Android串口BLE蓝牙通信Java版
0. 导语
我们都知道,在物联网中,BLE蓝牙是通信设备的关键设备。在传统的物联网应用中,无线WIFI、蓝牙和Zigbee,还有一些其他的2.4GHz的无线网卡等。对于一个面向物联网的嵌入式工程师来讲,不单单是要学会底层硬件嵌入式或者是嵌入式Linux驱动的开发,还要掌握上层应用,以理解开发流程,方便未来和软件应用工程师协作开发。“也只有穿别人的鞋子,才知道别人的感觉”似乎就是这个道理吧。
16年的时候,我尝试做过Qt版本的Android,使用的是C++语言,搭建完环境之后开发出了基于Qt的蓝牙通信demo。虽然Qt在不断的完善对于Android的支持,但终究C++向Java转变的时候,效率是一方面的问题,库同样是一方面的问题。Qt的定位也只能是临时应付,或者说应用内的C++算法繁琐的时候,选择C++开发Android才是一个上上策。
对于面向物联网的嵌入式工程师,对于Android不需要掌握太深刻,重头戏不在这里,但是必须要有了解,也要会开发,我猜Android工程师的精髓在于业务逻辑处理上,而对于我们嵌入式工程师来讲,我们只在乎功能的实现,也只是Android工程师掌握的一个边角而已。后继,我们还会开发基于Java Android的Socket编程和服务器通信,还有Wifi编程。
本文的功能和Qt on Android 蓝牙通信开发一样,只是使用Java进行重写。也不得不说,Java的UI比Qt好多了,(在没有专业的UI制作下),在物联网通信中BLE蓝牙适合传输一些控制命令,或者一些家居数据包括温度湿度等等。
1. 蓝牙通信组成
我们将使用蓝牙功能按顺序分成三个部分。第一个部分,蓝牙的控制,对于蓝牙的开启和关闭;第二部分,对于蓝牙的搜索,并且可以增加到UI列表里面;第三部分,蓝牙数据传输和通信,可以发送数据,可以接收数据。如图所示,为整个蓝牙demo区域,实现了最基本的功能,同Qt on Android蓝牙通信开发一样,有蓝牙列表显示+接收和发送和蓝牙控制的基本功能。下一步就进行蓝牙通信的开发介绍。
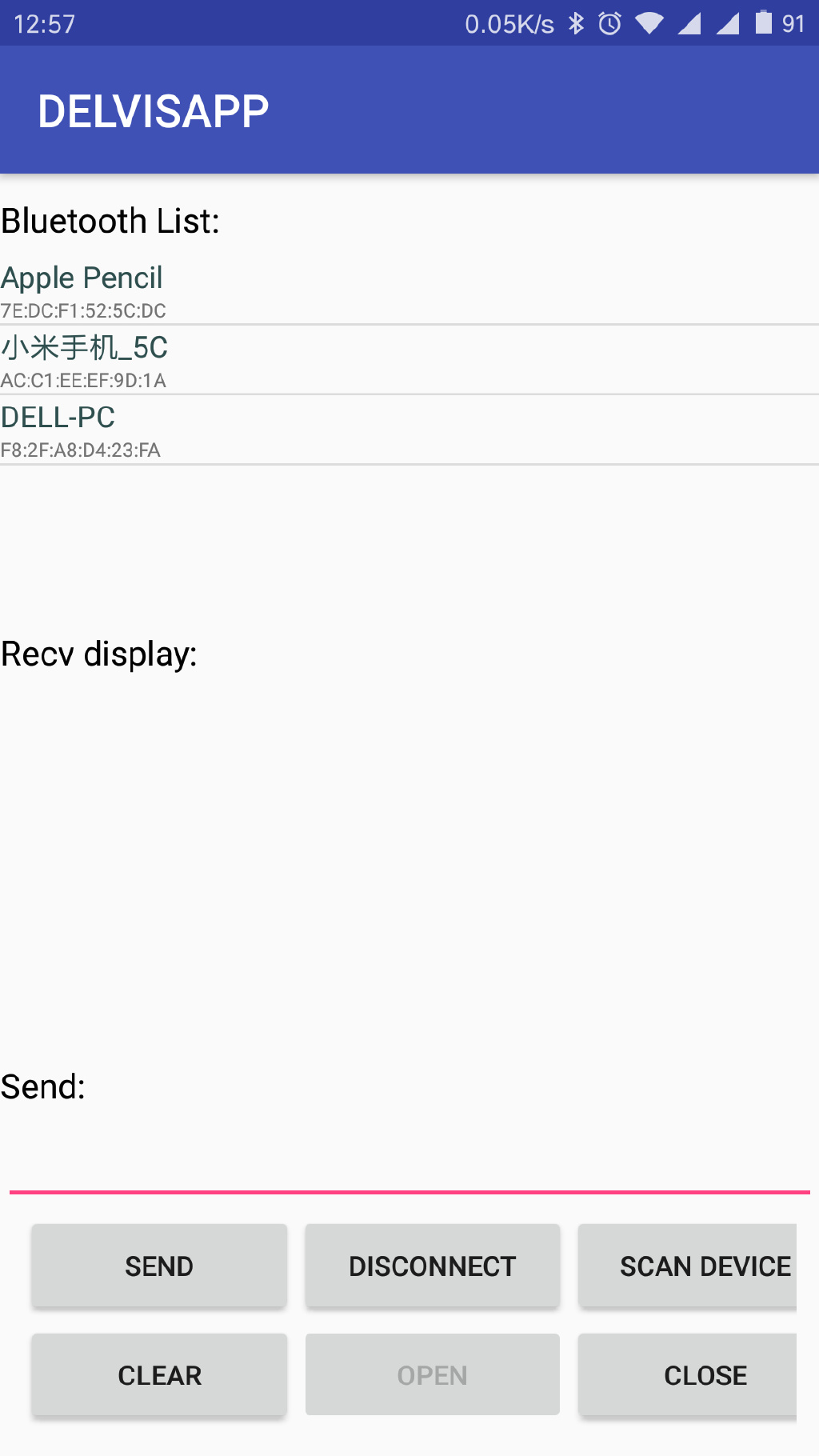
1.1 蓝牙开发架构
如图所示,为蓝牙Activity的界面,里面包含了,TextView,ListView,LineEdit,和一些按钮,使用的是相对布局,为该蓝牙开发提供最基本的功能控制。
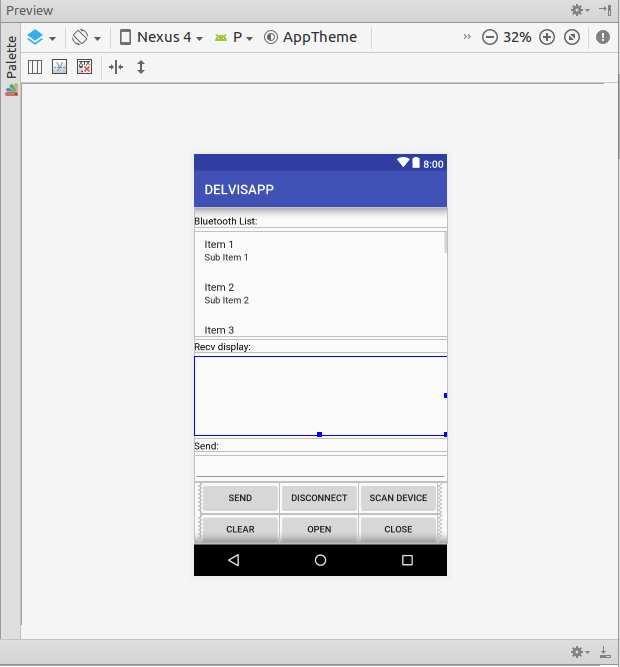
XML布局代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_bluelist"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:text="Bluetooth List:"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="15dp"
/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv_bluelist"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="160dp"
android:paddingTop="1dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp">
</ListView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Recv display:"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_recv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="160dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:textColor="#000"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Send:"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_send"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="12dp"
/>
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="10dp"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_send"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Send" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_disconnect"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Disconnect" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_scan"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Scan Device" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="10dp"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_clear"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Clear" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_open"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Open" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_close"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Close" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
值得注意的是,按钮使用的是TableLayout进行布局,里面请注意观察TableRow对按钮进行划分。
1.2 权限申请
在Android 6.0 以前,申请蓝牙的控制权限只需在mainfest.xml中加入permission项目即可,但是Android 6.0系统需要动态申请权限,而且使用蓝牙搜索需要申请位置权限,否则无法申请蓝牙的权限。
- AndroidManifest.xml文件中
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
分别是蓝牙权限和定位权限。
- 在蓝牙的activity oncreate中动态申请定位权限
/*
* GPS COARSE LOCATION permission checked.
