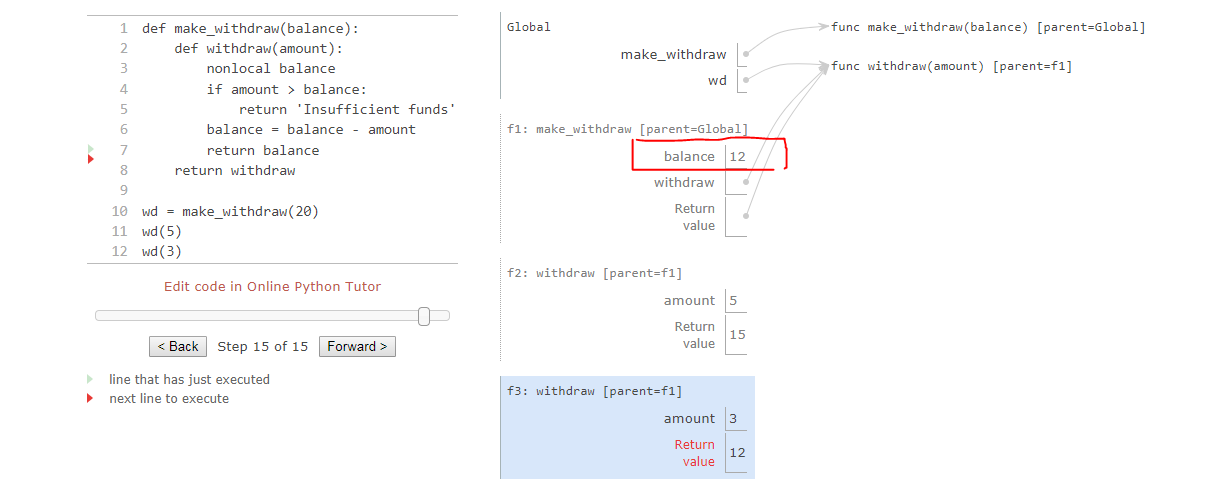
Local state
Lists and dictionaries have local state, the word “state” implies an evolving process.
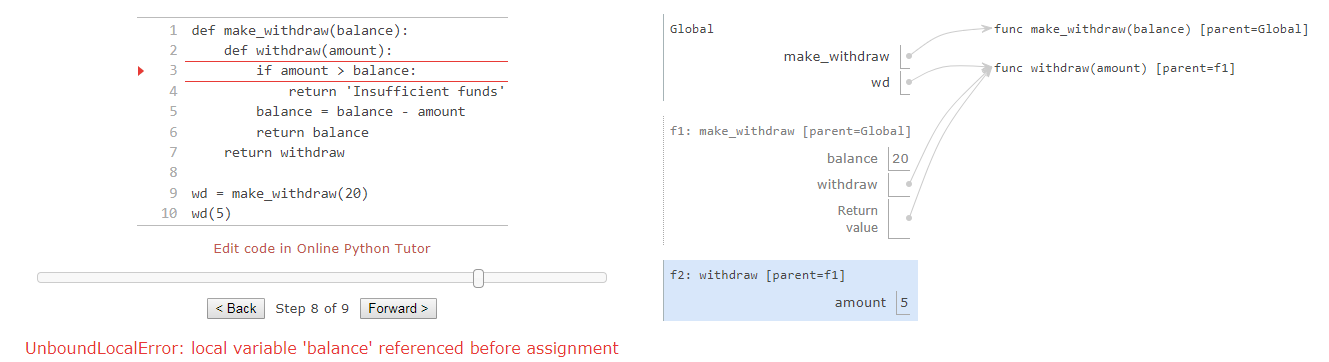
nonlocal statements
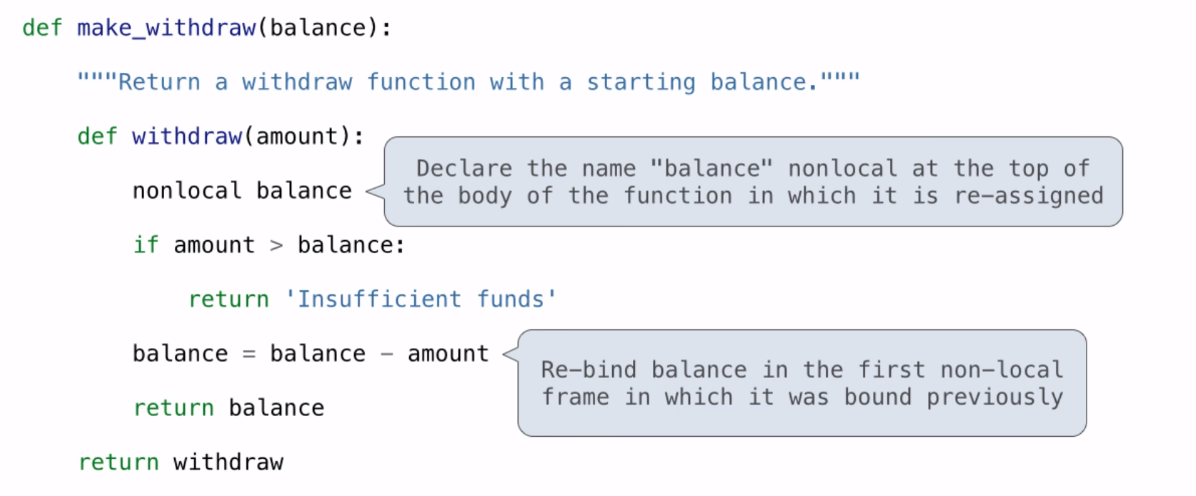
