线程安全使用单例模式,保证了每次只创建单个对象,代码如下:
Singleton.h
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//线程安全
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_SINGLETON_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_SINGLETON_H
//单例
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // atexit
namespace muduo
{
template<typename T>
class Singleton : boost::noncopyable//继承自noncopyable表示不可被拷贝
{
public:
static T& instance()//返回该类单例对象
{
pthread_once(&ponce_, &Singleton::init);//ponce_能够保证该函数只被执行一次,而且能够保证线程安全
return *value_;
}
private:
Singleton();//构造函数
~Singleton();//析构函数
static void init()//在内部创建的对象
{
value_ = new T();
::atexit(destroy);//在程序结束的时候会自动调用destroy
}
static void destroy()//在内部销毁的对象
{//这句保证了T是一个完全类型的类,否则该数组的大小为-1,编译时会产生警告
typedef char T_must_be_complete_type[sizeof(T) == 0 ? -1 : 1];
delete value_;
}
private:
static pthread_once_t ponce_;//这个对象能够保证一个函数只被执行一次
static T* value_;
};
template<typename T>
pthread_once_t Singleton<T>::ponce_ = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
template<typename T>
T* Singleton<T>::value_ = NULL;
}
#endif测试代码如下,该代码在主线程中创建一个单例对象,然后在子线程中改变该对象的名称,由于是单例对象,最后主线程打印的时候名称也是改变了的
//线程安全测试程序
#include <muduo/base/Singleton.h>
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <muduo/base/Thread.h>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
//定义Test类
class Test : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
Test()
{//%p是指针的值
printf("tid=%d, constructing %p
", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this);
}
~Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, destructing %p %s
", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this, name_.c_str());
}
const muduo::string& name() const { return name_; }
void setName(const muduo::string& n) { name_ = n; }//设置名称
private:
muduo::string name_;//名称
};
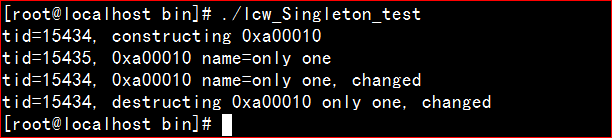
单独编译后运行结构如下: