1. 图的相关概念
树是一种特殊的图,相比树,图更能用来表示现实世界中的的实体,如路线图,网络节点图,课程体系图等,一旦能用图来描述实体,能模拟和解决一些非常复杂的任务。图的相关概念和词汇如下:
顶点vertex:图的节点
边Edge:顶点间的连线,若边具有方向时,组成有向图(directed graph)
权重weight:从一个顶点到其他不同顶点的距离不一样,因此边具有权重,来表示不同的距离
路径path:从一个顶点到另一个的所有边的集合
回路cycle:在有向图中,从一个顶点开始,最后又回到起始顶点的路径为一个回路
图可以表示为G={V,E},其中V为顶点的集合,E为边的集合,如下图所示:
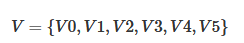
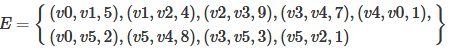
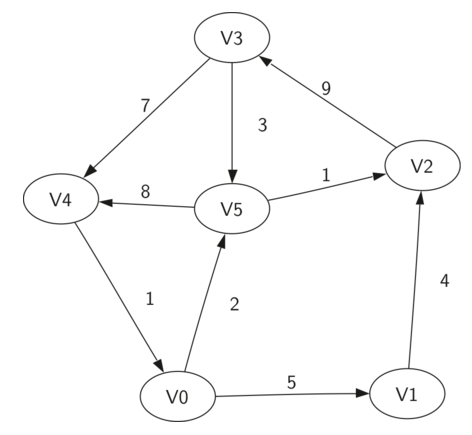
2,图的实现
图的相关操作如下:
Graph() #创建图 addVertex(vert) #添加顶点 addEdge(fromVert, toVert) #添加边 addEdge(fromVert, toVert, weight) #添加边及其权重 getVertex(vertKey) #获取某个顶点 getVertices() #获取所有顶点 in #判断是否包括某个顶点
可以通过邻接矩阵(adjacency matrix)或领接表(adjacency list)来实现图。邻接矩阵表示图的结构如下,图中的数字表示两个顶点相连,且边的权重为该值。可以发现邻接矩阵更加适合于边较多的图,不然会造成内存空间的浪费。
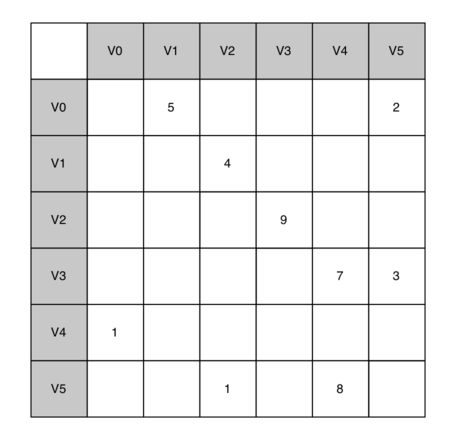
邻接表表示图的结构如下,一个主列表中包含图的所有顶点,每个顶点又各包含列表记录与其相连的边。可以发现邻接表更适合边较少的图。
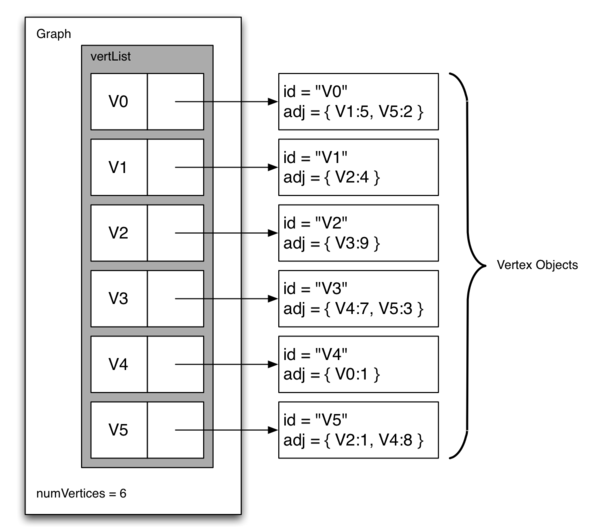
python实现邻接表代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 class Vertex(object): def __init__(self,key): self.id=key self.connectedTo={} def __str__(self): return str(self.id) + "connected to" +str([x.id for x in self.connectedTo]) #nbr为vertex对象 def addNeighbor(self,nbr,weight=0): self.connectedTo[nbr]=weight def getConnections(self): return self.connectedTo.keys() def getId(self): return self.id def getWeight(self,nbr): return self.connectedTo[nbr] class Graph(object): def __init__(self): self.vertList = {} self.numVertices = 0 def addVertex(self,key): newVertex = Vertex(key) self.vertList[key]=newVertex self.numVertices +=1 return newVertex def getVertex(self,key): if key in self.vertList: return self.vertList[key] else: return None def __contains__(self, key): return key in self.vertList #fromVert,toVert为起始和终止节点的key def addEdge(self,fromVert,toVert,weight=0): if fromVert not in self.vertList: self.addVertex(fromVert) if toVert