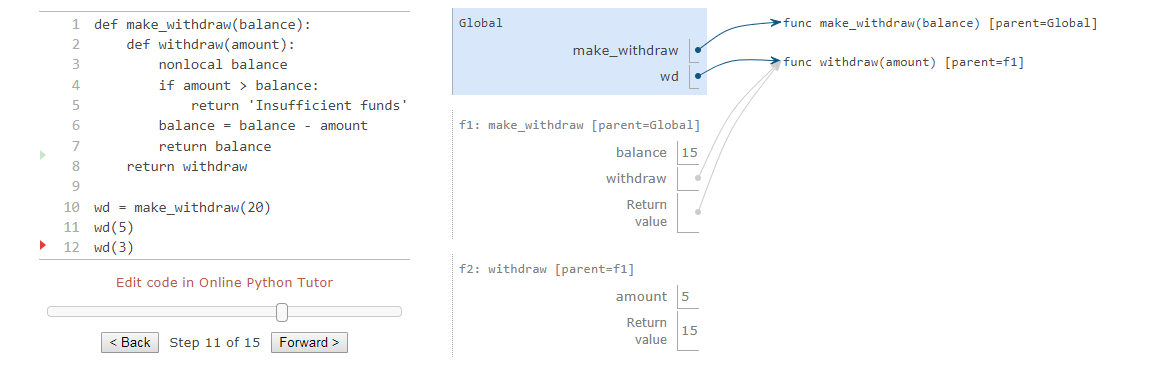
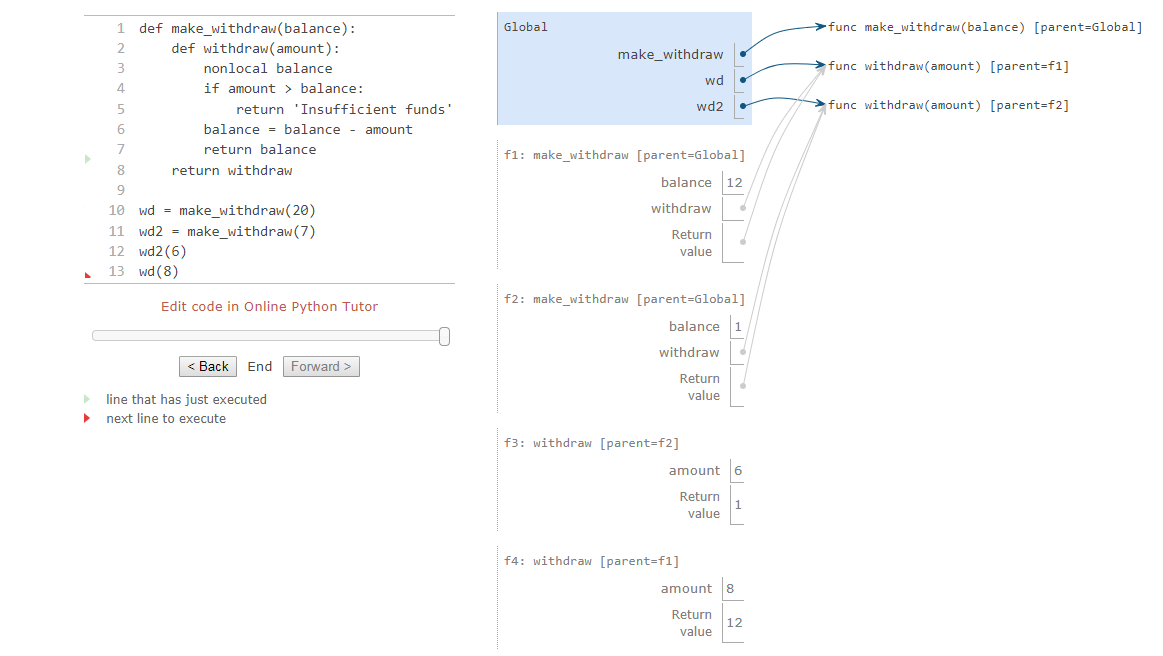
it’s critical to understand that all instances of a name must refer to the same frame.
Two bindings for the name balance in two different frames, and each withdraw function has a different parent.