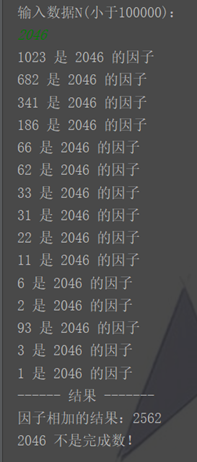
1. 代码
import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class 线程完全数 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // 线程池 System.out.println("输入数据N(小于100000):"); int N = in.nextInt(); int sum = 0; Divisor p[] = new Divisor[100000]; for (int i = N-1; i > 0; i--) { p[i] = new Divisor(i, N); exec.execute(p[i]); // start } exec.shutdown(); // 不在生成新的线程 while(true) { if (exec.isTerminated()) { // 判断所有线程是否结束 for (int i = 0; i < Global.index; i++) { sum += Global.buffer[i]; } System.out.println("------ 结果 -------"); System.out.println("因子相加的结果:" + sum); if (sum == N) { System.out.println(N + " 是完全数!"); } else System.out.println(N + " 不是完成数!"); break; } } } } class Global{ static int index = 0; static syn empty = new syn(3); // 信号量为3 static int[] buffer = new int[10000]; // 公共缓冲区 } class syn{ int count = 1; syn(){} syn(int count){this.count = count;} public synchronized void Wait(){ // P操作 count--; if(count < 0) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public synchronized void Singnal(){ // V操作 count++; if(count <= 0) this.notify(); } } class Divisor extends Thread{ public int divisor = 0, N; Divisor(int divisor, int N){ this.divisor = divisor; this.N = N; } public void run(){ Global.empty.Wait(); // 临界区 if(N % divisor == 0){ System.out.println(divisor + " 是 " + N + " 的因子"); Global.buffer[Global.index++] = divisor; } // try{ // Thread.sleep(1); // 让效果明显一点,会慢 // }catch (InterruptedException d){ // d.printStackTrace(); // } // 结束临界区 Global.empty.Singnal(); } }
2. 结果: