一、前言
最近有个需求,需要在js中调用java,这样能避免更新java,从而实现代码的热更新。
于是想到用 Nashorn JavaScript 引擎。
二、概述
通过 JDK 8 的 Nashorn JavaScript 引擎 ,可以很方便的实现在java中调用js,以及在js中调用java。
三、简单示例
1.java中调用js

@Test public void testDemo1() throws ScriptException { //1.创建引擎 ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager(); ScriptEngine engine = manager.getEngineByName("JavaScript"); //2.要执行的脚本 String script = "var sum = n1 + n2;print(msg + ' n1= '+ n1 + '; n2 ='+ n2 + '; sum=' + sum);"; manager.put("n1", 1); //3.执行脚本 //3.1 直接传参,并执行脚本 engine.put("n2", 2); //使用put(key,value)直接传参到到脚本中,在脚本中通过key来取值 engine.put("msg", "a string"); engine.eval(script); //3.2 通过绑定传参,并执行脚本 Bindings bindings = engine.createBindings(); bindings.put("n2", 3); // AbstractScriptEngine.put(key,value)的内部实现就是使用的Bindings.put(key,value) bindings.put("msg", "another string"); engine.eval(script, bindings); //3.3 通过上下文来传参,并执行脚本 ScriptContext ctx = new SimpleScriptContext(); Bindings ctxGlobalBindings = engine.createBindings(); ctx.setBindings(ctxGlobalBindings, GLOBAL_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("n1", 4, GLOBAL_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("n2", 5, ENGINE_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("msg", "ScriptContext:", ENGINE_SCOPE); engine.eval(script, ctx); //使用指定上下文来执行脚本 engine.eval(script); //使用默认上下文执行脚本 }
2.js中调用java
HelloWorld.java

public class HelloWorld { public void sayHello(){ System.out.println("hello"); } }
测试用例:

@Test public void test2() throws ScriptException { //1.创建引擎 ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager(); ScriptEngine engine = manager.getEngineByName("JavaScript"); //2.设置要执行的脚本 String script="$hello.sayHello();"; //3.传参,并执行脚本 engine.put("$hello", new HelloWorld()); engine.eval(script); //使用指定上下文来执行脚本 }
3.通过js实现java接口
四、脚本引擎类结构图
脚本引擎相关源码的类和接口如下:
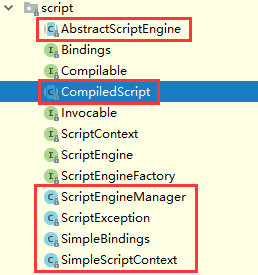
先关注这几个基本实现类
1. ScriptEngineManager
源码如下:

/* * Copyright (c) 2005, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * */ package javax.script; import java.util.*; import java.security.*; import java.util.ServiceLoader; import java.util.ServiceConfigurationError; /** * The <code>ScriptEngineManager</code> implements a discovery and instantiation * mechanism for <code>ScriptEngine</code> classes and also maintains a * collection of key/value pairs storing state shared by all engines created * by the Manager. This class uses the <a href="../../../technotes/guides/jar/jar.html#Service%20Provider">service provider</a> mechanism to enumerate all the * implementations of <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>. <br><br> * The <code>ScriptEngineManager</code> provides a method to return a list of all these factories * as well as utility methods which look up factories on the basis of language name, file extension * and mime type. * <p> * The <code>Bindings</code> of key/value pairs, referred to as the "Global Scope" maintained * by the manager is available to all instances of <code>ScriptEngine</code> created * by the <code>ScriptEngineManager</code>. The values in the <code>Bindings</code> are * generally exposed in all scripts. * * @author Mike Grogan * @author A. Sundararajan * @since 1.6 */ public class ScriptEngineManager { private static final boolean DEBUG = false; /** * The effect of calling this constructor is the same as calling * <code>ScriptEngineManager(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader())</code>. * * @see java.lang.Thread#getContextClassLoader */ public ScriptEngineManager() { ClassLoader ctxtLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); init(ctxtLoader); } /** * This constructor loads the implementations of * <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> visible to the given * <code>ClassLoader</code> using the <a href="../../../technotes/guides/jar/jar.html#Service%20Provider">service provider</a> mechanism.<br><br> * If loader is <code>null</code>, the script engine factories that are * bundled with the platform and that are in the usual extension * directories (installed extensions) are loaded. <br><br> * * @param loader ClassLoader used to discover script engine factories. */ public ScriptEngineManager(ClassLoader loader) { init(loader); } private void init(final ClassLoader loader) { globalScope = new SimpleBindings(); engineSpis = new HashSet<ScriptEngineFactory>(); nameAssociations = new HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory>(); extensionAssociations = new HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory>(); mimeTypeAssociations = new HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory>(); initEngines(loader); } private