几种不同类型的输出对齐总结:
先看效果:
采用.format打印输出时,可以定义输出字符串的输出宽度,在 ':' 后传入一个整数, 可以保证该域至少有这么多的宽度。 用于美化表格时很有用。
>>> table = {'Google': 1, 'Runoob': 2, 'Taobao': 3}
>>> for name, number in table.items():
... print('{0:10} ==> {1:10d}'.format(name, number))
...
Runoob ==> 2
Taobao ==> 3
Google ==> 1
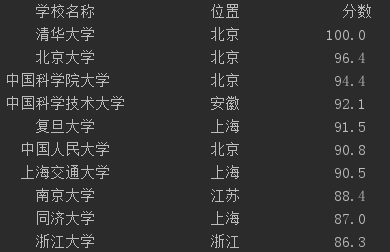
但是在打印多组中文的时候,不是每组中文的字符串宽度都一样,当中文字符宽度不够的时候,程序采用西文空格填充,中西文空格宽度不一样,就会导致输出文本不整齐
如下,打印中国高校排名。
tplt = "{0:^10} {1:^10} {2:^10}" print(tplt.format("学校名称", "位置", "分数")) for i in range(num): u = ulist[i] print(tplt.format(u[0], u[1], u[2]))
把字符串宽度都定义为10,但是中文本身的宽度都不到10所以会填充西文空格,就会导致字符的实际宽度长短不一。
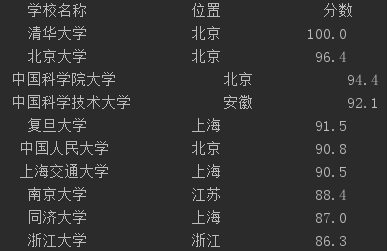
解决方法:宽度不够时采用中文空格填充
中文空格的编码为chr(12288)
tplt = "{0:{3}^10} {1:{3}^10} {2:^10}" print(tplt.format("学校名称", "位置", "分数", chr(12288))) for i in range(num): u = ulist[i] print(tplt.format(u[0], u[1], u[2], chr(12288)))
用0填充:Python zfill()方法
描述
Python zfill() 方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。
语法
zfill()方法语法:
str.zfill(width)
参数
-
width -- 指定字符串的长度。原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。
返回值
返回指定长度的字符串。
实例
以下实例展示了 zfill()函数的使用方法:
#!/usr/bin/python str = "this is string example....wow!!!"; print str.zfill(40); print str.zfill(50);
以上实例输出结果如下:
00000000this is string example....wow!!! 000000000000000000this is string example....wow!!!
如果不想用0填充:
使用
Str.rjust() 右对齐
或者
Str.ljust() 左对齐
或者
Str.center() 居中的方法有序列的输出。
>>> dic = { "name": "botoo", "url": "http://www.123.com", "page": "88", "isNonProfit": "true", "address": "china", } >>> >>> d = max(map(len, dic.keys())) #获取key的最大值 >>> >>> for k in dic: print(k.ljust(d),":",dic[k]) name : botoo url : http://www.123.com page : 88 isNonProfit : true address : china >>> for k in dic: print(k.rjust(d),":",dic[k]) name : botoo url : http://www.123.com page : 88 isNonProfit : true address : china >>> for k in dic: print(k.center(d),":",dic[k]) name : botoo url : http://www.123.com page : 88 isNonProfit : true address : china >>>
>>> s = "adc" >>> s.ljust(20,"+") 'adc+++++++++++++++++' >>> s.rjust(20) ' adc' >>> s.center(20,"+") '++++++++adc+++++++++' >>>
"+"可以换成自己想填充的字符。