*
* */
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION},
MY_PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION);
if(ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(this,
Manifest.permission.READ_CONTACTS)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
在运行蓝牙的activity中会执行权限扫描,确认用户是否具备定位申请的权限。
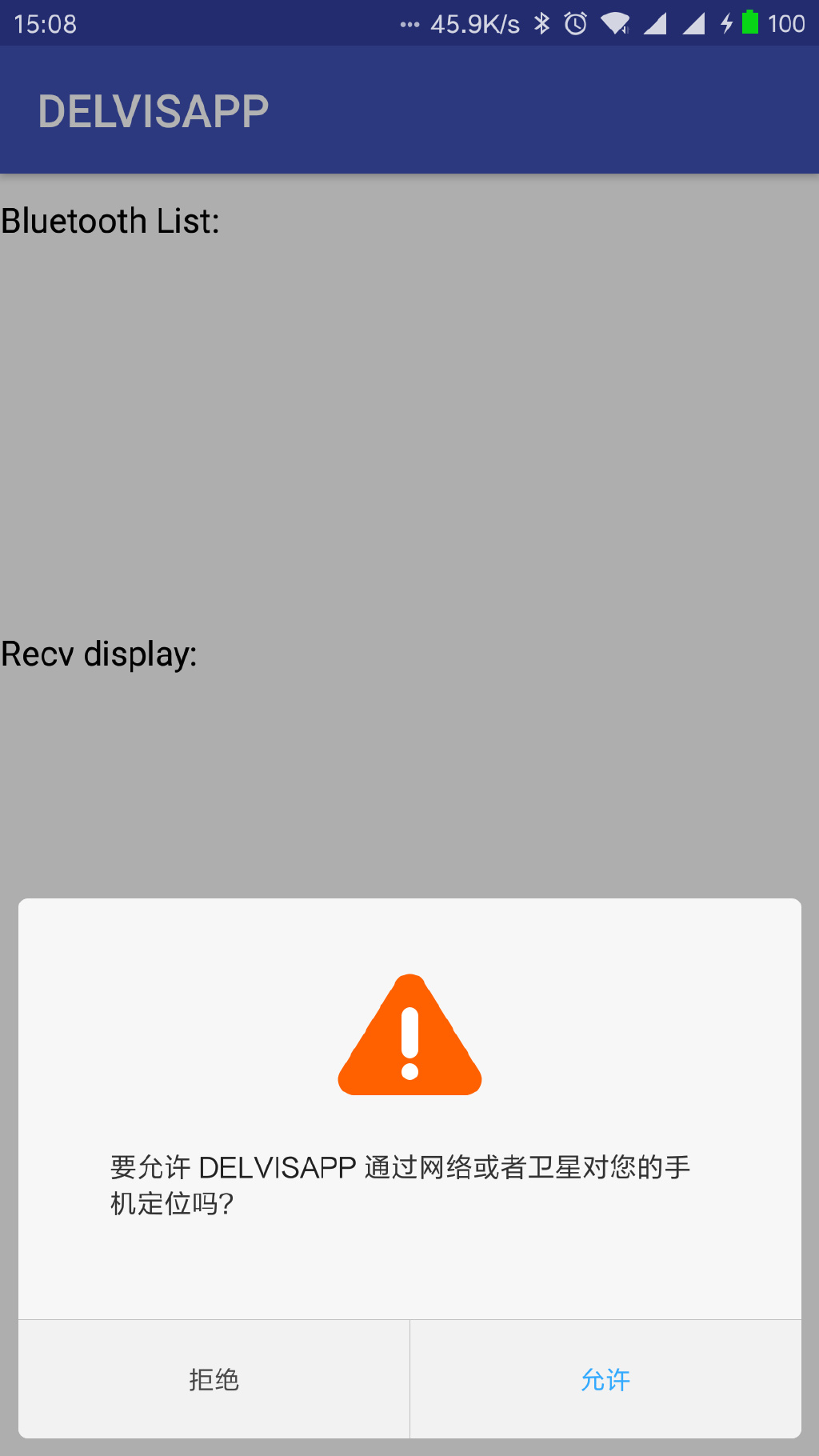
2 蓝牙操作
2.1 蓝牙的开启和关闭
在demo中提供了蓝牙打开和关闭的功能,通过控制类来完成对于蓝牙的开启关闭。
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
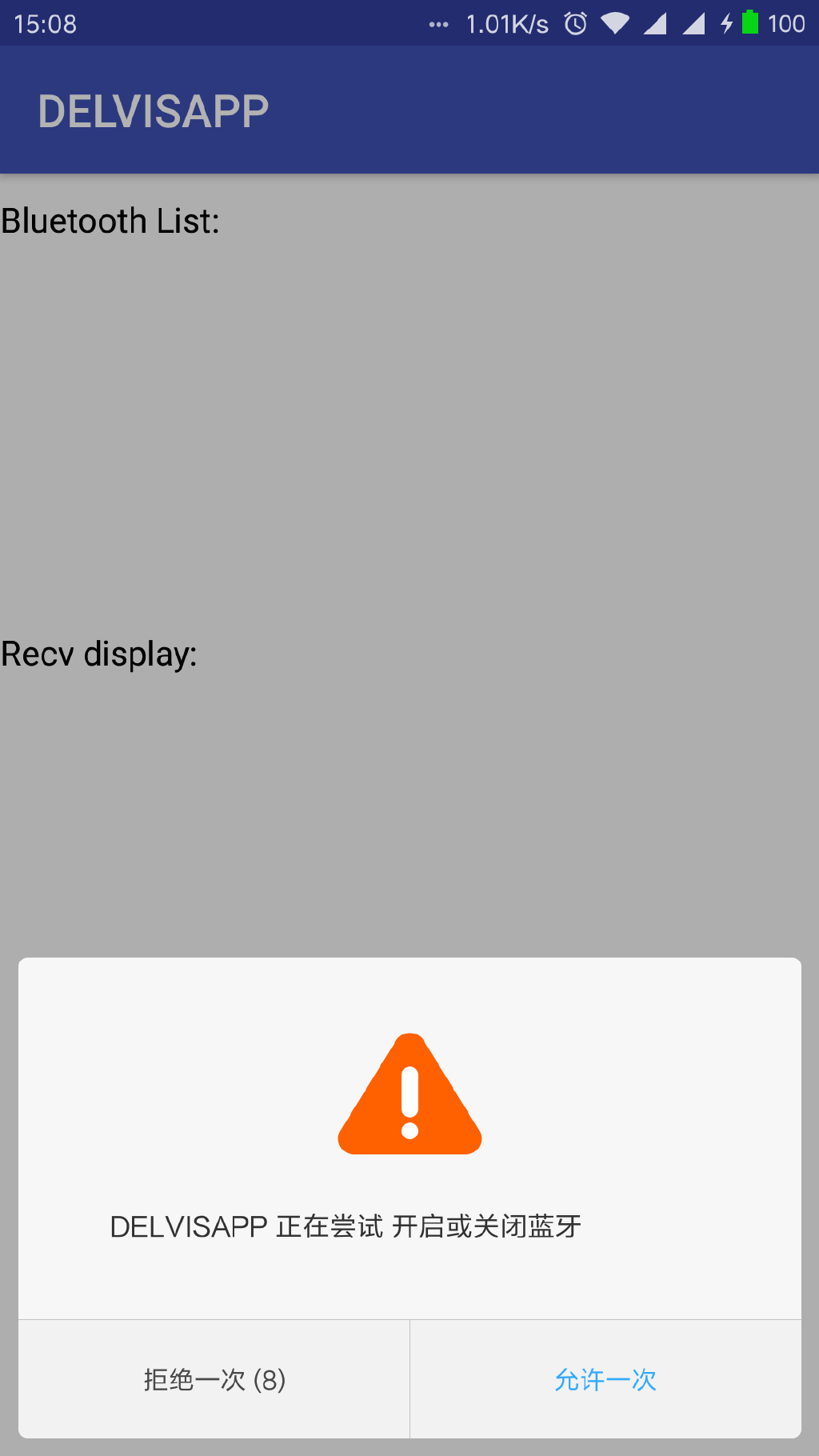
BluetoothAdapter类就是对蓝牙实行开启和控制的类,包括打开蓝牙,关闭蓝牙,查看蓝牙开启关闭状态。如下代码为开机对于蓝牙设备的开启和关闭检测。
/*
* Check bluetooth state.
