1.需求分析:
1. 根据用户输入的题目个数,产生含有三个数字,两种运算符的题目,并显示出来。
2. 根据生成的题目,进行计算,显示计算后的结果。
2. 具体设计:
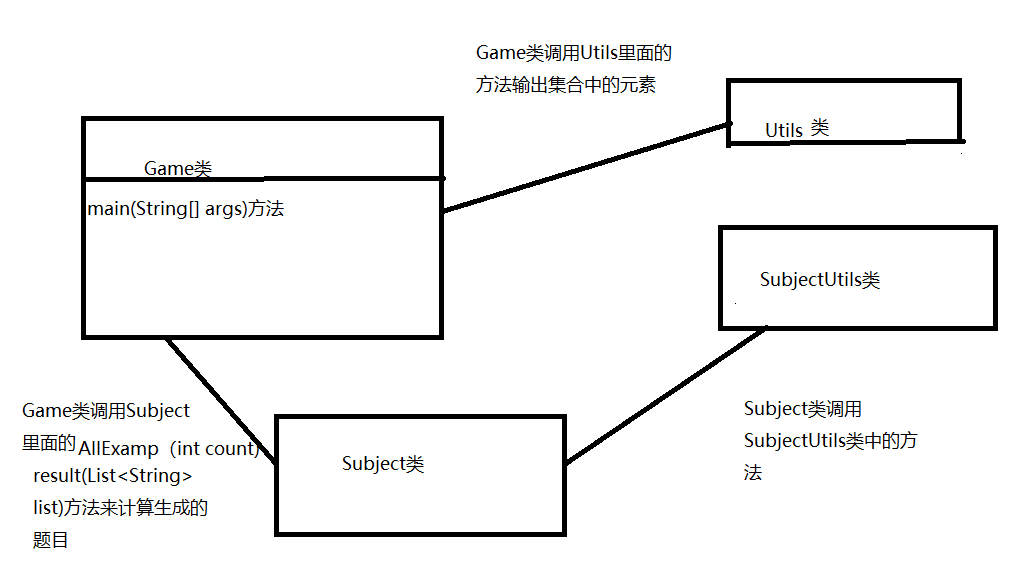
各个类的作用:
1. Game类:主界面类,显示给用户的。
2. Subject类:题目类,主要作用:根据用户输入的个数产生题目、对所产生的所有进行计算。
3. SubjectUtils类:Subject类的工具类,主要作用:产生随机运算符、产生四则运算题、根据传入的题目进行计算。
4. Utils类:主界面类所用的工具类,主要作用:遍历数组、遍历集合。
5. TestSubject类:对Subject类里面的方法进行测试。
3.核心代码:
Game类: 主界面
1 package game; 2 3 import java.util.List; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 import prctice.Subject; 6 import utils.Utils; 7 8 public class Game { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Subject subject = new Subject(); 11 System.out.println("尊敬的顾客,请输入要生成几道题目:"); 12 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 13 int count = sc.nextInt(); 14 System.out.println("---------*生成的题目如下*-----------------"); 15 List<String> allExamp = subject.AllExamp(count); 16 Utils.showList(allExamp); 17 System.out.println("请输入你的答案:(一题一行):"); 18 String[] answer = Utils.retrunArray(count); 19 for (int i = 0; i < answer.length; i++) { 20 String ele = sc.next(); 21 answer[i]=ele; 22 } 23 System.out.println("您的答案是:"); 24 Utils.showArrayElement(answer); 25 System.out.println(); 26 System.out.println("-----------*在线为您解答如下*----------"); 27 List<String> result = subject.result(allExamp); 28 Utils.showList(result); 29 30 } 31 32 }
Subject类: 随机产生四则运算的类
1 package prctice; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.Random; 6 7 import javax.script.ScriptEngine; 8 import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager; 9 import javax.script.ScriptException; 10 11 import utils.SubjectUtils; 12 13 /** 14 * 习题类 定义了生成习题的方法 15 * 16 * @author Asus 17 * 18 */ 19 public class Subject { 20 private static String[] fu = { "+", "-", "*", "/" }; 21 22 /** 23 * 功能1. 根据传入的个数来生成题目 24 * 25 * @param List<String> 26 */ 27 public List<String> AllExamp(int count) { 28 List<String> examList = new ArrayList<String>(); 29 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 30 String create = SubjectUtils.create(); 31 examList.add(create); 32 } 33 return examList; 34 } 35 36 /** 37 * 功能2.对生成的题目进行运算 38 * 39 * @return List<String> 40 */ 41 42 public List<String> result(List<String> list) { 43 List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<String>(); 44 for (String s : list) { 45 String newStr = s.substring(0, s.length() - 1); 46 String d = SubjectUtils.count(newStr); 47 resultList.add(d); 48 } 49 return resultList; 50 } 51 52 }
SubjectUtils类: Subject类的工具类
