模拟物体变形最简单的方法就是采用弹簧质点系统(Spring-Mass System),由于模型简单并且实用,它已被广泛应用于服饰、毛发以及弹性固体的动态模拟。对于三角网格而言,弹簧质点系统将网格中的顶点看作系统中的质点,而网格的边则是连接这些质点的弹簧。这样,弹簧质点系统模型就将物体简化成由弹簧和质点组成的系统,并利用弹簧质点的运动规律来描述物体的弹性变形过程。
Verlet积分是求解牛顿运动方程的数值方法,原理简单描述如下:首先将系统t+dt时刻的位置x(t+dt)以及系统t-dt时刻的位置x(t-dt)用泰勒公式展开:
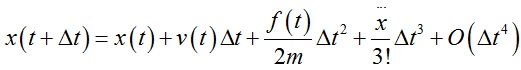
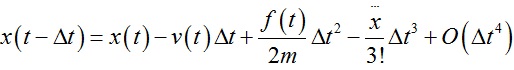
上面两式相加后得到:
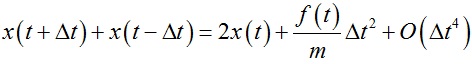
进一步变化得到:
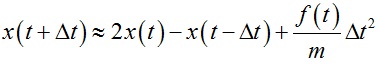
因此通过上式可以根据系统前两时刻的状态求解系统的当前状态,这与”基于网格的波动方程模拟“一文中的求解过程有些类似。
为了真实模拟物体变形效果,需要对弹簧质点系统进行受力分析:1. 每个质点有自身重力的影响;2. 每个质点受到与它相连的弹簧弹力影响,弹簧弹力遵守胡克定律;3. 质点运动时受到与其速度成正比的阻尼约束;4. 质点会受到其他外力的影响,由于施加的外力在每个三角面片上有一个法向分量,我们只需对每个质点周围三角片上的这些分量相加即可。

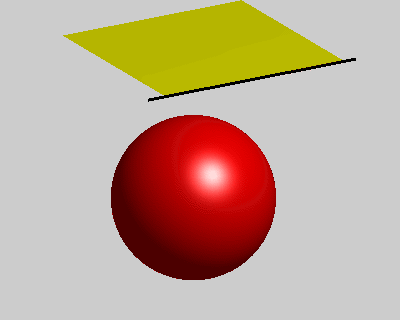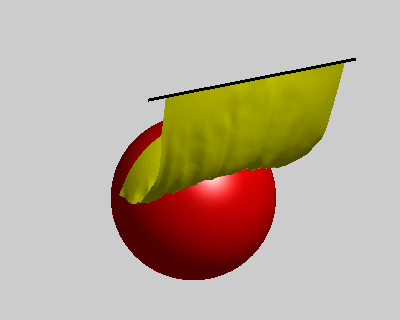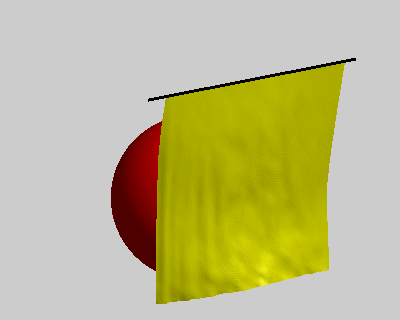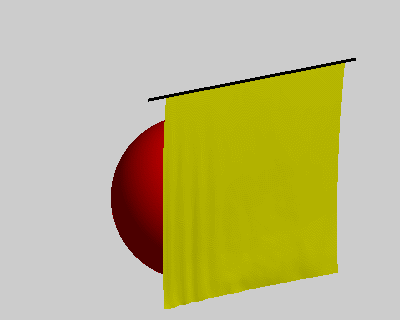
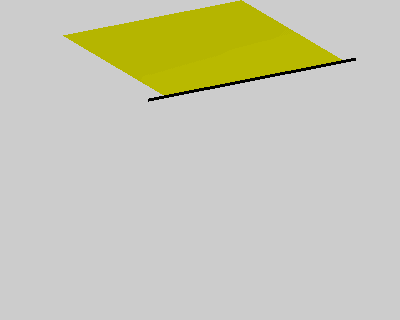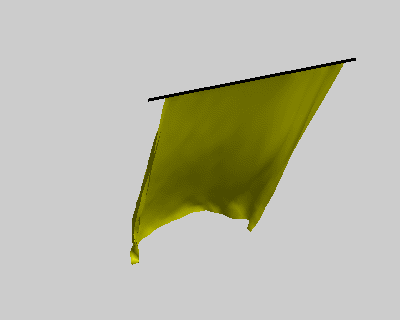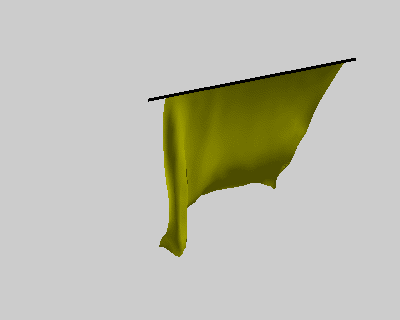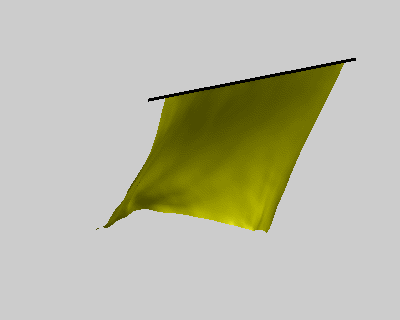
% constrains option wind = false; ball = true; pins = false; figure('Position', [400, 400, 400, 320]); fh = drawMesh(V,F,'facecolor','y','edgecolor','none'); if ball center = [50 60 -80]; radius = 40; drawSphere([center radius], 'facecolor','r', 'nPhi',96, 'nTheta',48); end if pins plot3([-10;110], [0;0], [0;0], 'k-', 'linewidth',2); end view([-30 20]) axis equal axis off axis([-10 100 -10 100 -110 0]); camlight lighting gouraud