not in self.vertList: self.addVertex(toVert) self.vertList[fromVert].addNeighbor(self.vertList[toVert],weight) def getVertices(self): return self.vertList.keys() def __iter__(self): return iter(self.vertList.values()) if __name__ == '__main__': g = Graph() for i in range(6): g.addVertex(i) g.addEdge(0, 1, 5) g.addEdge(0, 5, 2) g.addEdge(1, 2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 3, 9) g.addEdge(3, 4, 7) g.addEdge(3, 5, 3) g.addEdge(4, 0, 1) g.addEdge(5, 4, 8) g.addEdge(5, 2, 1) for v in g: for w in v.getConnections(): print("( %s , %s )" % (v.getId(), w.getId()))
3.图的应用
3.1 Word ladder problem
word ladder规则:从单词‘FOOL’变为单词‘SAGE’,每次只能改变一个字母,且改变一个字母后的单词必须存在,求可能的变化路径。
一个路径示意:FOOL POOL POLL POLE PALE SALE SAGE
解决思路:
1,创建图,以单词为顶点,若两个单词间只相差一个字母,则两个单词间有一条边(双向的边)
2,对图进行宽度优先搜索,找到合适的路径
创建图:
下载四个字母的单词,构造成一行一个单词的文本文件(大概5200个单词)。按照下面的格式构造一个字典,方块中的_OPE为键,其对应的单词组成一个列表,为字典的值,对每一个单词,都可以构造如下四个这样的键值对。然后再根据字典创建图。

上述过程,用python代码实现如下:(由于数据量较大,构建图过程中可能出现memory error)

#coding:utf-8 from graphDemo import Graph,Vertex def buildGraph(): with open('fourLetters.txt', 'r') as f: lines = f.readlines() d={} for line in lines: word = line.strip() #删除换行符 for i in range(len(word)): label = word[:i]+'_'+word[i+1:] if label in d: d[label].append(word) else: d[label]=[word] #print d.keys() g = Graph() for label in d.keys(): for word1 in d[label]: for word2 in d[label] if word1!=word2: g.addEdge(word1,word2) return g
宽度优先搜索(breadth first search,BFS):即先搜索同级的顶点,再搜索下一级的顶点。代码中引入了队列Queue,并用三种颜色标记顶点的状态,白色表示顶点未被搜索,灰色表示顶点被搜索,且被放入了队列中,黑色表示顶点被搜索,且其所有下一级顶点都被加入了队列中,如下图所示。
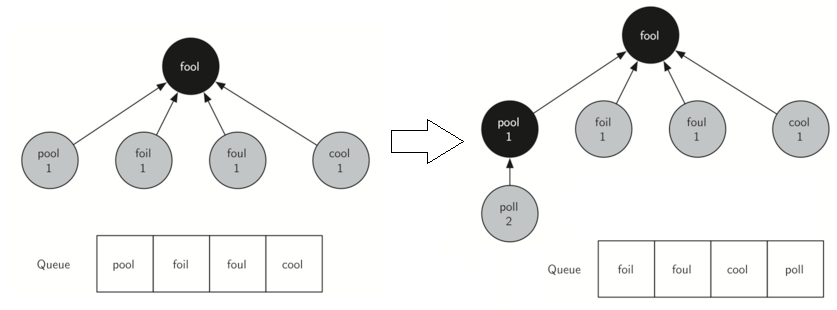
用python实现宽度优先搜索,并寻找从FOOL 到SAGE的最短路径,代码如下:

from graphDemo import Graph,Vertex from queueDemo import Queue #class Vertex(object): # def __init__(self,key): # self.id=key # self.connectedTo={} # self.color = 'white' # self.distance = None # self.predecessor = None # # def __str__(self): # return str(self.id) + "connected to" +str([x.id for x in self.connectedTo]) # # #nbr为vertex对象 # def addNeighbor(self,nbr,weight=0): # self.connectedTo[nbr]=weight # # def getConnections(self): # return self.connectedTo.keys() # # def getId(self): # return self.id # # def getWeight(self,nbr): # return self.connectedTo[nbr] # # def setColor(self,color): # self.color = color # # def getColor(self): # return self.color # # def setDistance(self,distance): # self.distance = distance # # def getDistance(self): # return self.distance # # def setPred(self,pred): # self.predecessor = pred # # def getPred(self): # return self.predecessor def buildGraph(): with open('fourLetters.txt', 'r') as f: lines = f.readlines() d={} for line in lines: word = line.strip() #删除换行符 for i in range(len(word)): label = word[:i]+'_'+word[i+1:] if label in d: d[label].append(word) else: d[label]=[word] #print d.keys() g = Graph() for label in d.keys(): for word1 in d[label]: for word2 in d[label] if word1!=word2: g.addEdge(word1,word2) return g def bfs(g,start): start.setDistance(0) start.setPred(None) vertQueue = Queue() vertQueue.enqueue(start) while vertQueue.size()>0: currentVert = vertQueue.dequeue() for vert in currentVert.getConnections(): if (vert.getColor()=='white'): vert.setDistance(currentVert.getDistance()+1) vert.setColor('gray') vert.setPred(currentVert) vertQueue.enqueue(vert) currentVert.setColor('black') def traverse(y): x = y while (x!=None): print x.getId() x = x.getPred() if __name__ =='__main__': g = buildGraph() start = g.getVertex('FOOL') bfs(g,start) end =g.getVertex('SAGE') traverse(end)
另外,上述代码中宽度优先搜索的复杂度为O(V+E),V为顶点的数量,E为边的数量
3.2 Knight‘s tour problem (骑士跳马棋游历问题)
knight's tour问题描述:在国际象棋棋盘上(8*8方格),骑士只能走“日字”路线(和象棋中马一样),骑士如何才能不重复的走遍整个棋盘?
解决思路:
1,创建图:将棋盘中的每个方格编号,以方格做为顶点,建立图。对于每个顶点n,骑士若能从n跳到下一个顶点m,则n和m间建立边。
2,对图进行深度优先搜索(depth first search, DFS)
创建图:如左图的5*5棋盘,编号0-24,骑士现在所在位置为12,右图中构建了顶点12所有的边(从12出发,骑士下一步能到达的顶点编号)
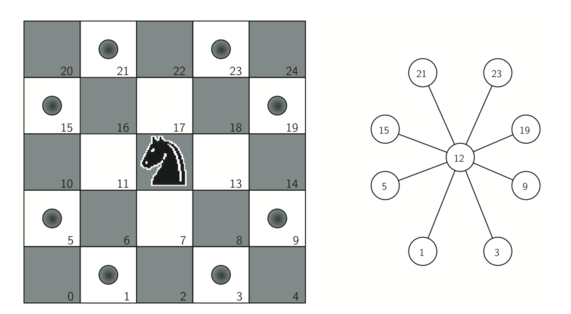
用python实现创建图的代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 from graphDemo import Graph def knightGraph(boardSize): g = Graph() for row in range(boardSize): for col in range(boardSize): nodeID = posToNodeId(row,col,boardSize) #对棋盘每个方格编号 nextMoves= genLegalMoves(row,col,boardSize) #获取骑士下一步能到达的顶点 for pos in nextMoves: g.addEdge(nodeID,pos) return g def posToNodeId(row,col,size): return row*size+col def genLegalMoves(row,col,size): nextMoves=[] moveOffset = [(-1,2),(1,2),(-2,1),(2,1),(-2,-1),(2,-1),(-1,-2),(1,-2)] for i in moveOffset: x = row+i[0] y = col+i[1] if legalCoord(x,size) and legalCoord(y,size): #判断该坐标是否在棋盘上 nodeId = posToNodeId(x,y,size) nextMoves.append(nodeId) return nextMoves def legalCoord(x,size): if x>=0 and x<size: return True else: return False if __name__ == '__main__': g = knightGraph(5) print g.vertList[0].id for vert in g.vertList[0].getConnections(): print vert.id
深度优先搜索:先找下一级的顶点,再找同级的顶点。此处的问题中,总共有64个节点,若骑士能够依次不重复的访问64个节点,便找到了一条成功遍历的路径,实现代码如下:

def knightTour(n, path, u, limit): ''' :param n: 一遍历顶点数,初始为0 :param path: 遍历的路径 :param u: 当前顶点 :param limit:限制访问顶点数 :return: ''' u.setColor('gray') path.append(u) if n < limit: nextVerts = list(u.getConnections()) i = 0 done = False while i < len(nextVerts) and not done: if nextVerts[i].getColor() == 'white': done = knightTour(n + 1, path, nextVerts[i], limit) i = i + 1 if not done: path.pop() u.setColor('white') else: done = True return done
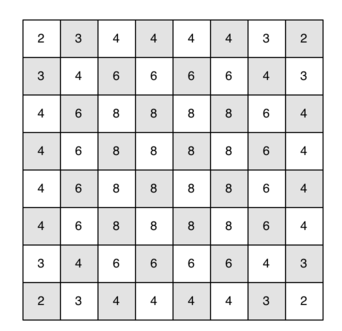
上述代码中的深度遍历中,复杂发为O(kN),K为常数,N为顶点个数,随着顶点数增加,算法复杂度指数级增长,对于5*5的方格能较快完成,而对于8*8的方格,得几小时才能完成算法。可以对深度优先算法进行轻微的改进,对于棋盘上所有顶点,其边的数量分布如下图所示,可以发现,棋盘边缘的顶点边数较少,棋盘中央的顶点边数多,若先访问棋盘边缘的顶点,再访问棋盘中央的顶点,能降低算法复杂度,相应代码如下:

def knightTour(n, path, u, limit): ''' :param n: 一遍历顶点数,初始为0 :param path: 遍历的路径 :param u: 当前顶点 :param limit:限制访问顶点数 :return: ''' u.setColor('gray') path.append(u) if n < limit: # nextVerts = list(u.getConnections()) nextVerts = orderByAvail(u) i = 0 done = False while i < len(nextVerts) and not done: if nextVerts[i].getColor() == 'white': done = knightTour(n + 1, path, nextVerts[i], limit) i = i + 1 if not done: path.pop() u.setColor('white') else: done = True return done def orderByAvail(n): resList = [] for v in n.getConnections(): if v.getColor() == 'white': c = 0 for w in v.getConnections(): if w.getColor() == 'white': c = c + 1 resList.append((c,v)) resList.sort(key=lambda x: x[0]) return [y[1] for y in resList]
上述骑士游历问题中的深度优先搜索算法是一种特殊的深度优先搜索,对于普通的问题,深度优先搜索的代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 from graphDemo import Graph class DFSGraph(Graph): def __init__(self): super(DFSGraph,self).__init__() self.time = 0 def dfs(self): for vert in self: self.dfsVisit(vert) def dfsVisit(self,startVert): startVert.setColor('gray') self.time += 1 #注意self.time是DFSGraph的属性,不是Vertex的 startVert.setDiscovery(self.time) for vert in startVert.getConnections(): if vert.getColor()=='white': vert.setPred(startVert) self.dfsVisit(vert) startVert.setColor('black') self.time += 1 startVert.setFinish(self.time) def traverse(y): x=y while x!=None: print x.getId() x = x.getPred() if __name__ == '__main__': g = DFSGraph() for i in range(6): g.addVertex(i) g.addEdge(0, 1, 5) g.addEdge(0, 5, 2) g.addEdge(1, 2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 3, 9) g.addEdge(3, 4, 7) g.addEdge(3, 5, 3) g.addEdge(4, 0, 1) g.addEdge(5, 4, 8) g.addEdge(5, 2, 1) g.dfs() traverse(g.getVertex(1))
上述DFS的复杂度和BFS一样,也为O(V+E)
DFS和BFS搜索

G = {'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D', 'E'],
'C': ['A', 'F'],
'D': ['B'],
'E': ['B', 'F'],
'F': ['C', 'E']}
#Breadth first search
def bfs(G,start):
seen = [start]
q = [start] #先进先出的队列
while q:
cur = q.pop(0)
for vertex in G[cur]:
if vertex not in seen:
seen.append(vertex)
q.append(vertex)
return seen
print(bfs(G,'C'))
# depth first search
def dfs(G, start):
seen = [start]
stack = [start] #先进后出的栈
path = []
while stack:
cur = stack.pop()
path.append(cur)
for vertex in G[cur]:
if vertex not in seen:
seen.append(vertex)
stack.append(vertex)
return path
print(dfs(G,"C"))
4.拓扑排序(Topological sorting)
拓扑排序适用于有向无环图(图中不存在回路),表示各个事件(顶点)的线性执行顺序,如图中若存在边(v,w),则事件v在w之前发生。
拓扑排序的执行过程如下:
1,先对图进行深度优先搜索,计算每个顶点的finish time
2,根据finish time,对顶点进行降序排列,并存储在一个列表中,返回列表即为拓扑排序结果
如下图是一张表示煎饼过程的有向无环图,箭头表示执行先后顺序:
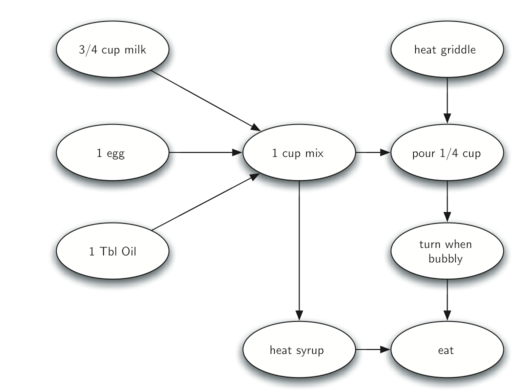
若要知道整个煎饼过程的执行流程,可以对上面的图进行拓扑排序,计算的时间(discovery time/ finish time)和最后得到执行流程如下,即越晚结束的事件(finish time越大),应先执行。
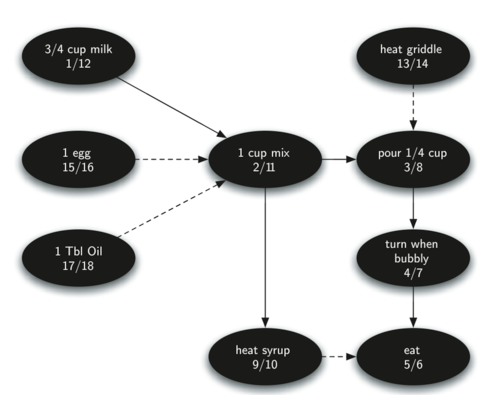
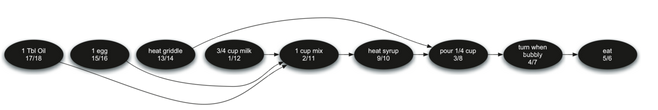
5.最短路径算法
5.1迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra's Algorithm)
Dijkstra算法:寻找最短路径算法之一,即在边的权值不为负的有向图中,寻找任意一点到其他任意结点(在两点相互联通的情况下)之间的最小路径。