* */
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = new BluetoothAdapter();
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if( mBluetoothAdapter == null ) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Bluetooth is not available.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
finish();
return;
}
if( !mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled() ) {
//Toast.makeText(this, "Please enable your Bluetooth and re-run this program.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
mBtnOpen.setEnabled(true);
mBtnClose.setEnabled(false);
System.out.println("is enable");
}else{
mBtnOpen.setEnabled(false);
mBtnClose.setEnabled(true);
System.out.println("is not enable");
}
蓝牙的打开:mBluetoothAdapter.enable();
蓝牙的关闭:mBluetoothAdapter.disable();
把他们相应的放在按钮的点击事件即可。
2.2 蓝牙的搜索
蓝牙搜索的功能需要使用安卓的广播功能在UI上还要创建一个ListView将搜索到的周边蓝牙设备加入到设备列表,在demo中就是这样实现的,还能通过ListView的点击事件和该蓝牙设备进行配对连接。
2.2.1 创建Listview列表
新建一个Activity类:
public class BluetoothDeviceAdapter extends BaseAdapter
专门来处理搜寻到的设备然后加入到Listview列表里面。
package com.mltbns.root.delvisapp;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.content.res.ColorStateList;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class BluetoothDeviceAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private ArrayList<BluetoothDevice> mLeDevices;
//LayoutInflater是用来找res/layout/下的xml布局文件,并且实例化
//它的作用类似于findViewById()
private LayoutInflater mInflator;
private Activity mContext;//获得 LayoutInflater 实例的一种方法就是使用Activity;
public BluetoothDeviceAdapter(Activity c) {
super();
mContext = c;
mLeDevices = new ArrayList<BluetoothDevice>();
mInflator = mContext.getLayoutInflater();
}
public void addDevice(BluetoothDevice device) {
if (!mLeDevices.contains(device)) {
mLeDevices.add(device);
System.out.println(device.getName() + " " + device.getAddress());
}
}
// 获取子项中对应的设备
public BluetoothDevice getDevice(int position) {
return mLeDevices.get(position);
}
// 清空列表的数据
public void clear() {
mLeDevices.clear();
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mLeDevices.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return mLeDevices.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View view, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
// General ListView optimization code.
if (view == null) {
view = mInflator.inflate(R.layout.activity_bluetooth_device_adapter, null);//实例化这个控件
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.deviceAddress = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.Address);
viewHolder.deviceName = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.Name);
view.setTag(viewHolder);
} else {
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) view.getTag();
//the Object stored in this view as a tag
}
// 对应的设备进行处理
BluetoothDevice device = mLeDevices.get(position);
final String deviceName = device.getName();
if (deviceName != null && deviceName.length() > 0) {
viewHolder.deviceName.setText(deviceName);
} else {
viewHolder.deviceName.setText("未知设备");
}
if( device.getBondState() == BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED ) {
viewHolder.deviceName.setTextColor(Color.rgb(75,0,130));
}else{
viewHolder.deviceName.setTextColor(Color.rgb(47,79,79));
}
viewHolder.deviceAddress.setText(device.getAddress());
return view;
}
final class ViewHolder {
TextView deviceName;
TextView deviceAddress;
}
}
2.2.2 创建BluetoothReceiver
public class BluetoothReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {}
该类集成BroadcastReceiver类,里面有个onReceive的事件,当搜索到蓝牙的时候,就会将该蓝牙的设备信息传送进来。
public class BluetoothReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
private String pair_info;
private String unpair_info;
private String state_info;
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent ) {
String action = intent.getAction();
System.out.println ( "SYSTEM: action triggered: " + action );
if(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra( BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE );
mLvDeviceList.setAdapter(mBluetoothDeviceAdapter);
System.out.println ( "SYSTEM: Find a device : " + device.getName() + " : " + device.getAddress() );
// Scanned a device add to List
mBluetoothDeviceAdapter.addDevice(device);
// 数据改变并更新列表
mBluetoothDeviceAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
