一、理论知识部分
继承:用已有类来构建新类的一种机制。当定义了一个新类继承了一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域,同时在新类中添加新的方法和域以适应新的情况。
继承的特点:具有层次结构;子类继承了父类的域和方法。
继承的优点:代码可重用性;父类的域和方法可用于子类;设计应用程序变得更加简单;可以轻松定义子类。
类继承的格式: class 新类名 extends 已有类名
已有类称为:超类(superclass)、基类(base class) 或父类(parent class)
新类称作:子类(subclass)、派生类(derived class)或孩子类(child class)
通过扩展超类定义子类时,仅需要指出子类与超类的不同之处。在子类中可以增加域、增加方法或覆盖(override)超类的方法,但绝对不能删除超类的任何域和方法。
super是一个指示编译器调用超类方法的特有关键字,它不是一个对象的引用,不能将super赋给另一个对象变量。super关键字一般有两个用途:一是调用超类的方法(格式:super.方法名()),二是调用超类的构造器(格式:super())。
若子类构造器没有显式地调用超类的构造器,则将自动地调用超类默认构造器。如果超类只定义了带参数的构造器,若子类构造器没有显式地调用超类的构造器,则Java编译器将报告错误。
从一个超类扩展而来的类集合称为继承层次。在继承层次中,从某个类到其祖先的路径被称为该类的继承链。
Java不支持多继承。
多态性泛指在程序中同一个符号在不同的情况下具有不同解释的现象。
超类中定义的域或方法,被子类继承之后,可以具有不同的数据类型或表现出不同的行为。 这使得同一个域或方法在超类及其各个子类中具有不同的语义。超类中的方法在子类中可方法重写。
不允许继承的类称为final类,在类的定义中用final修饰符加以说明。
类中的方法可定义为final的。这时子类就不能覆盖该方法。如果一个类声明为final,属于它的方法会被自动设为final,但不包括域(如果域定义为final,在对象构造以后,final域就不能再修改了)。
如果要把一个超类对象赋给一个子类对象变量,就必须进行强制类型转换。其格式为: 子类对象=(子类)(超类对象)。
为了提高程序的清晰度,包含一个或多个抽象方法的类本身必须被声明为抽象类。除了抽象方法之外 ,抽象类还可以包含具体数据和具体方法。抽象方法充当着占位的角色,它们的具体实现在子类中。扩展抽象类可以有两种选择:一种是在子类中实现部分抽象方法,这样就必须将子类也标记为抽象类;另一种是实现全部抽象方法,这样子类就可以不是抽象类。此外,类即使不含抽象方法,也可以将类声明为抽象类。抽象类不能被实例化,即不能创建对象,只能产生子类。可以创建抽象类的对象变量,只是这个变量必须指向它的非抽象子类的对象。
如果希望超类的某些方法或域允许被子类访问,就需要在超类定义时,将这些方法或域声明为protected 。实际中要谨慎使用protected的属性。假设需要将设计的类提供给其他程序员使用,而在这个类中设置了一些受保护域,由于其他程序员可以由这个类再派生出新类,并访问其中的受保护域。在这种情况下,如果对这个类进行修改,就必须通知所有使用这个类的程序员。这违背了OOP提倡的数据封装原则。
访问修饰符:private:只有该类可以访问 protected:该类及其子类的成员可以访问,同一个包中的类也可访问 public:该类或非该类均可访问 默认:相同包中的类可以访问
注:不写访问修饰符时默认为friendly
使用访问修饰符的原因:实现受限信息隐藏。
信息隐藏目的:对类中任何实现细节的更改不会影响使用该类的代码;防止用户意外删除数据;易于使用类。
Object类是Java中所有类的祖先——每一个类都由它扩展而来。在不给出超类的情况下,Java会自动把Object 作为要定义类的超类。可以使用类型为Object的变量指向任意类型的对象。但要对它们进行专门的操作都要进行类型转换。
Object类中的equals方法用于测试某个对象是否同另一个对象相等。它在Object类中的实现是判断两个对象是否具有相同的引用。如果两个对象具有相同的引用,它们一定是相等的。
Object类中的hashCode方法导出某个对象的散列码。散列码是任意整数,表示对象的存储地址。两个相等对象的散列码相等。
Object类的toString方法返回一个代表该对象域值的字符串。toString方法返回字符串的格式:类名,然后在方括号中列举域值。通过 getClass().getName()获得类名的字符串。
toString的调用方式:一个字符串与对象名通过操作符“+”连接起来,就会自动调用toString方法。 String message = “The current employee is”+x;
如果x是任意一个对象,调用System.out.println(x),就会直接地调用x.toString(),并打印输出字符串。
定义子类的toString方法时,可先调用超类的toString方法。super.toString( )
Java中,利用ArrayList类,可允许程序在运行时确定数组的大小。ArryList是一个采用类型参数的泛型类。为指定数组列表保存元素的对象类型,需要用一对尖括号将数组元素对象类名括起来加在后面。 ArryList staff=new ArrayList();
没有<>的ArrayList将被认为是一个删去了类型参数的“原始”类型。
所有基本数据类型都有着与之对应的预定义类,它们被称为对象包装器(wrapper)。对象包装器类是不可变的,即一旦构造了包装器,就不允许更改包装在其中的值。且对象包装器类还是final,因此不能定义它们的子类。
使用对象包装器的好处:基本类型转化为对象;定义一些有用的基本方法(static方法)。
声明枚举类 public enum Grade { A, B, C, D, E };
它包括一个关键字enum,一个新枚举类型的名字 Grade以及为Grade定义的一组值,这里的值既非整型,亦非字符型。
枚举类说明:枚举类是一个类,它的隐含超类是java.lang.Enum。枚举值并不是整数或其它类型,是被声明的枚举类的自身实例。枚举类不能有public修饰的构造函数,构造函数都是 隐含private,编译器自动处理。枚举值隐含都是由public、static、final修饰的,无须自己添加这些修饰符。在比较两个枚举类型的值时,永远不需要调用 equals 方法,直接使用"=="进行相等比较。
二、实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解继承的定义;
(2) 掌握子类的定义要求
(3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法;
(4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途;
(5) 掌握类中4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;
(6) 掌握抽象类的定义方法及用途;
(7)掌握Object类的用途及常用API;
(8) 掌握ArrayList类的定义方法及用法;
(9) 掌握抽象类的定义方法及用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第5章示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
在elipse IDE中编辑、调试、运行程序5-1 (教材152页-153页) ;
掌握子类的定义及用法;
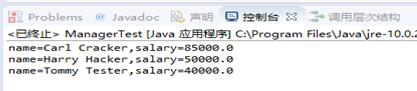
结合程序运行结果,理解并总结OO风格程序构造特点,理解Employee和Manager类的关系子类的用途,并在代码中添加注释。
1 package test06; 2 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates inheritance. 5 * @version 1.21 2004-02-21 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class ManagerTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 //构造一个Manager对象 13 Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); 14 boss.setBonus(5000); 15 16 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; 17 18 19 20 staff[0] = boss; 21 staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 22 staff[2] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); 23 24 // 输出所有Employee对象的所有信息
25 for (Employee e : staff) 26 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); 27 } 28 }
1 package test06; 2 3 import java.time.*; 4 5 public class Employee 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private double salary; 9 private LocalDate hireDay; 10 //构造器 11 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 12 { 13 this.name = name; 14 this.salary = salary; 15 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 16 } 17 //访问器 18 public String getName() 19 { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public double getSalary() 24 { 25 return salary; 26 } 27 28 public LocalDate getHireDay() 29 { 30 return hireDay; 31 } 32 33 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 34 { 35 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 36 salary += raise; 37 } 38 }
1 package test06; 2 3 public class Manager extends Employee//extends表示继承 4 { 5 private double bonus; 6 7 /** 8 * @param name the employee's name 9 * @param salary the salary 10 * @param year the hire year 11 * @param month the hire month 12 * @param day the hire day 13 */
//子类构造器 14 public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 15 { 16 super(name, salary, year, month, day);//通过super实现对超类构造器的调用,调用超类中Employee中含有name、salary、year、month、day参数的构造器 17 bonus = 0; 18 } 19 //返回薪水和奖金的总和 20 public double getSalary() 21 { 22 double baseSalary = super.getSalary();//使用关键字super调用超类 23 return baseSalary + bonus; 24 } 25 26 public void setBonus(double b) 27 { 28 bonus = b; 29 } 30 }
测试程序2:
编辑、编译、调试运行教材PersonTest程序(教材163页-165页);
掌握超类的定义及其使用要求;
掌握利用超类扩展子类的要求;
在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
1 package test05; 2 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates abstract classes. 5 * @version 1.01 2004-02-21 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class PersonTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 Person[] people = new Person[2]; 13 14 // 用student和雇员对象填充 15 people[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 16 people[1] = new Student("Maria Morris", "computer science"); 17 18 // 输出所有关于person对象的姓名和描述 19 for (Person p : people) 20 System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getDescription()); 21 } 22 }
1 package test05; 2 3 public abstract class Person 4 {
//抽象方法 5 public abstract String getDescription(); 6 private String name; 7 //构造方法 8 public Person(String name) 9 { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 //访问器 13 public String getName() 14 { 15 return name; 16 } 17 }
1 package test05; 2 3 import java.time.*; 4 5 public class Employee extends Person 6 { 7 private double salary; 8 private LocalDate hireDay; 9 10 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 11 { 12 super(name); 13 this.salary = salary; 14 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 15 } 16 17 public double getSalary() 18 { 19 return salary; 20 } 21 22 public LocalDate getHireDay() 23 { 24 return hireDay; 25 } 26 27 public String getDescription() 28 { 29 return String.format("an employee with a salary of $%.2f", salary); 30 } 31 32 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 33 { 34 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 35 salary += raise; 36 } 37 }
1 package test05; 2 3 public class Student extends Person 4 { 5 private String major; 6 7 /** 8 * @param nama the student's name 9 * @param major the student's major 10 */
//student构造器 11 public Student(String name, String major) 12 { 13 // pass n to superclass constructor 14 super(name);//访问父类 15 this.major = major; 16 } 17 //访问器方法 18 public String getDescription() 19 { 20 return "a student majoring in " + major; 21 } 22 }

测试程序3:
编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
掌握Object类的定义及用法;
在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
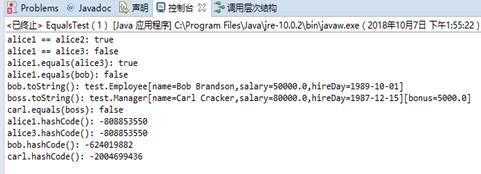
1 package test; 2 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates the equals method. 5 * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class EqualsTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); 13 Employee alice2 = alice1; 14 Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); 15 Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 16 17 System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); 18 19 System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); 20 21 System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); 22 23 System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); 24 25 System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); 26 27 Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); 28 Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); 29 boss.setBonus(5000); 30 System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); 31 System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); 32 System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); 33 System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