python实现代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 from graphDemo import Graph from binaryHeap import BinaryHeap import sys class PriorityQueue(BinaryHeap): def decreaseKey(self,item,cost): i=1 done=False while i<=self.size and not done: if self.heapList[i][1]==item: #先找到该元素,再将元素向上移 self.heapList[i]=(cost,item) self._percUp(i) done = True i = i+1 def dijkstra(aGraph,start): for vert in aGraph: vert.setDistance(sys.maxint) start.setDistance(0) q = PriorityQueue() q.buildHeap([(v.getDistance(),v) for v in aGraph]) #元组做为最小堆(优先队列)的元素 while q.size>0: #元组进行比较时,先比较第一个元素,所以距离做为元素第一个值,距离相等时算法有问题? currentVert = q.delMin()[1] for nextVert in currentVert.getConnections(): newDistance = currentVert.getDistance()+currentVert.getWeight(nextVert) if newDistance<nextVert.getDistance(): nextVert.setDistance(newDistance) nextVert.setPred(currentVert) q.decreaseKey(nextVert,newDistance) if __name__ == '__main__': g = Graph() for i in range(6): g.addVertex(i) g.addEdge(0, 1, 5) g.addEdge(0, 5, 2) g.addEdge(1, 2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 3, 9) g.addEdge(3, 4, 7) g.addEdge(3, 5, 3) g.addEdge(4, 0, 1) g.addEdge(5, 4, 8) g.addEdge(5, 2, 1) dijkstra(g, g.getVertex(5)) for vert in g: print vert.getId(),vert.getDistance()

#coding:utf-8 from collections import defaultdict import heapq nodes=['s1','s2','s3','s4','s5'] M = float('inf') #M为无穷大数, 表示两个节点间无该方向的链接 #邻接矩阵实现图 graph_list=[ [M,3,2,4,5], [2,M,1,M,4], [3,3,M,4,4], [2,1,2,M,5], [M,3,4,4,M], ] #邻接矩阵的边和权重 graph_edges=[] for i in nodes: for j in nodes: if i!=j and graph_list[nodes.index(i)][nodes.index(j)]!=M: graph_edges.append((i,j,graph_list[nodes.index(i)][nodes.index(j)])) """ print graph_edges [ ('s1', 's2', 3), ('s1', 's3', 2), ('s1', 's4', 4), ('s1', 's5', 5), ('s2', 's1', 2), ('s2', 's3', 1), ('s2', 's5', 4), ('s3', 's1', 3), ('s3', 's2', 3), ('s3', 's4', 4), ('s3', 's5', 4), ('s4', 's1',2), ('s4', 's2', 1), ('s4', 's3', 2), ('s4', 's5', 5), ('s5', 's2', 3), ('s5', 's3', 4), ('s5', 's4', 4) ] """ graph_dict = defaultdict(list) for from_node,to_node,weight in graph_edges: graph_dict[from_node].append((to_node,weight)) #print graph_dict """ { graph_dict,邻接表实现图 's3': [('s1', 3), ('s2', 3), ('s4', 4), ('s5', 4)], 's2': [('s1', 2), ('s3', 1), ('s5', 4)], 's1': [('s2', 3), ('s3', 2), ('s4', 4), ('s5', 5)], 's5': [('s2', 3), ('s3', 4), ('s4', 4)], 's4': [('s1', 2), ('s2', 1), ('s3', 2), ('s5', 5)] } """ def djkstra(graph_dict, start_node, end_node): seen = set() ret_path=[] path = () q = [(0,start_node,path)] while q: cost,current_node,path = heapq.heappop(q) #当cost相同时,会比较start_node,如"s1"和"s2" if current_node not in seen: seen.add(current_node) path = (current_node,path) if current_node==end_node: break for next_node, weight in graph_dict[current_node]: if next_node not in seen: heapq.heappush(q,(cost+weight,next_node,path)) if current_node!