知识点:RandomAccessFile (随机访问文件)类
(一)描述
前一篇博客中https://www.cnblogs.com/shuaifing/p/11490160.html,主要描述FileInputStream/FileOutPutStream、FileReader/FileWriter、BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader/BufferedWriter的使用,文件时,都是从文件的开头写入数据,第二次执行写操作时,会覆盖文件之前的内容,那么如果我们想,在访问一个文件时,在某个指定的位置写入数据,可以使用RandomAccessFile(随机访问文件)类。
RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode):name为文件名,model操作模式
“r” : 只读
“rw” : 读写,支持文件读取或者写入,文件不存在,创建
“rws” : s为synchronous 同步 (每次同步更新到潜在的设备中去),更新文件内容而且更新元数据(metadata),因此至少要求1次低级别的I/O操作
“rwd” : 每次同步更新到潜在的设备中去
(二)实例
(1)在文本的一行中的,某个位置插入字符串
文本文档test6.txt

//文本文档,中hello后面加上ab字符串
@Test
public void testRandomAccessFileInsertLine(){
RandomAccessFile raf2=null;
try {
raf2=new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/test/io/test6.txt"),"rw");
//插入 ab
raf2.seek(5);//指针指向5的位置
String str= raf2.readLine();//读取文本的5位置开始第一行数据,指针指向第一行数据的末尾
raf2.seek(5);//指针从新指向5的位置
raf2.write("ab".getBytes());//在5的位置写入ab字符串
raf2.write(str.getBytes());//在ab字符串后面写入之前读取的第一行后面的数据
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(raf2!=null) {
try {
raf2.close();//关闭流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
结果:

如果文本中有多行数据,则会显现问题如下
原文本内容:

执行代码后:
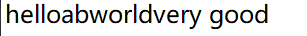
(2)在文本文档中的,任意一行的某个位置插入字符串
//文本文档,任意一行的某个位置插入字符串
@Test
public void testRandomAccessFileInsertAll(){
RandomAccessFile raf2=null;
try {
raf2=new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/test/io/test6.txt"),"rw");
//插入 ab
raf2.seek(5);//指针指向位置5
byte[] b=new byte[20];
int len;
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();//指针5位置后面的数据存放到 sb中
if((len = raf2.read(b))!=-1){
sb.append(new String(b,0,len));
}
raf2.seek(5);//指针从新指向5的位置
raf2.write("ab".getBytes());//在5的位置写入ab字符串
raf2.write(sb.toString().getBytes());//将存放到sb中的数据写入文本文件中
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(raf2!=null) {
try {
raf2.close();//关闭流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
效果:

(3)文件复制
//文件读写
@Test
public void testRandomAccessFile1(){
RandomAccessFile raf1=null;
RandomAccessFile raf2=null;
try {
raf1=new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/test/io/test.txt"),"r");
raf2=new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/test/io/test6.txt"),"rw");
byte[] b=new byte[10];
int len;
while((len=raf1.read(b))!=-1){
raf2.write(b,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(raf2!=null) {
try {
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf1!=null) {
try {
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}