1 package utils; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 5 import javax.script.ScriptEngine; 6 import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager; 7 import javax.script.ScriptException; 8 9 import prctice.Subject; 10 11 /** 12 * Subject类所用的工具类 13 * 14 * @author Asus 15 * 16 */ 17 public class SubjectUtils { 18 private static String[] fu = { "+", "-", "*", "/" }; 19 20 // 方法一:随机产生运算符 21 public static String createFu() { 22 Random random = new Random(); 23 int index = random.nextInt(4); 24 return fu[index]; 25 } 26 27 // 方法二:用于产生四则三维运算题 28 public static String create() { 29 String ti = " "; 30 // 1. 先产生第一位数字 31 Random rand = new Random(); 32 int first = rand.nextInt(100) + 1; 33 // 2.产生第二位数字 34 int two = rand.nextInt(100) + 1; 35 // 3.产生第三位数字 36 int three = rand.nextInt(100) + 1; 37 // 4.产生运算符 38 String fu = SubjectUtils.createFu(); 39 String fu2 = SubjectUtils.createFu(); 40 if ((first < two) && fu.equals("-")) { 41 ti = two + fu + first + fu2 + three + "="; 42 } else if ((first < two) && fu.equals("/")) { 43 ti = two + fu + first + fu2 + three + "="; 44 } else { 45 ti = first + fu + two + fu2 + three + "="; 46 } 47 48 return ti; 49 50 } 51 52 // 方法三:对生成的题目进行计算,并以字符串的结果进行返回 53 public static String count(String s) { 54 ScriptEngine jse = new ScriptEngineManager().getEngineByName("JavaScript"); 55 Object o_res; 56 String res = null; 57 try { 58 o_res = jse.eval(s); 59 String string = o_res.toString(); 60 if (string.equals(".")) { 61 int indexOf = string.indexOf("."); 62 String res2 = string.substring(0, indexOf); 63 if (res2.equals(".")) { 64 int i2 = res.indexOf("."); 65 res = res2.substring(0, i2); 66 } else { 67 res = res2; 68 } 69 } else { 70 res = string; 71 } 72 } catch (ScriptException e1) { 73 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 74 e1.printStackTrace(); 75 } 76 return res; 77 } 78 79 }
Utils类: Main()方法的工具类
1 package utils; 2 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 /** 6 * main测试所用的工具类 7 * 8 * @author Asus 9 * 10 */ 11 public class Utils { 12 /** 13 * 功能 1 : 根据用户输入的数,创建对应长度的数组 14 */ 15 public static String[] retrunArray(int length) { 16 return new String[length]; 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * 功能2: 根据用户传入的答案数组,遍历输出 21 */ 22 public static void showArrayElement(String[] userArray) { 23 System.out.print("[ "); 24 for (int i = 0; i < userArray.length; i++) { 25 System.out.print(userArray[i]); 26 System.out.print(","); 27 } 28 System.out.print(" ]"); 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 功能3 : 根据用户传入的集合,进行遍历 33 */ 34 public static void showList(List<String> userList) { 35 for (String s : userList) { 36 System.out.println(s); 37 } 38 } 39 }
TestSubject类:测试Subject类中的方法
1 package test; 2 3 import java.util.List; 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 import prctice.Subject; 6 import utils.SubjectUtils; 7 8 /** 9 * 测试编写的四则运算程序 10 * 11 * @author Asus 12 * 13 */ 14 public class TestSubject { 15 private Subject subject = new Subject(); 16 17 @Test 18 // 测试运算符 19 public void testFu() { 20 String fu = SubjectUtils.createFu(); 21 String fu2 = SubjectUtils.createFu(); 22 System.out.println(fu + "->" + fu2); 23 } 24 25 // 测试生成表达式 26 @Test 27 public void testShow() { 28 List<String> show = subject.AllExamp(2); 29 for (String s : show) { 30 System.out.println(s); 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 // 测试计算方法 36 @Test 37 public void testCount() { 38 String count = SubjectUtils.count("45+(48/3)+7.8"); 39 System.out.println(count); 40 } 41 42 /** 43 * 测试两种方法: 1.生成题目的方法 2.计算结果的方法 44 */ 45 @Test 46 public void testResult() { 47 List<String> allExamp = subject.AllExamp(5); 48 System.out.println("-------------*生成的题目:*--------------"); 49 for (String s : allExamp) { 50 System.out.println(s); 51 } 52 System.out.println("对应的结果"); 53 List<String> result = subject.result(allExamp); 54 for (String i : result) { 55 System.out.println(i); 56 } 57 } 58 59 }
测试结果: 所有方法都已经通过了测试。
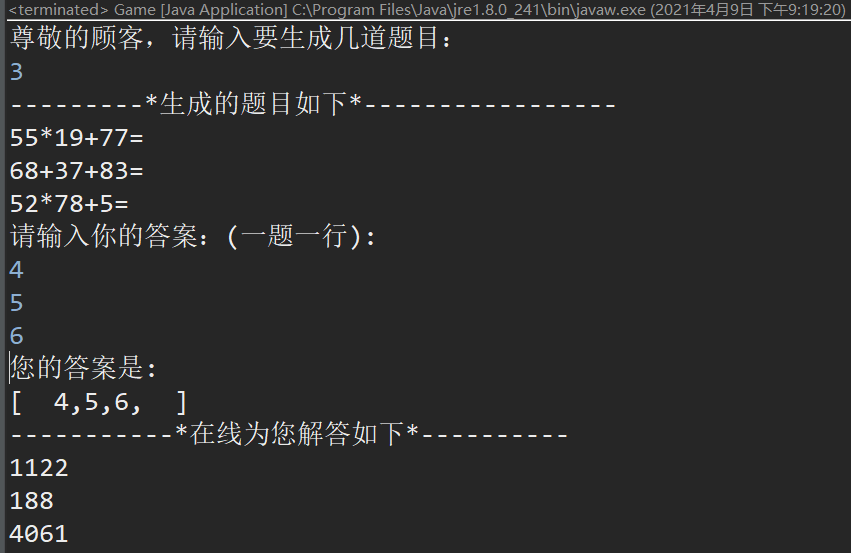
4.项目的运行结果:
5. PSP(个人软件开发流程)
|
PSP阶段 |
预估时间(分钟) |
实际时间(分钟) |
|
计划 |
15 |
20 |
|
明确需求和其他相关因素,估计每个阶段的时间和成本 |
15 |
20 |
|
开发 |
370 |
430 |
|
需求分析 |
20 |
25 |
|
生成设计文档 |
20 |
20 |
|
设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
25 |
|
代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
15 |
|
具体设计 |
20 |
25 |
|
具体编码 |
260 |
270 |
|
代码复审 |
20 |
25 |
|
测试(自测、修改代码、提交修改) |
20 |
25 |
|
报告 |
35 |
40 |
|
测试报告 |
10 |
10 |
|
计算工作量 |
10 |
10 |
|
事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
20 |
所查阅的资料:
1.指定范围的随机数如何生成
2.Object如何转为String类型
3.如何对以字符串形式的四则运算式子进行拆分计算
6. 小总结:
- 具体设计较浪费时间,不断进行了重构,理解了代码是由重构得来的。
- Java的好多知识都忘记了,需要查好多资料。eg:生成指定范围的字符串。
- 单元测试能降低集成测试的成本。我每写一个方法后,我都会对其进行测试,根据测试结果判断是哪出了问题,提高了解决问题的能力。
- 代码编写完成后,考虑可扩展问题,发现没有任何思路,还是自己学的少,学的浅。所以,自己更要对知识学的深入,要对其进行建构,多多扩展知识,还要多写代码,不能光学理论,实践最重要,能加深我们对知识的理解。
- 遇到一个项目时,只能想到一种做法,这说明自己设计模式没好好学,我将从现在起,去把设计模式的几个原则以及找几个喜欢的设计模式学习一下。
- 这一次是我自己独立完成一个项目,很有成就感,觉得态度决定一切,你只要想把一件事情干好,什么困难都不会难倒你。