if( device.getBondState() == BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED ) {
pair_info = device.getAddress();
}else {
unpair_info = device.getAddress();
}
}else if(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)){
System.out.println ( "SYSTEM: Discovery finished..." );
}
}
public void set_pairInfo( String val ) {
pair_info = val;
}
public String get_pairInfo() {
return pair_info;
}
public void set_unpairInfo( String val ) {
unpair_info = val;
}
public String get_unpairInfo() {
return unpair_info;
}
public void set_stateInfo( String val ) {
state_info = val;
}
public String get_stateInfo() {
return state_info;
}
}
当搜索到了信息之后就将该设备传入BluetoothDeviceAdapter中,然后该设备的信息都显示。搜索到的信息调入这个方法mBluetoothDeviceAdapter.addDevice(device);就完成了设备的添加,然后刷新显示:mBluetoothDeviceAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();这样就完成了最终的显示。
使用mBluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();开始对蓝牙进行查找。
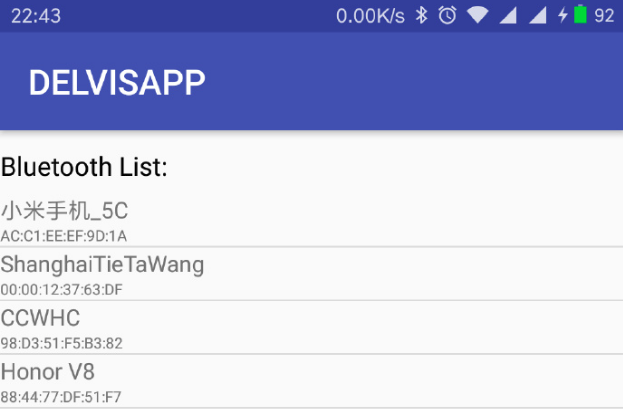
如图所示,上面显示的是蓝牙的名字,下面显示的MAC地址,对于已经配对的设备可以用if( device.getBondState() == BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED ) 来进行判断,然后设定已配对蓝牙的名字为更鲜艳的颜色区分未配对设备。
2.3 连接设备
本demo在listview增加点击事件,当点击设备的时候激发对于该device的连接。这个连接的过程我们需要新建立一个线程进行连接,连接成功之后使用回调函数的方法通知主线程已经连接了,可以进行操作了。在主线程(我们的蓝牙主activity中新建handler函数专门处理其他线程回调信息的)
2.3.1 constant常量类
相当于C++的#include 里面定义一些通信协议的常量,我们在主线程和一会儿创建的搜索线程中会使用该信息。
public class Constant {
public static final String CONNECTTION_UUID = "00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB";
/**
* 开始监听
*/
public static final int MSG_START_LISTENING = 1;
/**
* 结束监听
*/
public static final int MSG_FINISH_LISTENING = 2;
/**
* 有客户端连接
*/
public static final int MSG_GOT_A_CLINET = 3;
/**
* 连接到服务器
*/
public static final int MSG_CONNECTED_TO_SERVER = 4;
/**
* 获取到数据
*/
public static final int MSG_GOT_DATA = 5;
/**
* 出错
*/
public static final int MSG_ERROR = -1;
}
2.3.2 connect线程
package com.mltbns.root.delvisapp;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import android.os.Handler;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 客户端连接线程
*/
public class ConnectThread extends Thread {
private static final UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
private final BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private final BluetoothDevice mmDevice;
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
private final Handler mHandler;
private ConnectedThread mConnectedThread;
public ConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device, BluetoothAdapter adapter, Handler handler) {
BluetoothSocket tmp = null;
mmDevice = device;
mBluetoothAdapter = adapter;
mHandler = handler;
//根据给定的设备获取一个BluetoothSocket对象
try {
// 和服务器端使用相同的UUID
tmp = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
} catch (IOException e) { }
mmSocket = tmp;
}
public void run() {
// 取消搜索设备因为会关闭连接
System.out.println(" Connect +: "+ mmDevice.getName());
mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
try {
// Connect the device through the socket. This will block
// until it succeeds or throws an exception
mmSocket.connect();
System.out.println("Connecting.... ");
} catch (Exception connectException) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(Constant.MSG_ERROR, connectException));
// Unable to connect; close the socket and get out
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException closeException) { }
return;
}
// Do work to manage the connection (in a separate thread)
manageConnectedSocket(mmSocket);
}
private void manageConnectedSocket(BluetoothSocket mmSocket) {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(Constant.MSG_CONNECTED_TO_SERVER);
mConnectedThread = new ConnectedThread(mmSocket, mHandler);
mConnectedThread.start();
System.out.println("Connected thread start... ");
}
/** Will cancel an in-progress connection, and close the socket */
public void cancel() {
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) { }
}
public void sendData(byte[] data) {
if( mConnectedThread!=null){
mConnectedThread.write(data);
}
}
}
我们在对listview里面有点击事件的函数,点击的项目索引编号和device的信息进行了绑定,然后进行了连接。通过该线程就完成了对于蓝牙设备的连接。
2.4 蓝牙数据传输
2.4.1 connected线程
连接完成之后,进入的线程,主要是进行收发消息的。
package com.mltbns.root.delvisapp;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* Created by Rex on 2015/5/30.
*/
public class ConnectedThread extends Thread {
private final BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private final InputStream mmInStream;
private final OutputStream mmOutStream;
private final Handler mHandler;
public ConnectedThread(BluetoothSocket socket, Handler handler) {
mmSocket = socket;
InputStream tmpIn = null;
OutputStream tmpOut = null;
mHandler = handler;
// 获取输入输出流
try {
tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) { }
mmInStream = tmpIn;
mmOutStream = tmpOut;
}
public void run() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // buffer store for the stream
int bytes;
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs
while (true) {
try {
// 从输入流读取数据
bytes = mmInStream.read(buffer);
// Send the obtained bytes to the UI activity
if( bytes >0) {
Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(Constant.MSG_GOT_DATA, new String(buffer, 0, bytes, "utf-8"));
mHandler.sendMessage(message);
}
Log.d("GOTMSG", "message size" + bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(Constant.MSG_ERROR, e));
break;
}
}
}
/* 发送数据岛远程设备*/
public void write(byte[] bytes) {
try {
mmOutStream.write(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) { }
}
/* 关闭连接 */
public void cancel() {
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) { }
}
}
2.4.2 主线程的handler
private void showToast(String text) {
if( mToast == null) {
mToast = Toast.makeText(this, text, Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
}
else {
mToast.setText(text);
}
mToast.show();
}
/**
* 处理消息
*/
private class MyHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what) {
