static List<int> GetInitialData()
{ return new List<int>(){1,2,3,4};}打印出所有值大于2的元素
不使用yield return的实现
static IEnumerable<int> FilterWithoutYield(){ List<int> result = new List<int>(); foreach (int i in GetInitialData()) { if (i > 2) { result.Add(i); } } return result;}使用yeild return实现
static IEnumerable<int> FilterWithYield(){ foreach (int i in GetInitialData()) { if (i > 2) { yield return i; } } yield break; Console.WriteLine("这里的代码不执行");}总结:
通过单步调试发现:
虽然2种方法的输出结果是一样的,但运作过程迥然不同。第一种方法,是把结果集全部加载到内存中再遍历;第二种方法,客户端每调用一次,yield return就返回一个值给客户端,是"按需供给"。
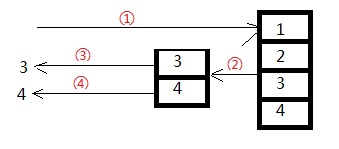
第一种方法,客户端调用过程大致为:
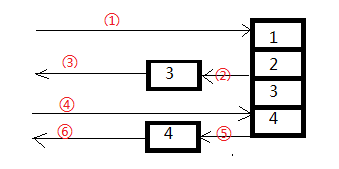
使用yield return,客户端调用过程大致为:
so,like this is cool:


/// <summary>
/// 递归构造商品分类
/// </summary>
/// <param name="source"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private IEnumerable<ProductCategory> RecursionCategory(IEnumerable<ProductCategoryExt> source)
{
if (source.IsHasRow())
{
foreach (var item in source)
{
yield return new ProductCategory()
{
ParentId = item.ParentId,
CateId = item.ProductCategoryId,
CateName = item.VchMobileShowName,
IcoUrl = item.CatePic,
};
}
}
}