NOIP Simulated Test
这个名字一听就很高端.
T1:sGCD:http://uoj.ac/problem/48
题意概述:给定一个长度为$n$的序列,求$sgcd(a_1,a_i)$,定义$sgcd(a,b)$为$a,b$的次大公约数.$n<=1e5$
我的做法:因为唯一分解定理,$sgcd(a,b)$一定是$(a,b)$再除去一个质因子,那当然是除去最小的质因子最合适啦,每次求出最大公约数再求它的最小质因子,总复杂度$O(NlogNsqrt{a_i})$,有点卡常,考试时$A$了,但是在UOJ上只得了$80$分.
正解:充分利用$gcd(a,b)|a$的条件,首先分解$a_1$的质因子,每次求出$(a_1,a_i)$后再进行试除.一个数的质因子个数是比$sqrt{X}$要小很多的,可以愉快的通过此题.

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # define R register int 4 # define ll long long 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const int maxn=100005; 9 long long a[maxn],g,ans,p[maxn],h; 10 int n; 11 12 long long read() 13 { 14 long long x=0; 15 char c=getchar(); 16 while (!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); 17 while (isdigit(c)) { x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48); c=getchar(); } 18 return x; 19 } 20 21 ll gcd (ll a,ll b) { return b?gcd(b,a%b):a; } 22 23 ll m (ll a) 24 { 25 for (R i=1;i<=h;++i) 26 if(a%p[i]==0) return p[i]; 27 return a; 28 } 29 30 void div (ll x) 31 { 32 for (R i=2;(ll)i*i<=x;++i) 33 { 34 if(x%i==0) p[++h]=i; 35 while (x%i==0) x/=i; 36 } 37 if(x!=1) p[++h]=x; 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 scanf("%d",&n); 43 for (R i=1;i<=n;++i) 44 a[i]=read(); 45 div(a[1]); 46 for (R i=1;i<=n;++i) 47 { 48 g=gcd(a[1],a[i]); 49 if(g==1) ans=-1; 50 else ans=g/m(g); 51 printf("%lld",ans); 52 if(i!=n) putchar(' '); 53 } 54 return 0; 55 }
T2:School:http://uoj.ac/contest/39/problem/308
题意概述:$n$个点的图使用$k$种颜色染色,要求每条边两边的颜色都不相同的染色方案数量模$6$。
今天考的时候和这道题给的部分分略有差异,数据为树的数据提高到了三个点.图的染色问题是一个没有多项式时间解法的难题,所以这道题一定有什么神仙解法。
我的做法_数据分治:
·对于小数据搜索.
·对于树的数据打表找规律发现颜色数直接模$6$不影响答案,所以写了一个树形$dp$.
·其他时间:$printf("\%d",rand()\%6);$
后来学到了正解:
答案可以表示为 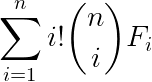
不过这是什么意思...?首先考虑用多少种颜色进行染色,就是上式中枚举的$i$,设一个新函数$f_i$表示用$i$种颜色染色的方案数,从$n$种颜色中选出$i$种来,最后是一个阶乘,用于把...和那个组合放在一起看就是一个排列啊,因为$123$和$321$毕竟还是不同的.拆出这个阶乘来主要是为了化简.注意到:当$i>2$时,这个式子模$6$等于$0$,所以我们只需要算$i$等于$1$或者是$2$的情况.对于$i$等于一,只要有边答案就为$0$,所以很好统计,对于$i$等于$2$的情况,只要确定了一个点就可以确定其他所有联通的点,求出每个联通块的答案个数,乘法原理统计答案即可.
$APIO$的题拿来做$NOIP$模拟赛真的好吗...
题意比较麻烦,就不说了。其实这是一个树形$dp$的题目,关键是要想好状态的表示,我考场上想的是$dp[i][1]$记录以$i$为根的子树上边连的是红边的答案,再记录上边为蓝边的答案,结果发现非常复杂,终于过了样例之后发现一条链就可以把我的程序$Hack$掉了.这个做法为什么难做呢?主要是情况比较多,如果上边是红边还好说,如果上面是蓝边就要分为根是后来插入的点和本来就有的点两种情况分别讨论.其实问题的关键也就在这里,如果以$i$点是后来插入的点还是本就有的点作为状态就会简单许多了.其实这样做还是很麻烦...还有一种更合理的方法是记录$i$是否是由他的一个儿子和父亲断边重连得来的。
这样的做法还要枚举根,不过也可以通过记录次大值来$O(1)$换根.

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <cstring> 4 # include <cmath> 5 # include <algorithm> 6 # include <string> 7 # define R register int 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 //dp[i][0]表示点i不是通过2操作加入的,1表示是 12 13 const int maxn=10005; 14 int n,h,x,y,co,firs[maxn],dp[maxn][2],dep[maxn],ans; 15 struct edge 16 { 17 int too,nex,co; 18 }g[maxn<<1]; 19 20 void add (int x,int y,int co) 21 { 22 g[++h].too=y; 23 g[h].nex=firs[x]; 24 firs[x]=h; 25 g[h].co=co; 26 } 27 28 void dfs (int x) 29 { 30 int j,G=-1000000000; 31 for (R i=firs[x];i;i=g[i].nex) 32 { 33 j=g[i].too; 34 if(dep[j]) continue; 35 dep[j]=dep[x]+1; 36 dfs(j); 37 G=max(G,dp[j][0]+g[i].co-max(dp[j][0],dp[j][1]+g[i].co)); 38 dp[x][0]+=max(dp[j][0],dp[j][1]+g[i].co); 39 dp[x][1]+=max(dp[j][0],dp[j][1]+g[i].co); 40 } 41 dp[x][1]+=G; 42 } 43 44 int read() 45 { 46 int x=0; 47 char c=getchar(); 48 while (!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); 49 while (isdigit(c)) { x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48); c=getchar(); } 50 return x; 51 } 52 53 int main() 54 { 55 scanf("%d",&n); 56 for (R i=1;i<n;++i) 57 { 58 x=read(),y=read(),co=read(); 59 add(x,y,co); 60 add(y,x,co); 61 } 62 for (R i=1;i<=n;++i) 63 { 64 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); 65 memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); 66 dep[i]=1; 67 dfs(i); 68 ans=max(ans,dp[i][0]); 69 } 70 printf("%d",ans); 71 return 0; 72 }
/shzr咕咕咕了,不过还是决定贴上代码/

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <cstring> 4 # include <cmath> 5 # include <algorithm> 6 # include <string> 7 # define inf 0x3f3f3f3f 8 # define R register int 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 //f[i][0]表示点i不是通过2操作加入的,1表示是 13 14 const int maxn=200005; 15 int n,h,x,y,co,firs[maxn],f[maxn][2],dp[maxn][2],dep[maxn],ans; 16 struct edge 17 { 18 int too,nex,co; 19 }g[maxn<<1]; 20 21 void add (int x,int y,int co) 22 { 23 g[++h].too=y; 24 g[h].nex=firs[x]; 25 firs[x]=h; 26 g[h].co=co; 27 } 28 29 void dfs (int x) 30 { 31 int j,t,t1,G=-inf,mG=-inf; 32 for (R i=firs[x];i;i=g[i].nex) 33 { 34 j=g[i].too; 35 if(dep[j]) continue; 36 dep[j]=dep[x]+1; 37 dfs(j); 38 f[x][0]+=max(f[j][0],f[j][1]+g[i].co); 39 t=f[j][0]+g[i].co-max(f[j][0],f[j][1]+g[i].co); 40 if(t>=G) mG=G,G=t; else mG=max(mG,t); 41 } 42 f[x][1]=f[x][0]+G; 43 for (R i=firs[x];i;i=g[i].nex) 44 { 45 j=g[i].too; 46 if(dep[j]<dep[x]) continue; 47 t=-max(f[j][0],f[j][1]+g[i].co); 48 if(t+f[j][0]+g[i].co==G) 49 t1=mG; 50 else 51 t1=G; 52 dp[j][0]=t; 53 dp[j][1]=t1; 54 } 55 } 56 57 int read() 58 { 59 int x=0; 60 char c=getchar(); 61 while (!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); 62 while (isdigit(c)) { x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48); c=getchar(); } 63 return x; 64 } 65 66 void Dp (int x,int r) 67 { 68 ans=max(ans,f[x][0]); 69 int j,t1,t2; 70 for (R i=firs[x];i;i=g[i].nex) 71 { 72 j=g[i].too; 73 if(dep[j]<dep[x]) continue; 74 t1 =f[x][0]+dp[j][0]; 75 t2=f[x][0]+dp[j][0]+max(r,dp[j][1]); 76 f[j][0]+=max(t1,t2+g[i].co); 77 Dp(j,t1+g[i].co-max(t1,t2+g[i].co)); 78 } 79 } 80 81 int main() 82 { 83 scanf("%d",&n); 84 for (R i=1;i<n;++i) 85 { 86 x=read(),y=read(),co=read(); 87 add(x,y,co); 88 add(y,x,co); 89 } 90 dep[1]=1; 91 dfs(1); 92 Dp(1,-inf); 93 printf("%d",ans); 94 return 0; 95 }
