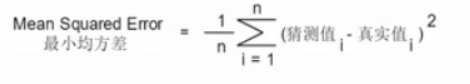问题1:扔下圆球的位置(feature特征变量)变化,最终掉落奖项(label结果标签)的变化
- feature ----输入
- f(x) ----模型,算法
- label ----输出
大量已知的数据,训练得出f(x)
- 一般的三步
- 收集数据feature,label
- 选择数据模型建立feature,label的关系--f(x)
- 根据选择的模型进行预测
- 人类建立模型:多次尝试增加经验提高预测到达公司的时间
- 机器学习:利用统计学,概率论,信息论的数学方法,利用已知的数据,创建一种模型,利用这种模型进行预测(高考与之类似)
- 机器学习经典模型:KNN模型(人以类聚,物以群分)
- 基本步骤
- 1.采集数据
- 2.计算实验数据与预测位置的距离
- 3.按照距离从小到大排序
- 4.选取最顶部的K条记录,得到最大概率的落点
- 5.预测预测位置的落点
- python实现
-
import numpy as np import collections as c # 1.采集数据 data = np.array([ [154, 1], [126, 2], [70, 2], [196, 2], [161, 2], [371, 4], ]) # feature,label feature = data[:, 0] label = data[:, -1] # 2.计算实验数据与预测点的距离 predictPoint = 200 distance = list(map(lambda x: abs(x - predictPoint), feature)) # 3.按照距离从小到大排序,排序下标 sortindex = np.argsort(distance) # 4.选取最顶部的K条记录,得到最大概率的落点,假设K=3 sortedlabel = label[sortindex] k = 3 # 预测结果[(结果,次数)] # 5.预测预测位置的落点 predictlabel = c.Counter(sortedlabel[0:k]).most_common(1)[0][0] print(predictlabel)
-
- 代码封装
-
import numpy as np import collections as c # 代码封装 def knn(k, predictPoint, feature, label): distance = list(map(lambda x: abs(x - predictPoint), feature)) sortindex = np.argsort(distance) sortedlabel = label[sortindex] predictlabel = c.Counter(sortedlabel[0:k]).most_common(1)[0][0] return predictlabel if __name__ == '__main__': data = np.array([ [154, 1], [126, 2], [70, 2], [196, 2], [161, 2], [371, 4], ]) # feature,label feature = data[:, 0] label = data[:, -1] k = 3 predictPoint = 200 res = knn(k, predictPoint, feature, label) print(res)
-
- 实际数据验证
- 数据集https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rw5aFlVzZb6SBdY09Rckhg
-
import numpy as np import collections as c # 代码封装 def knn(k, predictPoint, feature, label): distance = list(map(lambda x: abs(x - predictPoint), feature)) sortindex = np.argsort(distance) sortedlabel = label[sortindex] predictlabel = c.Counter(sortedlabel[0:k]).most_common(1)[0][0] return predictlabel if __name__ == '__main__': data = np.loadtxt("数据集/data0.csv", delimiter=",") # feature,label feature = data[:, 0] label = data[:, -1] k = 3 predictPoint = 300 res = knn(k, predictPoint, feature, label) print(res) - 打散数据得到训练集和测试集
- import numpy as np
-