34 System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); 35 System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); 36 } 37 }
1 package test; 2 3 import java.time.*; 4 import java.util.Objects; 5 6 public class Employee 7 { 8 private String name; 9 private double salary; 10 private LocalDate hireDay; 11 12 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 13 { 14 this.name = name; 15 this.salary = salary; 16 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 17 } 18 19 public String getName() 20 { 21 return name; 22 } 23 24 public double getSalary() 25 { 26 return salary; 27 } 28 29 public LocalDate getHireDay() 30 { 31 return hireDay; 32 } 33 34 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 35 { 36 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 37 salary += raise; 38 } 39 40 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 41 { 42 // 快速测试对象是否相同 43 if (this == otherObject) return true; 44 45 // 如果显示参数为空,则返回false 46 if (otherObject == null) return false; 47 48 // 如果类不匹配,它们不可能相等
49 if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; 50 51 // 我们知道其他的Employee对象是非空的员工 52 Employee other = (Employee) otherObject; 53 54 // 测试字段是否具有相同的值
55 return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); 56 } 57 58 public int hashCode() 59 { 60 return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); 61 } 62 63 public String toString() 64 { 65 return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay 66 + "]"; 67 } 68 }
1 package test; 2 3 public class Manager extends Employee 4 { 5 private double bonus; 6 7 public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 8 { 9 super(name, salary, year, month, day); 10 bonus = 0; 11 } 12 13 public double getSalary() 14 { 15 double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); 16 return baseSalary + bonus; 17 } 18 19 public void setBonus(double bonus) 20 { 21 this.bonus = bonus; 22 } 23 24 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 25 { 26 if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; 27 Manager other = (Manager) otherObject; 28 // super.equals检查这个和其他属于同一个类 29 return bonus == other.bonus; 30 } 31 32 public int hashCode() 33 { 34 return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); 35 } 36 37 public String toString() 38 { 39 return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; 40 } 41 }
测试程序4:
在elipse IDE中调试运行程序5-11(教材182页),结合程序运行结果理解程序;
掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
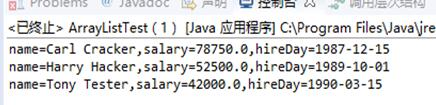
1 package test04; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. 7 * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class ArrayListTest 11 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) 13 { 14 //用三个Employee对象填充人员数组列表 15 ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>(); 16 17 staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); 18 staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); 19 staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); 20 21 // 每人提高5%的工资 22 for (Employee e : staff)】 23 e.raiseSalary(5); 24 25 //输出所有关于Employee对象的信息
26 for (Employee e : staff) 27 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" 28 + e.getHireDay()); 29 } 30 }
1 package test04; 2 3 import java.time.*; 4 5 public class Employee 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private double salary; 9 private LocalDate hireDay; 10 11 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 12 { 13 this.name = name; 14 this.salary = salary; 15 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 16 } 17 18 public String getName() 19 { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public double getSalary() 24 { 25 return salary; 26 } 27 28 public LocalDate getHireDay() 29 { 30 return hireDay; 31 } 32 33 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 34 { 35 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 36 salary += raise; 37 } 38 }
测试程序5:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页),结合运行结果理解程序;
掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