ServiceLoader<ScriptEngineFactory> getServiceLoader(final ClassLoader loader) { if (loader != null) { return ServiceLoader.load(ScriptEngineFactory.class, loader); } else { return ServiceLoader.loadInstalled(ScriptEngineFactory.class); } } private void initEngines(final ClassLoader loader) { Iterator<ScriptEngineFactory> itr = null; try { ServiceLoader<ScriptEngineFactory> sl = AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedAction<ServiceLoader<ScriptEngineFactory>>() { @Override public ServiceLoader<ScriptEngineFactory> run() { return getServiceLoader(loader); } }); itr = sl.iterator(); } catch (ServiceConfigurationError err) { System.err.println("Can't find ScriptEngineFactory providers: " + err.getMessage()); if (DEBUG) { err.printStackTrace(); } // do not throw any exception here. user may want to // manage his/her own factories using this manager // by explicit registratation (by registerXXX) methods. return; } try { while (itr.hasNext()) { try { ScriptEngineFactory fact = itr.next(); engineSpis.add(fact); } catch (ServiceConfigurationError err) { System.err.println("ScriptEngineManager providers.next(): " + err.getMessage()); if (DEBUG) { err.printStackTrace(); } // one factory failed, but check other factories... continue; } } } catch (ServiceConfigurationError err) { System.err.println("ScriptEngineManager providers.hasNext(): " + err.getMessage()); if (DEBUG) { err.printStackTrace(); } // do not throw any exception here. user may want to // manage his/her own factories using this manager // by explicit registratation (by registerXXX) methods. return; } } /** * <code>setBindings</code> stores the specified <code>Bindings</code> * in the <code>globalScope</code> field. ScriptEngineManager sets this * <code>Bindings</code> as global bindings for <code>ScriptEngine</code> * objects created by it. * * @param bindings The specified <code>Bindings</code> * @throws IllegalArgumentException if bindings is null. */ public void setBindings(Bindings bindings) { if (bindings == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Global scope cannot be null."); } globalScope = bindings; } /** * <code>getBindings</code> returns the value of the <code>globalScope</code> field. * ScriptEngineManager sets this <code>Bindings</code> as global bindings for * <code>ScriptEngine</code> objects created by it. * * @return The globalScope field. */ public Bindings getBindings() { return globalScope; } /** * Sets the specified key/value pair in the Global Scope. * @param key Key to set * @param value Value to set. * @throws NullPointerException if key is null. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is empty string. */ public void put(String key, Object value) { globalScope.put(key, value); } /** * Gets the value for the specified key in the Global Scope * @param key The key whose value is to be returned. * @return The value for the specified key. */ public Object get(String key) { return globalScope.get(key); } /** * Looks up and creates a <code>ScriptEngine</code> for a given name. * The algorithm first searches for a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> that has been * registered as a handler for the specified name using the <code>registerEngineName</code> * method. * <br><br> If one is not found, it searches the set of <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> instances * stored by the constructor for one with the specified name. If a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> * is found by either method, it is used to create instance of <code>ScriptEngine</code>. * @param shortName The short name of the <code>ScriptEngine</code> implementation. * returned by the <code>getNames</code> method of its <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>. * @return A <code>ScriptEngine</code> created by the factory located in the search. Returns null * if no such factory was found. The <code>ScriptEngineManager</code> sets its own <code>globalScope</code> * <code>Bindings</code> as the <code>GLOBAL_SCOPE</code> <code>Bindings</code> of the newly * created <code>ScriptEngine</code>. * @throws NullPointerException if shortName is null. */ public ScriptEngine getEngineByName(String shortName) { if (shortName == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //look for registered name first Object obj; if (null != (obj = nameAssociations.get(shortName))) { ScriptEngineFactory spi = (ScriptEngineFactory)obj; try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } for (ScriptEngineFactory spi : engineSpis) { List<String> names = null; try { names = spi.getNames(); } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } if (names != null) { for (String name : names) { if (shortName.equals(name)) { try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } } } } return null; } /** * Look up and create a <code>ScriptEngine</code> for a given extension. The algorithm * used by <code>getEngineByName</code> is used except that the search starts * by looking for a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> registered to handle the * given extension using <code>registerEngineExtension</code>. * @param extension The given extension * @return The engine to handle scripts with this extension. Returns <code>null</code> * if not found. * @throws NullPointerException if extension is null. */ public ScriptEngine getEngineByExtension(String extension) { if (extension == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //look for registered extension first Object obj; if (null != (obj = extensionAssociations.get(extension))) { ScriptEngineFactory spi = (ScriptEngineFactory)obj; try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } for (ScriptEngineFactory spi : engineSpis) { List<String> exts = null; try { exts = spi.getExtensions(); } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } if (exts == null) continue; for (String ext : exts) { if (extension.equals(ext)) { try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } } } return null; } /** * Look up and create a <code>ScriptEngine</code> for a given mime type. The algorithm * used by <code>getEngineByName</code> is used except that the search starts * by looking for a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> registered to handle the * given mime type using <code>registerEngineMimeType</code>. * @param mimeType The given mime type * @return The engine to handle scripts with this mime type. Returns <code>null</code> * if not found. * @throws NullPointerException if mimeType is null. */ public ScriptEngine getEngineByMimeType(String mimeType) { if (mimeType == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //look for registered types first Object obj; if (null != (obj = mimeTypeAssociations.get(mimeType))) { ScriptEngineFactory spi = (ScriptEngineFactory)obj; try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } for (ScriptEngineFactory spi : engineSpis) { List<String> types = null; try { types = spi.getMimeTypes(); } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } if (types == null) continue; for (String type : types) { if (mimeType.equals(type)) { try { ScriptEngine engine = spi.getScriptEngine(); engine.setBindings(getBindings(), ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE); return engine; } catch (Exception exp) { if (DEBUG) exp.printStackTrace(); } } } } return null; } /** * Returns a list whose elements are instances of all the <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> classes * found by the discovery mechanism. * @return List of all discovered <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>s. */ public List<ScriptEngineFactory> getEngineFactories() { List<ScriptEngineFactory> res = new ArrayList<ScriptEngineFactory>(engineSpis.size()); for (ScriptEngineFactory spi : engineSpis) { res.add(spi); } return Collections.unmodifiableList(res); } /** * Registers a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> to handle a language * name. Overrides any such association found using the Discovery mechanism. * @param name The name to be associated with the <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>. * @param factory The class to associate with the given name. * @throws NullPointerException if any of the parameters is null. */ public void registerEngineName(String name, ScriptEngineFactory factory) { if (name == null || factory == null) throw new NullPointerException(); nameAssociations.put(name, factory); } /** * Registers a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> to handle a mime type. * Overrides any such association found using the Discovery mechanism. * * @param type The mime type to be associated with the * <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>. * * @param factory The class to associate with the given mime type. * @throws NullPointerException if any of the parameters is null. */ public void registerEngineMimeType(String type, ScriptEngineFactory factory) { if (type == null || factory == null) throw new NullPointerException(); mimeTypeAssociations.put(type, factory); } /** * Registers a <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code> to