/********************************************************************** * 版权所有 (C)2017, Wang maochun。 * * 文件名称:stu.c * 文件标识:无 * 内容摘要:演示程序 * 其它说明:主要学习三点知识: 1.建立一个结构体,类型名为student 2.当定义结构体变量时,通过成员操作符访问成员(.) 当定义指向结构体的指针时,通过间接访问操作符(->) 3.传值操作,子函数对实参进行了一份拷贝,对其的操作不会影响到orginal value,我们通过打印地址和实参不同可以看到 传址操作,子函数传递了实参地址,此时操作的是orginal value,优点是节省空间和花销。如果子函数不修改需const修饰 * 当前版本:V1.0 * 作 者:Wang maochun * 完成日期:2017.7.23 * **********************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> struct student{ int code; char name[10]; char sex[10]; int age; }; void printStuInfobyValue(student stu) { printf("in fun结构体传值:学号、姓名、性别、年龄: "); printf("%5d [%p] %5s [%p] %5s [%p] %5d [%p] ",stu.code,&stu.code,stu.name,&stu.name, stu.sex,&stu.sex,stu.age,&stu.age); } void printStuInfoByAdress(student* pstu) { printf("in fun结构体传地址:学号、姓名、性别、年龄: "); printf("%6d [%p] %6s [%p] %6s [%p] %6d [%p] ",pstu->code,&pstu->code,pstu->name,&pstu->name, pstu->sex,&pstu->sex,pstu->age,&pstu->age); } int main(){ //struct student stu; student stu = {123,"wsq","Male",23}; student *pstu = &stu; printf("in main:学号、姓名、性别、年龄: "); //scanf("%d %s %s %d",&stu.code,stu.name,stu.sex,&stu.age); printf("%5d [%p] %5s [%p] %5s [%p] %5d [%p] ",stu.code,&stu.code,stu.name,&stu.name, stu.sex,&stu.sex,stu.age,&stu.age); printf("%6d [%p] %6s [%p] %6s [%p] %6d [%p] ",pstu->code,&pstu->code,pstu->name,&pstu->name, pstu->sex,&pstu->sex,pstu->age,&pstu->age); printStuInfobyValue(stu); //结构体传值 printStuInfoByAdress(&stu); //结构体传地址 return 0; }
运行效果:
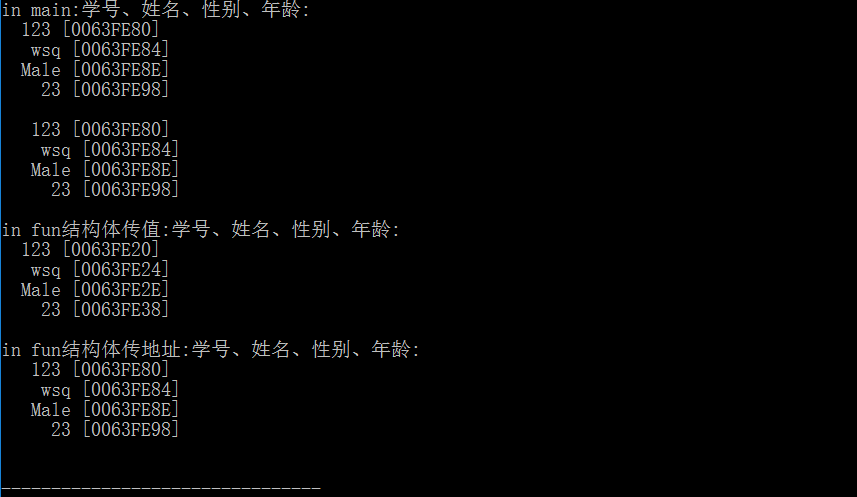
我们可以看到:
结构体对象作为参数时,编译器对其进行了copy,(我们通过传入的地址和main中不同可以发现)。此时在函数中的操作都是对其拷贝的操作,不影响main函数中的origin value
缺点是,当结构体变量非常大时,编译器对其进行复制,开销较大。
用结构体变量作实参时,采取的是"值传递"的方式,将结构体变量所占的内存单元的内容全部顺序传递给形参.形参也必须是同类型的结构体变量.在函数调用期间形参也要占用内存单元. 这种传递方式在空间和时间上开销较大,如果结构体的规模很大时,开销是很可观的.
结构体地址作为参数时,子函数中操作和main函数操作的是同一个结构体,此时传递的参数时一个地址。
优点是不需要进行copy,但是使用时要小心,如果不想修改其值,需用const关键字修饰