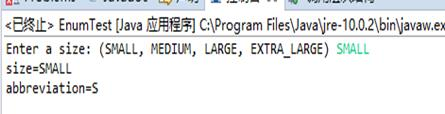
1 package test11; 2 import java.util.*; 3 4 /** 5 * This program demonstrates enumerated types. 6 * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 7 * @author Cay Horstmann 8 */ 9 public class EnumTest 10 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) 12 { 13 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 14 System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); 15 String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); 16 Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); 17 System.out.println("size=" + size); 18 System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); 19 if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) 20 System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); 21 } 22 } 23 24 enum Size 25 { 26 SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); 27 28 private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } 29 public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } 30 31 private String abbreviation; 32 }
实验2:编程练习1
定义抽象类Shape:
属性:不可变常量double PI,值为3.14;
方法:public double getPerimeter();public double getArea())。
让Rectangle与Circle继承自Shape类。
编写double sumAllArea方法输出形状数组中的面积和和double sumAllPerimeter方法输出形状数组中的周长和。
main方法中
1)输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则再输入长和宽。如果输入cir,则再输入半径。
2) 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。
3) 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型,使用类似shape.getClass()(获得类型),shape.getClass().getSuperclass()(获得父类型);
思考sumAllArea和sumAllPerimeter方法放在哪个类中更合适?
输入样例:
3
rect
1 1
rect
2 2
cir
1
输出样例:
18.28
8.14
[Rectangle [width=1, length=1], Rectangle [width=2, length=2], Circle [radius=1]]
class Rectangle,class Shape
class Rectangle,class Shape
class Circle,class Shape
1 package test1; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Main { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 9 System.out.println("请输入图形个数:"); 10 int n=in.nextInt(); 11 String rect="rect"; 12 String cir="cir"; 13 shape [] a=new shape[n]; 14 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 15 System.out.println("请输入图形的形状:"); 16 String input=in.next(); 17 if(input.equals(rect)) { 18 int length=in.nextInt(); 19 int width=in.nextInt(); 20 System.out.println("长方形:"+" "+"长:"+length+" "+"宽:"+width); 21 a[i]=new Rectangle(length,width); 22 } 23 if(input.equals(cir)) { 24 int radius=in.nextInt(); 25 System.out.println("圆形:"+"半径:"+radius); 26 a[i]=new Circle(radius); 27 } 28 } 29 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 30 { 31 System.out.println(a[i]); 32 } 33 34 Main b=new Main(); 35 System.out.println(b.sumAllPerimeter(a)); 36 System.out.println(b.sumAllArea(a)); 37 for(shape s:a) { 38 System.out.println(s.getClass()+","+s.getClass().getSuperclass()); 39 } 40 } 41 public double sumAllArea(shape a[]) 42 { 43 double sum=0; 44 for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) 45 sum=sum+a[i].getArea(); 46 return sum; 47 } 48 public double sumAllPerimeter(shape a[]) 49 { 50 double sum=0; 51 for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) 52 sum=sum+a[i].getPerimeter(); 53 return sum; 54 } 55 }
1 package test1; 2 3 public abstract class shape { 4 double PI=3.14; 5 public abstract double getPerimeter(); 6 public abstract double getArea(); 7 8 }
1 package test1; 2 public class Rectangle extends shape 3 { 4 5 private int width; 6 private int length; 7 public Rectangle(int wid,int len) 8 { 9 this.width=wid; 10 this.length=len; 11 } 12 public double getPerimeter() 13 { 14 return (width+length)*2; 15 } 16 @Override 17 public double getArea() { 18 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 public double getWidth() 23 { 24 return width; 25 } 26 public double getLength() 27 { 28 return length; 29 } 30 public String toString() 31 { 32 return "Rectangle"+ "[ width=" + width + ","+ "length=" + length + "]"; 33 } 34 }
1 package test1; 2 3 public class Circle extends shape{ 4 5 private int radius; 6 public Circle(int r) 7 { 8 radius=r; 9 } 10 public double getPerimeter() 11 { 12 return 2*PI*radius; 13 } 14 public double getArea() 15 { 16 return PI*radius*radius; 17 } 18 public double getRadius() 19 { 20 return radius; 21 } 22 23 public String toString() 24 { 25 return "Circle"+"["+"radius=" + radius + "]"; 26 } 27 28 }

实验3:编程练习2