set(gca, 'position', [0 0 1 1]); % initial condition x_pre = V; x_cur = V; % rest length E = edges(F); l0 = vectorNorm3d(V(E(:,1),:) - V(E(:,2),:)); nV = size(V,1); draw_t = 0; tic; while true % spring force Fs = stiffness * (vectorNorm3d(x_cur(E(:,1),:) - x_cur(E(:,2),:)) - l0); dir = normalizeVector3d(x_cur(E(:,2),:) - x_cur(E(:,1),:)); M1 = sparse(E, E, [Fs.*dir(:,1);-Fs.*dir(:,1)]); M2 = sparse(E, E, [Fs.*dir(:,2);-Fs.*dir(:,2)]); M3 = sparse(E, E, [Fs.*dir(:,3);-Fs.*dir(:,3)]); as = [diag(M1), diag(M2), diag(M3)] ./ m; % wind force aw = zeros(nV,3); if wind N = normalizeVector3d(normals(x_cur,F)); Fw = N * wind_force(i/10)' .* wind_strength; M1 = sparse(F, F, repmat(Fw.*N(:,1),1,3)); M2 = sparse(F, F, repmat(Fw.*N(:,2),1,3)); M3 = sparse(F, F, repmat(Fw.*N(:,3),1,3)); aw = [diag(M1), diag(M2), diag(M3)] ./ m; end % verlet integration with a simple damping model x_new = drag*(x_cur - x_pre) + x_cur + bsxfun(@plus, as+aw, g)*dt*dt; x_pre = x_cur; x_cur = x_new; % ball constrains if ball diff = bsxfun(@minus, x_cur, center); index = vectorNorm3d(diff) < radius+1; x_cur(index,:) = bsxfun(@plus, center, bsxfun(@times, normalizeVector3d(diff(index,:)), radius+1)); end % pin constrains if pins x_pre(pin_idx,:) = V(pin_idx,:); x_cur(pin_idx,:) = V(pin_idx,:); end % updata figure
if toc > 0.033 set(fh, 'Vertices', x_cur); drawnow;
tic; end end
本文为原创,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/shushen。