import collections as c # 代码封装 def knn(k, predictPoint, feature, label): distance = list(map(lambda x: abs(x - predictPoint), feature)) sortindex = np.argsort(distance) sortedlabel = label[sortindex] predictlabel = c.Counter(sortedlabel[0:k]).most_common(1)[0][0] return predictlabel if __name__ == '__main__': data = np.loadtxt("数据集/data0.csv", delimiter=",") # 打散数据 np.random.shuffle(data) # 训练90% traindata = data[100:-1] # 测试10% testdata = data[0:100] # 保存训练数据,测试数据 np.savetxt("data0-test.csv", testdata, delimiter=",", fmt="%d") np.savetxt("data0-train.csv", traindata, delimiter=",", fmt="%d") traindata = np.loadtxt("data0-train.csv", delimiter=",") # feature,label feature = traindata[:, 0] label = traindata[:, -1] max_accuracy = 0 max_k = [] # 预测点,来自测试数据的每一条记录 testdata = np.loadtxt("data0-test.csv", delimiter=",") for k in range(1,100): count = 0 for item in testdata: predict = knn(k, item[0], feature, label) real = item[1] if predict == real: count += 1 accuracy = count * 100.0 / len(testdata) if accuracy >= max_accuracy: max_accuracy = accuracy max_k.append(k) print("k = {},准确率:{}%".format(k,count*100.0/len(testdata))) print(set(max_k)) -
多维数据的距离的选取
-
欧式距离即可
-
- 预测不是很准确
- 1.模型的参数选择不够好,调参---调参工程师
- K选择太小,噪音干扰太明显
- K选择太大,其他类型的会涵盖
- K值的评价标准
- 训练集trainData---得到模型
- 测试集testData---验证模型
- 经验:K一般选取样本集开平方
- 2.影响因子不够多
- 增加数据的维度
- 球的颜色导致弹性不同
- 特殊数据的导入
-
import numpy as np def colornum(str): dict = {"红":0.50,"黄":0.51,"蓝":0.52,"绿":0.53,"紫":0.54,"粉":0.55} return dict[str] data = np.loadtxt('数据集/data1.csv',delimiter=",",converters={1:colornum},encoding="gbk") print(data)
-
- 增加数据的维度
- 3.样本数据量不够
- 4.选择的模型不够好,选择其他机器学习的模型
- 1.模型的参数选择不够好,调参---调参工程师
- 基本步骤
- 线性回归
- 是一种总结规律,总结模型的解决方法。不需要全数据集
- 损失函数:评测算法的好坏
- 最小均方差
- 最小均方差越接近0越好
- 步骤
- 1.随机选取m和b
- 2.分别计算m和b的偏导数
- 3.如果m和b的偏导都很小,就成功
- 4.根据学习速率,计算出修改的值
- 5.b和m分别减去要修改的值
- python实import numpy as np
-
# data = np.array([ # [80, 200], # [95, 230], # [104, 245], # [112, 274], # [125, 259], # [135, 262], # ]) data = np.loadtxt('数据集/cars.csv', delimiter=",", skiprows=1, usecols=(4, 1)) m = 1 b = 1 xarray = data[:, 0] yreal = data[:, -1] learningrate = 0.00001 # 梯度下降 def grandentdecent(): # 求斜率 bslop = 0 for index, x in enumerate(xarray): bslop = bslop + m * x + b - yreal[index] bslop = bslop * 2 / len(xarray) # print("对b求导的斜率={}".format(bslop)) mslop = 0 for index, x in enumerate(xarray): mslop = mslop + (m * x + b - yreal[index]) * x mslop = mslop * 2 / len(xarray) # print("对m求导的斜率={}".format(mslop)) return (bslop, mslop) def train(): for i in range(1, 10000000): bslop, mslop = grandentdecent() global m m = m - mslop * learningrate global b b = b - bslop * learningrate if (abs(mslop) < 0.5 and abs(bslop) < 0.5): break print("m={},b={}".format(m, b)) if __name__ == '__main__': train() # 用训练集得到公式 # 用测试集验证正确率 -
import numpy as np # 面积,房价 data = np.array([ [80, 200], [95, 230], [104, 245], [112, 274], [125, 259], [135, 262], ]) # 1.feature,label,axis=1保留原始维度 feature = np.expand_dims(data[:, 0], axis=1) # feature = data[:,0:1] label = np.expand_dims(data[:, -1], axis=1) # 2.weight m = 1 b = 1 weight = np.array([ [m], [b], ]) # 3.feature*weight,需要在feature后面补一列1---每一行代表mx+b feature = np.append(feature, np.ones(shape=(6, 1)), axis=1) print(feature) # 4.feature*weight - label 得到差值difference difference = np.dot(feature, weight) - label # 5.feature^T*difference/n 先将feature转置在乘,得到对B和M的偏导bslop,mslop bmslop = np.dot(feature.T, difference) bmslop = bmslop*2/len(feature) # 6.仅需使其数字接近0即可
-
图形变化
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import math points = np.array([ [0, 0], [0, 5], [3, 5], [3, 4], [1, 4], [1, 3], [2, 3], [2, 2], [1, 2], [1, 0], [0, 0], ]) plt.plot(points[:, 0], points[:, 1]) for i in range(1,13): # # 1.平移 # matrix = np.array([0.5*i, 0]) # newpoints = points + matrix # 2.旋转 # matrix = np.array([ # [math.cos(math.pi/6),-math.sin(math.pi/6)], # [math.sin(math.pi/6),math.cos(math.pi/6)], # ]) # points = np.dot(points,matrix) # 3.缩放 matrix = np.array([ [1.05,0], [0,1.05], ]) points = np.dot(points, matrix) plt.plot(points[:, 0], points[:, 1]) plt.xlim(-10,10) plt.ylim(-10,10) plt.show()
-
-
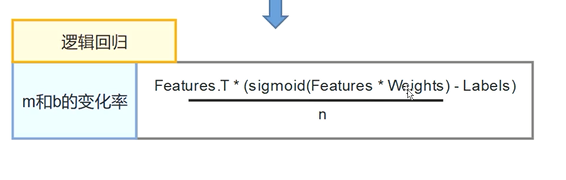
逻辑回归
-
将线性回归置于e的指数即可
-
e的求法
-
import math n = 1000000 e = math.pow((1+1.0/n),n) print(e)
-
-
激活函数,sigmoid
-
-
逻辑回归实现梯度下降
-
import numpy as np data = np.array([ [5, 0], [15, 0], [25, 1], [35, 1], [45, 1], [55, 1], ]) # 1.feature,label,axis=1保留原始维度 feature = np.expand_dims(data[:, 0], axis=1) # feature = data[:,0:1] label = np.expand_dims(data[:, -1], axis=1) learingrate = 0.00001 m = 1 b = 1 weight = np.array([ [m], [b], ]) feature = np.append(feature, np.ones(shape=(6, 1)), axis=1) def gradentDecent(): predict = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(feature, weight))) difference = predict - label bmslop = np.dot(feature.T, difference) bmslop = bmslop / len(feature) return bmslop def train(): for i in range(1, 10): slop = gradentDecent() global weight weight = weight - learingrate * slop print(slop) if __name__ == '__main__': train()
-
-
-
-
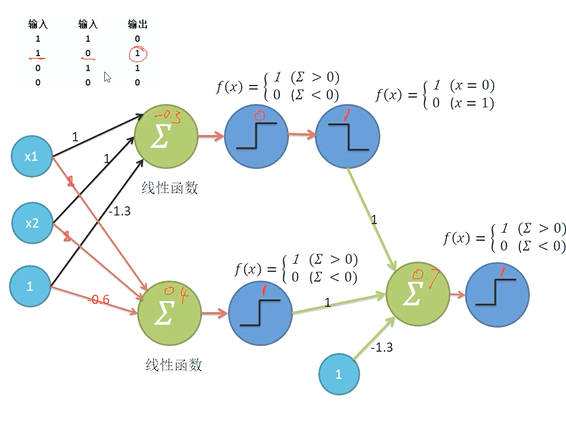
神经网络:主要用于分类和聚类
-
用一条线划分两种类型的属性---分割线计算
-
高维空间,只是变成了矩阵相乘---用面分割
-
神经元=激活函数=f(x)
-
手工拟合OR,AND,XOR
-
-
感知机:梯度下降实现
-
随便划线,感知点的情绪(- -),向着开心的方向进行移动
-
调整线的斜率,使结果更好