=end_node: print("There is no path to %s"%str(to_node)) cost = -1 ret_path=[] else: if len(path)>0: #将('s4', ('s3', ('s2', ())))路径转换成['s2', 's3', 's4'] left = path[0] ret_path.append(left) right = path[1] while len(right)>0: left = right[0] ret_path.append(left) right = right[1] ret_path.reverse() return cost,ret_path if __name__=="__main__": cost,path= djkstra(graph_dict,'s2','s4') print cost,path """ 任意两点间的最短路径 def dijkstra_all(graph_dict): Shortest_path_dict = defaultdict(dict) for i in nodes: for j in nodes: if i != j: cost,Shortest_path = dijkstra(graph_dict,i,j) Shortest_path_dict[i][j] = Shortest_path return Shortest_path_dict Shortest_path_dict = { 's1': {'s2': ['s1', 's3', 's2'], 's3': ['s1', 's3'] }, 's2': {'s1': ['s2', 's1'], 's3': ['s2', 's1', 's3'}, 's3': {'s1': ['s3', 's2', 's1'], 's2': ['s3', 's2'] }, } """
Dijkstra算法的复杂度为O((V+E)*log V):delMin()复杂度为O(log V),共V个元素,因此复杂度为O(V*log V);decreaseKey()复杂度为O(log V),共E条边,复杂度为O(E*log V),两者相加O((V+E)*log V)。
5.2 普里姆算法(Prim's Algorithm)
Prim's Algorithm:又叫最小生成树算法(Minimum spanning tree algorithm)
(步骤:在带权连通图g=(V,E),从图中某一顶点a开始,此时集合U={a},重复执行下述操作:在所有u∈U,w∈V-U的边(u,w)∈E中找到一条权值最小的边,将(u,w)这条边加入到已找到边的集合,并且将点w加入到集合U中,当U=V时,就找到了这颗最小生成树。)
python实现代码如下:

#coding:utf-8 from graphDemo import Graph from binaryHeap import BinaryHeap import sys class PriorityQueue(BinaryHeap): def decreaseKey(self,item,cost): i=1 done=False while i<=self.size and not done: if self.heapList[i][1]==item: #先找到该元素,再将元素向上移 self.heapList[i]=(cost,item) self._percUp(i) done = True i = i+1 def __contains__(self, item): i=1 found = False while i <= self.size and not found: if self.heapList[i][1] == item: found=True i = i+1 return found def prim(aGraph,start): for vert in aGraph: vert.setDistance(sys.maxint) q = PriorityQueue() start.setDistance(0) q.buildHeap([(v.getDistance(), v) for v in aGraph]) while q.size>0: currentVert = q.delMin()[1] for nextVert in currentVert.getConnections(): newCost = currentVert.getWeight(nextVert) # 每次从队列中,挑取边cost最小的点 if nextVert in q and newCost < nextVert.getDistance(): nextVert.setDistance(newCost) nextVert.setPred(currentVert) q.decreaseKey(nextVert, newCost) if __name__ == '__main__': g = Graph() for i in range(6): g.addVertex(i) g.addEdge(0, 1, 5) g.addEdge(0, 5, 2) g.addEdge(1, 2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 3, 9) g.addEdge(3, 4, 7) g.addEdge(3, 5, 3) g.addEdge(4, 0, 1) g.addEdge(5, 4, 8) g.addEdge(5, 2, 1) prim(g, g.getVertex(5)) for vert in g: print vert.getId(), vert.getPred()
参考:http://interactivepython.org/runestone/static/pythonds/Graphs/toctree.html