case Constant.MSG_START_LISTENING:
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
System.out.println("Start to listener...");
break;
case Constant.MSG_FINISH_LISTENING:
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(false);
System.out.println("stop listenner");
break;
case Constant.MSG_GOT_DATA:
mTextView.append(String.valueOf(msg.obj));
System.out.println("data: "+String.valueOf(msg.obj));
break;
case Constant.MSG_ERROR:
System.out.println("error: "+String.valueOf(msg.obj));
break;
case Constant.MSG_CONNECTED_TO_SERVER:
System.out.println("Connected to Server");
mLvDeviceList.setEnabled(false);
mLvDeviceList.setBackgroundColor(Color.rgb(119,136,153));
showToast("Bluetooth connection has been set up!");
break;
case Constant.MSG_GOT_A_CLINET:
System.out.println("Got a Client");
break;
}
}
}
在开始搜索设备线程的时候我们将handler也传递给了线程,线程在执行完搜索完成之后就会进入handler的函数按照回调信息进入case里面,输出相关信息。
这里有收到信息,信息错误,连接成功的事件,我们在相应的事件里面进行进行执行函数就好了。
2.4.3 函数的发送
String text = mEditText.getText().toString();
connectThread.sendData( text.getBytes() );
我们获取editText组件的字符串,然后用connectThread的send函数就能将数据发送出去。
2.4.4 函数的接收
mTextView.append(String.valueOf(msg.obj));
System.out.println("data: "+String.valueOf(msg.obj));
该函数在handler函数体内,是case Constant.MSG_GOT_DATA:里面的。
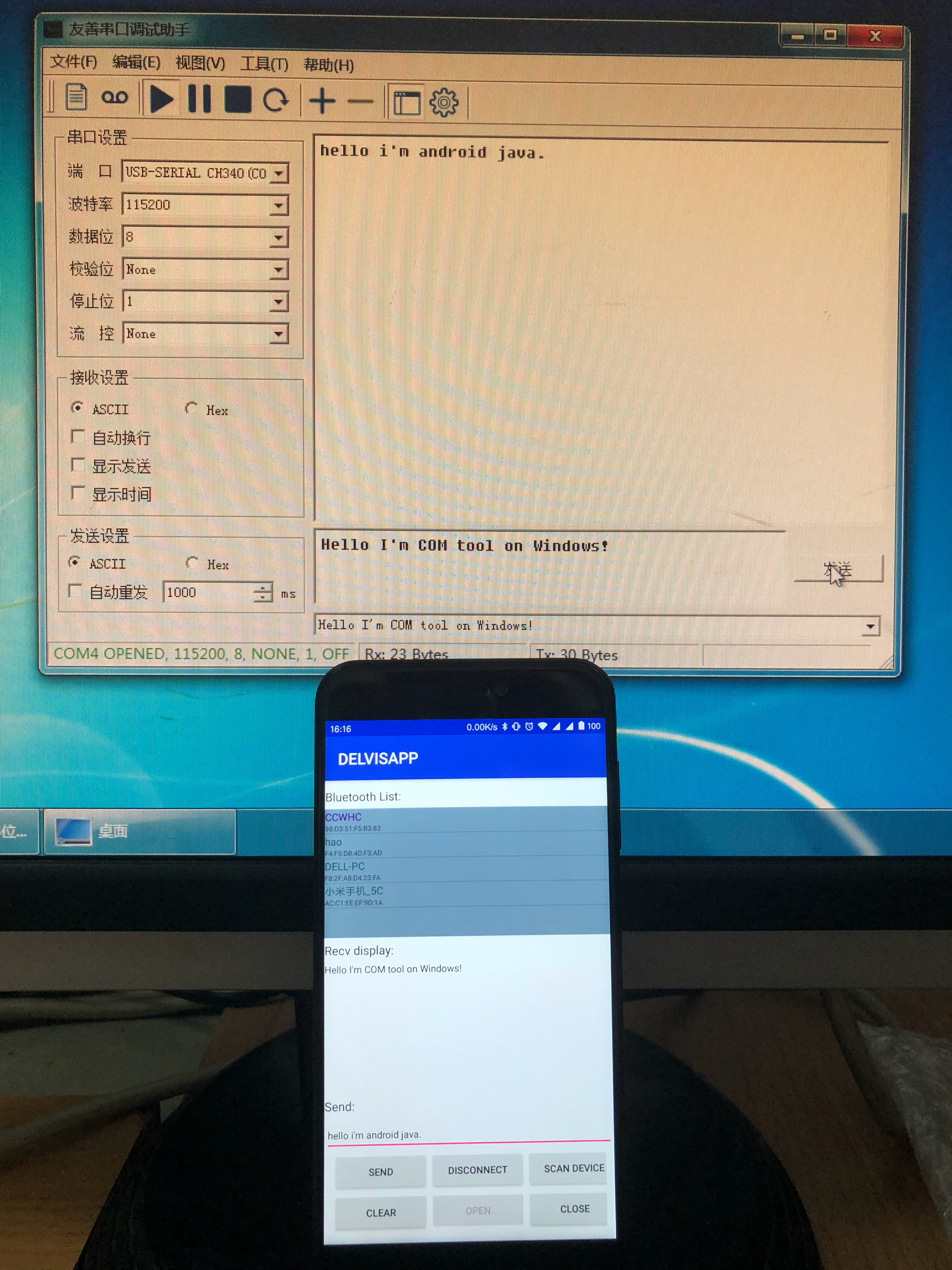
3 源代码下载
Github链接:https://github.com/lifimlt/android-study.git
4 参考文献
[1] zw1996, 安卓——蓝牙listView搜索以及点击事件
, csdn, 2017年7月15日
[2] qq_22252423, Android串口蓝牙开发实战
, csdn, 2017年07月18日
[3] MetalSeed, Android蓝牙串口通信模板及demo,trick
, csdn, 2012年9月17日
[4] Keep Do It, 蓝牙搜索显示结果到ListView(十分精简)
, csdn, 2016年11月26日
[5] Small_Lee, 蓝牙实战(三)
, csdn, 2016年3月15日