编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中,输入一个身份证号或姓名,查询显示查询对象的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地。
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.Scanner; 9 10 public class Test{ 11 private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist; 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 Personlist = new ArrayList<>(); 14 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 15 File file = new File("E:\WPS Office\身份证号.txt"); 16 try { 17 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); 18 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 19 String temp = null; 20 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { 21 22 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); 23 24 linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); 25 String name = linescanner.next(); 26 String ID = linescanner.next(); 27 String sex = linescanner.next(); 28 String age = linescanner.next(); 29 String birthplace =linescanner.nextLine(); 30 Person Person = new Person(); 31 Person.setname(name); 32 Person.setID(ID); 33 Person.setsex(sex); 34 Person.setage(age); 35 Person.setbirthplace(birthplace); 36 Personlist.add(Person); 37 38 } 39 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 40 System.out.println("查找不到信息"); 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 System.out.println("信息读取有误"); 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 boolean isTrue = true; 47 while (isTrue) { 48 49 System.out.println("1.按姓名查找"); 50 System.out.println("2.按身份证号查找"); 51 System.out.println("3.退出"); 52 int nextInt = scanner.nextInt(); 53 switch (nextInt) { 54 case 1: 55 System.out.println("请输入姓名:"); 56 String Personname = scanner.next(); 57 int nameint = findPersonByname(Personname); 58 if (nameint != -1) { 59 System.out.println("查找信息为:姓名:" 60 + Personlist.get(nameint).getname() + " 身份证号:" 61 + Personlist.get(nameint).getID() +" 年龄:" 62 +Personlist.get(nameint).getage() +" 性别:" 63 +Personlist.get(nameint).getsex()+" 出生地:" 64 +Personlist.get(nameint).getbirthplace() 65 ); 66 } else { 67 System.out.println("此人不存在!"); 68 } 69 break; 70 case 2: 71 System.out.println("请输入身份证号"); 72 String PersonID = scanner.next(); 73 int IDint = findPersonByID(PersonID); 74 if (IDint != -1) { 75 System.out.println("查找信息为:姓名:" 76 + Personlist.get(IDint).getname() + " 身份证号:" 77 + Personlist.get(IDint).getID() +" 年龄:" 78 +Personlist.get(IDint).getage() +" 性别:" 79 +Personlist.get(IDint).getsex()+" 出生地:" 80 +Personlist.get(IDint).getbirthplace() 81 ); 82 } else { 83 System.out.println("此人不存在!"); 84 } 85 break; 86 case 3: 87 isTrue = false; 88 System.out.println("退出程序!"); 89 break; 90 default: 91 System.out.println("输入有误"); 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 96 private static int findPersonByID(String personID) { 97 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 98 return 0; 99 } 100 101 private static int findPersonByname(String personname) { 102 103 return 0; 104 } 105 106 public static int findStudentByname(String name) { 107 int flag = -1; 108 int a[]; 109 for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { 110 if (Personlist.get(i).getname().equals(name)) { 111 flag= i; 112 } 113 } 114 return flag; 115 } 116 117 public static int findStudentByID(String ID) { 118 int flag = -1; 119 120 for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { 121 if (Personlist.get(i).getID().equals(ID)) { 122 flag = i; 123 } 124 } 125 return flag; 126 } 127 }
1 package test; 2 3 public class person { 4 private String name; 5 private String ID; 6 private String age; 7 private String sex; 8 private String birthplace; 9 10 public String getname() { 11 return name; 12 } 13 public void setname(String name) { 14 this.name = name; 15 } 16 public String getID() { 17 return ID; 18 } 19 public void setID(String ID) { 20 this.ID= ID; 21 } 22 public String getage() { 23 return age; 24 } 25 public void setage(String age) { 26 this.age= age; 27 } 28 public String getsex() { 29 return sex; 30 } 31 public void setsex(String sex) { 32 this.sex= sex; 33 } 34 public String getbirthplace() { 35 return birthplace; 36 } 37 public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) { 38 this.birthplace= birthplace; 39 } 40 41 }
三、总结:
通过这次课程学习及实验,我了解了什么是继承,继承的优点和特点,多态性的概念及用法,抽象类的定义方法及用途,抽象类的定义方法及用途。对于这次实验,有的知识都是自学,有很多都不是很了解,不是很会写代码,还有很多地方需要学习。