-
梯度下降:连续可导,可以求斜率
-
MSE最小均方差
-
Cross-entropy交叉熵
-
p(red)=p(blue)
-
sigmoid函数处理线性函数,
-
-
-
- 机器学习经典模型:KNN模型(人以类聚,物以群分)
-
聚类算法
-
相似的事务归为一类-标签化---物以类聚
- k-means
-
k:中心点的个数,质心
-
means:求平均
-
不断迭代,更新质心
-
步骤
-
1.选择聚类的个数K
-
2.生成K个聚类中心点
-
3.计算所有样本点到聚类中心点的距离
-
4.更新质心(求聚类后的x,y平均值),迭代聚类
-
5.重复4直到满足收敛要求
-
-
-
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans, KMeans # 测量 from sklearn import metrics # 球状簇 from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs # 生成数据集,样本数=1000,特征数=2,中心=以哪些点为中心生成样本点,标准差=围绕中心的标准差,随机状态值=每次运行生成散点图一致 x, y = make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=([-1, -1], [0, 0], [1, 1], [2, 2]), cluster_std=(0.4, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2), random_state=9) # 生成散点图 plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], marker="o") plt.show() # 可视化 for index, k in enumerate((2, 3, 4, 5)): plt.subplot(2, 2, index + 1) # 随机选取200个点,分别用特征2,3,4,5作为特征值,进行K——means y_pred = MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=k, batch_size=200, random_state=9).fit_predict(x) # 聚类效果评分 score = metrics.calinski_harabaz_score(x, y_pred) plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y_pred) plt.text(.99,.01, ('k=%d,score:%.2f' % (k, score)), fontsize=10, transform=plt.gca().transAxes, horizontalalignment="right") plt.show()
-
-
-
-
-
完整的预处理例子
-
''' 完整的机器学习流程 ''' # 1.导入库 import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import numpy.random as nr import math from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans, KMeans # 测量 from sklearn import metrics # 球状簇 from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs # 2.观察数据集 # 路径带中文,前面先用open打开 auto_prices = pd.read_csv(open('工业汽车数据集应用实践/Automobile price data _Raw_.csv')) # print(auto_prices.head(20)) # 3.数据的预处理,重新编码 auto_prices.columns = (str.replace('-', '_') for str in auto_prices.columns) # 4.处理缺失值 # 找出所有缺失值 (auto_prices.astype(np.object) == '?').any() for col in auto_prices.columns: if auto_prices[col].dtypes == object: count = 0 count = [count + 1 for x in auto_prices[col] if x == '?'] print(col + ' ' + str(sum(count))) # 处理缺失值 auto_prices.drop('normalized_losses', axis=1, inplace=True) cols = ['price', 'bore', 'stroke', 'horsepower', 'peak_rpm'] for column in cols: auto_prices.loc[auto_prices[column] == '?', column] = np.nan auto_prices.dropna(axis=0, inplace=True) print(auto_prices.shape) # 5.转换列数据类型 for column in cols: auto_prices[column] = pd.to_numeric(auto_prices[column]) print(auto_prices[cols].dtypes) # 6.