handle an extension. * Overrides any such association found using the Discovery mechanism. * * @param extension The extension type to be associated with the * <code>ScriptEngineFactory</code>. * @param factory The class to associate with the given extension. * @throws NullPointerException if any of the parameters is null. */ public void registerEngineExtension(String extension, ScriptEngineFactory factory) { if (extension == null || factory == null) throw new NullPointerException(); extensionAssociations.put(extension, factory); } /** Set of script engine factories discovered. */ private HashSet<ScriptEngineFactory> engineSpis; /** Map of engine name to script engine factory. */ private HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory> nameAssociations; /** Map of script file extension to script engine factory. */ private HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory> extensionAssociations; /** Map of script script MIME type to script engine factory. */ private HashMap<String, ScriptEngineFactory> mimeTypeAssociations; /** Global bindings associated with script engines created by this manager. */ private Bindings globalScope; }
此类主要有三个作用:
(1)设置全局变量
(2)获取脚本引擎
(3)注册脚本引擎工厂
(1)设置全局变量
/** Global bindings associated with script engines created by this manager. */ private Bindings globalScope; public void put(String key, Object value) { globalScope.put(key, value); } public Object get(String key) { return globalScope.get(key); }
可以看到,通过 ScriptEngineManager 设置的变量都绑定到了 globalScope 这个绑定中。
这里并不能说明这个一个全局绑定。
再往下看:
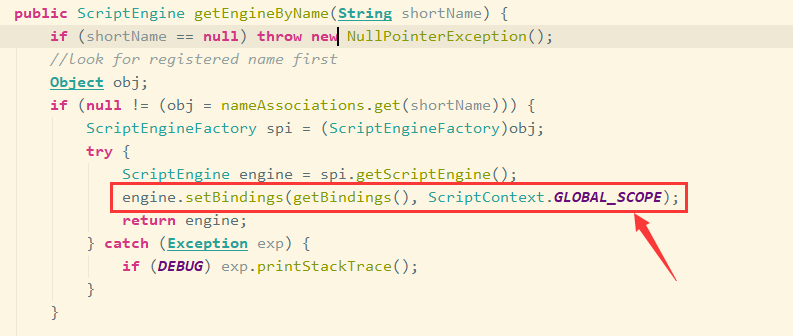
此处设置了绑定的作用域为全局。因此 可通过 ScriptEngineManager 设置全局变量
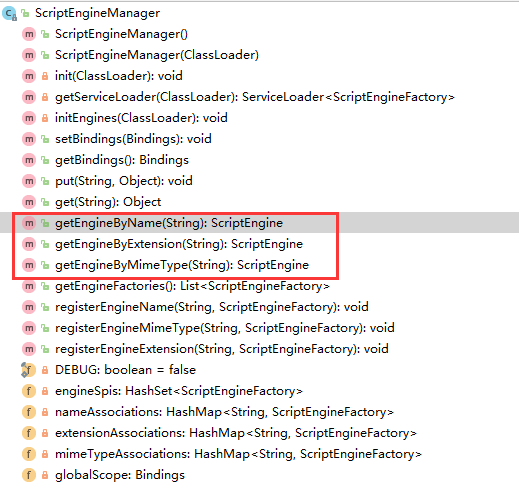
(2)获取脚本引擎
可通过以下方法获取脚本引擎
2. SimpleBindings
绑定是用来存放变量的。
simpleBingdings是 绑定的基本实现类,源码如下

/* * Copyright (c) 2005, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * */ package javax.script; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Set; /** * A simple implementation of Bindings backed by * a <code>HashMap</code> or some other specified <code>Map</code>. * * @author Mike Grogan * @since 1.6 */ public class SimpleBindings implements Bindings { /** * The <code>Map</code> field stores the attributes. */ private Map<String,Object> map; /** * Constructor uses an existing <code>Map</code> to store the values. * @param m The <code>Map</code> backing this <code>SimpleBindings</code>. * @throws NullPointerException if m is null */ public SimpleBindings(Map<String,Object> m) { if (m == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } this.map = m; } /** * Default constructor uses a <code>HashMap</code>. */ public SimpleBindings() { this(new HashMap<String,Object>()); } /** * Sets the specified key/value in the underlying <code>map</code> field. * * @param name Name of value * @param value Value to set. * * @return Previous value for the specified key. Returns null if key was previously * unset. * * @throws NullPointerException if the name is null. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the name is empty. */ public Object put(String name, Object value) { checkKey(name); return map.put(name,value); } /** * <code>putAll</code> is implemented using <code>Map.putAll</code>. * * @param toMerge The <code>Map</code> of values to add. * * @throws NullPointerException * if toMerge map is null or if some key in the map is null. * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if some key in the map is an empty String. */ public void putAll(Map<? extends String, ? extends Object> toMerge) { if (toMerge == null) { throw new NullPointerException("toMerge map is null"); } for (Map.Entry<? extends String, ? extends Object> entry : toMerge.entrySet()) { String key = entry.getKey(); checkKey(key); put(key, entry.getValue()); } } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public void clear() { map.clear(); } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified * key. More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if * this map contains a mapping for a key <tt>k</tt> such that * <tt>(key==null ? k==null : key.equals(k))</tt>. (There can be * at most one such mapping.) * * @param key key whose presence in this map is to be tested. * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified * key. * * @throws NullPointerException if key is null * @throws ClassCastException if key is not String * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is empty String */ public boolean containsKey(Object key) { checkKey(key); return map.containsKey(key); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean containsValue(Object value) { return map.containsValue(value); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entrySet() { return map.entrySet(); } /** * Returns the value to which this map maps the specified key. Returns * <tt>null</tt> if the map contains no mapping for this key. A return * value of <tt>null</tt> does not <i>necessarily</i> indicate that the * map contains no mapping for the key; it's also possible that the map * explicitly maps the key to <tt>null</tt>. The <tt>containsKey</tt> * operation may be used to distinguish these two cases. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * <tt>k</tt> to a value <tt>v</tt> such that <tt>(key==null ? k==null : * key.equals(k))</tt>, then this method returns <tt>v</tt>; otherwise * it returns <tt>null</tt>. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * @param key key whose associated value is to be returned. * @return the value to which this map maps the specified key, or * <tt>null</tt> if the map contains no mapping for this key. * * @throws NullPointerException if key is null * @throws ClassCastException if key is not String * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is empty String */ public Object get(Object key) { checkKey(key); return map.get(key); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean isEmpty() { return map.isEmpty(); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public Set<String> keySet() { return map.keySet(); } /** * Removes the mapping for this key from this map if it is present * (optional operation). More formally, if this map contains a mapping * from key <tt>k</tt> to value <tt>v</tt> such that * <code>(key==null ? k==null : key.equals(k))</code>, that mapping * is removed. (The map can contain at most one such mapping.) * * <p>Returns the value to which the map previously associated the key, or * <tt>null</tt> if the map contained no mapping for this key. (A * <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map previously * associated <tt>null</tt> with the specified key if the implementation * supports <tt>null</tt> values.) The map will not contain a mapping for * the specified key once the call returns. * * @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map. * @return previous value associated with specified key, or <tt>null</tt> * if there was no mapping for key. * * @throws NullPointerException if key is null * @throws ClassCastException if key is not String * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is empty String */ public Object remove(Object key) { checkKey(key); return map.remove(key); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public int size() { return map.size(); } /** {@inheritDoc} */ public Collection<Object> values() { return map.values(); } private void checkKey(Object key) { if (key == null) { throw new NullPointerException("key can not be null"); } if (!(key instanceof String)) { throw new ClassCastException("key should be a String"); } if (key.equals("")) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("key can not be empty"); } } }
可以发现绑定的内部实现时通过HashMap来实现的。
Bingding通过HashMap来存放变量。
3.SimpleScriptContext
脚本引擎是在脚本上下文中执行的。
脚本上下文由四个组件组成:
- 与不同范围相关联的绑定。上下文中的绑定将参数传递给脚本。
- 读取器读取输入
- 写入输出
- 写入错误输出的错误写入器
绑定是是有作用域的,有两个作用域:
- ScriptContext.ENGINE_SCOPE (引擎范围,值为100)
- ScriptContext.GLOBAL_SCOPE (全局范围,值为200)
(1) 设置变量:

public void setAttribute(String var1, Object var2, int var3) { this.checkName(var1); switch(var3) { case 100: this.engineScope.put(var1, var2); return; case 200: if (this.globalScope != null) { this.globalScope.put(var1, var2); } return; default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal scope value."); } } protected Bindings engineScope = new SimpleBindings(); protected Bindings globalScope = null;
可以看到全局绑定默认为空。回到 三、简单示例 中,如下:
//3.3 通过上下文来传参,并执行脚本 ScriptContext ctx = new SimpleScriptContext(); Bindings ctxGlobalBindings = engine.createBindings(); ctx.setBindings(ctxGlobalBindings, GLOBAL_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("n1", 4, GLOBAL_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("n2", 5, ENGINE_SCOPE); ctx.setAttribute("msg", "ScriptContext:", ENGINE_SCOPE); engine.eval(script, ctx); //使用指定上下文来执行脚本
设置全局变量的步骤:我们先设置了一个全局绑定,这样全局绑定就不为空,然后再设置全局变量。
4.ScriptEngine
ScriptEngine提供了如下接口,
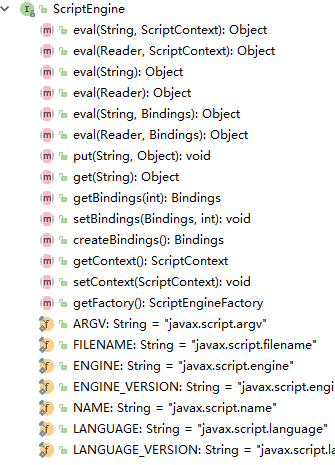
抽象类AbstractScriptEngine实现了ScriptEngine的部分基本方法。
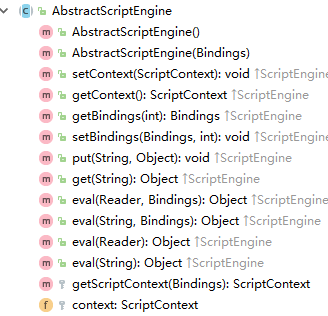
脚本引擎实际的执行者 NashornScriptEngine 继承自 AbstractScriptEngine 实现了 ScriptEngine的全部方法,功能强大。
五、参考资料
我的博客即将搬运同步至腾讯云+社区,邀请大家一同入驻:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/support-plan?invite_code=8rf7kovqfyoo
