一、spring对JDBC的支持
JdbcTemplate 简介
为了使 JDBC 更加易于使用, Spring 在 JDBC API 上定义了一个抽象层, 以此建立一个 JDBC 存取框架. 作为 Spring JDBC 框架的核心, JDBC 模板的设计目的是为不同类型的 JDBC 操作提供模板方法. 每个模板方法都能控制整个过程, 并允许覆盖过程中的特定任务. 通过这种方式, 可以在尽可能保留灵活性的情况下, 将数据库存取的工作量降到最低.
步骤:
1.在工程中加入相应的jar包
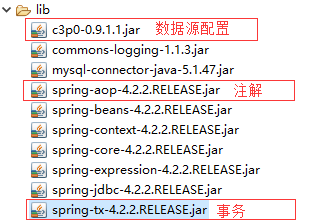
2.在spring的配置文件中配置数据源bean和配置JDBCTemplate的bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 包扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zhiyou100.xz"></context:component-scan> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置数据源:数据库交互的。c3p0 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置springjdbc的模板类 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> </beans>
3.spring配置文件中引入的属性文件
#数据源的信息 jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
二、spring中的事务管理
spring中的事务管理简单介绍
作为企业级应用程序框架, Spring 在不同的事务管理 API 之上定义了一个抽象层. 而应用程序开发人员不必了解底层的事务管理 API, 就可以使用 Spring 的事务管理机制.
Spring 既支持编程式事务管理, 也支持声明式的事务管理.
编程式事务管理: 将事务管理代码嵌入到业务方法中来控制事务的提交和回滚. 在编程式管理事务时, 必须在每个事务操作中包含额外的事务管理代码.
声明式事务管理: 大多数情况下比编程式事务管理更好用. 它将事务管理代码从业务方法中分离出来, 以声明的方式来实现事务管理. 事务管理作为一种横切关注点, 可以通过 AOP 方法模块化. Spring 通过 Spring AOP 框架支持声明式事务管理.
spring中的事务管理器
Spring 从不同的事务管理 API 中抽象了一整套的事务机制. 开发人员不必了解底层的事务 API, 就可以利用这些事务机制. 有了这些事务机制, 事务管理代码就能独立于特定的事务技术了.
Spring 的核心事务管理抽象是interface Platform TransactionManager, 它为事务管理封装了一组独立于技术的方法. 无论使用 Spring 的哪种事务管理策略(编程式或声明式), 事务管理器都是必须的.
1.用@Transactional 注解声明式的管理事务
添加事务与切面相关的jar包
用于在配置文件中引入的属性文件db.properties
#数据源的信息 jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring #不能使用user.name或username jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
配置spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd"> <!-- 包扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zhiyou100.xz"></context:component-scan> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置数据源:数据库交互的。c3p0 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置springjdbc的模板类 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 定义一个事物管理类 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 开始注解 :如果你的事务管理bean的id叫transactionManager 那么transaction-manager可以省略--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> </beans>
示例:以订购图书为例
建立接口BookShopDao
public interface BookShopDao { public void updateStock(String isbn); public double findByBookIsbn(String isbn); public void updateAccount(String username,double money); }
建立接口BookShopDao的实现类
@Repository public class BookShopDaoImp implements BookShopDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public void updateStock(String isbn) { //当库存不足时 //查询库存 String sql1="select stock from book_stock where isbn=?"; Integer stock=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql1,Integer.class ,isbn); if(stock<=0) { throw new RuntimeException("书的库存不足"); } String sql="update book_stock set stock=stock-1 where isbn=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,isbn); } @Override public double findByBookIsbn(String isbn) { String sql="select price from book where isbn=?"; return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Double.class, isbn); } @Override public void updateAccount(String username, double money) { //当余额不足时 String sql1="select balance from account where username=?"; double balance=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql1,Double.class ,username); if(balance<money) { throw new RuntimeException("账户余额不足"); } String sql="update account set balance=balance-? where username=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money,username); } }
建立接口BookShopService:购买业务
public interface BookShopService { public void purchase(String username,String isbn); }
建立接口BookShopService的实现类
@Service //事物注解 public class BookShopServiceImp implements BookShopService { @Autowired private BookShopDao bookShopDao; //订购 事物管理 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) public void purchase(String username, String isbn) { //1.查询该书的价格 double price=bookShopDao.findByBookIsbn(isbn); //2.修改书的库存 bookShopDao.updateStock(isbn); //3.修改用户余额 bookShopDao.updateAccount(username, price); } }
建立接口Cashier:结账功能
public interface Cashier { public void checkOut(String username,List<String> isbns); }
建立接口Cashier的实现类
@Component public class BookShopCashier implements Cashier { @Autowired private BookShopService bookShopService; public void checkOut(String username, List<String> isbns) { for(String isbn:isbns ) { bookShopService.purchase(username,isbn); } } }
测试
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app2.xml"); // BookShopService bookShopService=(BookShopService) app.getBean("bookShopServiceImp"); // bookShopService.purchase("TOM", "0001"); //当余额只能支付第一本书,不够支付第二本,就买第一本书 Cashier c=(Cashier) app.getBean("bookShopCashier"); List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("0001"); list.add("0002"); c.checkOut("TOM", list); } }
2.用xml方式完成声明式的管理事务
配置spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd"> <!-- 包扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zhiyou100.xz.service.xml,com.zhiyou100.xz.dao"></context:component-scan> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置数据源:数据库交互的。c3p0 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置springjdbc的模板类 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 定义一个事物管理类 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--建议:设置方法属性 --> <tx:advice id="advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- read-only设置只读 用于查询 --> <tx:method name="query*" read-only="true"/>
<!-- propagation="REQUIRED" 可省略不写,因为为默认 --> <tx:method name="purchase*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 切面的设置 --> <aop:config> <!-- 切点 业务层所在的包 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.zhiyou100.xz.service.xml.*.*(..))" id="pointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="advice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
去掉以上示例中BookShopServiceImp中的@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
测试
public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app3.xml"); BookShopService bookShopService=(BookShopService) app.getBean("bookShopServiceImp"); bookShopService.purchase("TOM", "0001"); } }