特征工程 # 汇总变量类别,转换ln,交互的变量合并 # 聚合特征变量 print(auto_prices['num_of_cylinders'].value_counts()) # print(auto_prices.columns) cylinder_categories = { 'three': 'three_four', 'four': 'three_four', 'five': 'five_six', 'six': 'five_six', 'eight': 'eight_twelve', 'twelve': 'eight_twelve', } auto_prices['num_of_cylinders'] = [cylinder_categories[x] for x in auto_prices['num_of_cylinders']] print(auto_prices['num_of_cylinders'].value_counts()) # 7.箱型图 # 哪个特征影响价格走向 def plot_box(auto_price, col, col_y='price'): sns.set_style('whitegrid') sns.boxplot(col, col_y, data=auto_price) plt.xlabel(col) plt.ylabel(col_y) plt.show() plot_box(auto_prices, 'num_of_cylinders') print(auto_prices['body_style'].value_counts()) body_cats = { 'sedan': 'sedan', 'hatchback': 'hatchback', 'wagon': 'wagon', 'hardtop': 'hardtop_convert', 'convertible': 'hardtop_convert', } auto_prices['body_style'] = [body_cats[x] for x in auto_prices['body_style']] print(auto_prices['body_style'].value_counts()) # 8.特征图 # 哪个特征有别于其他特征 def plot_box(auto_price, col, col_y='price'): sns.set_style('whitegrid') sns.boxplot(col, col_y, data=auto_price) plt.xlabel(col) plt.ylabel(col_y) plt.show() plot_box(auto_prices, 'body_style') # 9.转换变量 def hist_plot(vals, lab): sns.distplot(vals) plt.title('Histogram of' + lab) plt.xlabel('value') plt.ylabel('Density') plt.show() hist_plot(auto_prices['price'], 'prices') # 对数转换 auto_prices['log_price'] = np.log(auto_prices['price']) hist_plot(auto_prices['log_price'], 'log_price') # 10.可视化 # 看价格与其他特征是否存在线性或非线性的关系 def plot_scatter_shape(auto_prices, cols, shape_col='fuel_type', col_y='log_price', alpha=0.2): shapes = ['+', 'o', 's', 'x', '^'] unique_cats = auto_prices[shape_col].unique() for col in cols: sns.set_style('whitegrid') for i, cat in enumerate(unique_cats): temp = auto_prices[auto_prices[shape_col] == cat] sns.regplot(col, col_y, data=temp, marker=shapes[i], label=cat, scatter_kws={'alpha': alpha}, fit_reg=False, color='blue') plt.title('scatter plot of' + col_y + 'vs.' + col) plt.xlabel(col) plt.ylabel(col_y) plt.legend() plt.show() num_cols = ['curb_weight', 'engine_size', 'horsepower', 'city_mpg'] plot_scatter_shape(auto_prices, num_cols)
-
-
-
算法效果的衡量标准
-
SSE(Sum of Squear due to Error)误差平方和
- 每个点跟质心的距离
-
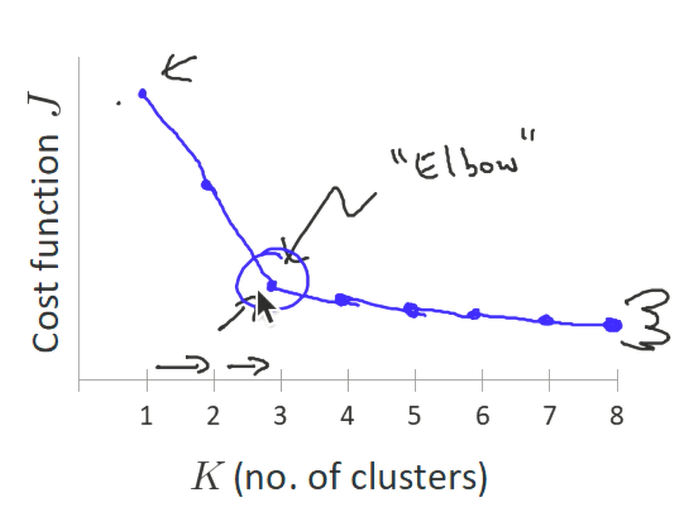
K值确定:Elbow method 肘方法
- SSE跟聚类个数画图
- 找出拐点来确定聚类数
- 轮廓系数法(Silhouette Coefficient)
- 根据轮廓边缘的变化感知聚类的凝聚度和分离度

-
CH(Calinski-Harabasz)
-
数据类别距离平方和越小越好,类别之间平方和越大越好
-

-
-
-