Treap树:平衡树的一种
数和堆的集合,每个节点有值,也有优先级,那么这棵树的形态就被确定了,和插入顺序无关了(有赖于优先级
避免退化成链:在生成节点时,随机生成优先级,然后插入时动态调整
删除:如果有两个子节点,找到优先级大的,把x向反方向旋转,也就是把x向树的下层调整,直到旋转到叶子节点
!很多题目涉及名次树
常用操作:
struct node,旋转rotate,插入insert(),查找第k大的数kth(),查询某个数find()【名次树】
旋转zig(右旋)/tag(左旋)操作
splay树和treap树https://www.cnblogs.com/shirlybaby/p/12393268.html
【一本通】
1565:【例 1】营业额统计

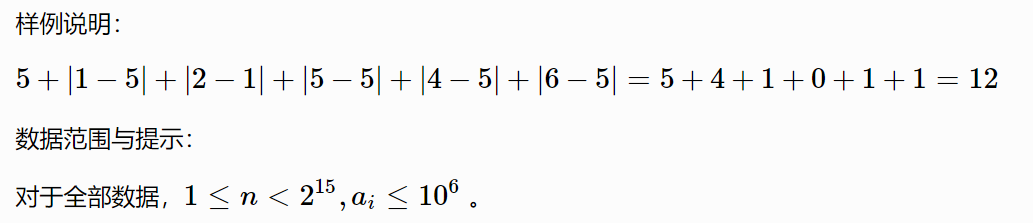
有很多种方法
第一种方法;直接用set做
但是注意一点(怎么看出来的...)就是有一个点差一个输入,其他直接lowerboundupperbound就可以了
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//可以用set过
//有一个点少了一个输入的样子
set<int> st;
int n,x;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
int ans;
scanf("%d",&x);
ans=x;
st.insert(INF);
st.insert(-INF);
//插入正无穷和负无穷,防止迭代器访问到一些奇奇怪怪的内存
st.insert(x); //第一个单独考虑
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
int l=*(--st.lower_bound(x)); //大于等于(第一个)所以减一就是小于
int r=*st.lower_bound(x); //大于
if(x-l>r-x) ans+=r-x;
else ans+=x-l;
st.insert(x);
}
if(scanf("%d",&x)==1){
int l=*(--st.lower_bound(x));
int r=*st.lower_bound(x);
if(x-l>r-x) ans+=r-x;
else ans+=x-l;
st.insert(x);
}
else{
x=0;
int l=*(--st.lower_bound(x));
int r=*st.lower_bound(x);
if(x-l>r-x) ans+=r-x;
else ans+=x-l;
st.insert(x);
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
第二种方法:离线+排序
用链表做,不容易想到
首先排序,然后插入链表
r[i]表示原来的a[i]在链表中的位置
倒序处理,把r[i]的ans贡献算出来,然后删除r[i]指向的位置
为什么这样可行呢?
因为是离线+排序,所以每个元素之间的关系是已知的
倒序处理时,对于每个a[i],链表就是前i个元素组成的【学会呀!】
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
/*
首先排序,然后插入链表
r[i]表示原来的a[i]在链表中的位置
倒序处理,把r[i]的ans贡献算出来,然后删除r[i]指向的位置
为什么这样可行呢?
因为是离线+排序,所以每个元素之间的关系是已知的
倒序处理时,对于每个a[i],链表就是前i个元素组成的
*/
typedef unsigned long long ull;
struct node{
int pre,next;
}b[32768];
struct data{
int d;
int rak;
}a[32768];
int r[32768];
int n,ans;
bool cmp(data x,data y){
if(x.d!=y.d) return x.d<y.d;
else return x.rak<y.rak;
}
void del(int x){
b[b[x].next].pre=b[x].pre;
b[b[x].pre].next=b[x].next;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i].d);
a[i].rak=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
r[a[i].rak]=i; //r[]表示的是原来的下标在现在的排名
if(i!=n) b[i].next=i+1;
b[i].pre=i-1;
}
int j,k;
for(int i=n;i;i--){
j=0;k=0;
int x=r[i]; //原来的输入里面第i个现在的排名
if(b[x].pre) j=abs(a[b[x].pre].d-a[x].d);
else j=INF;
if(b[x].next) k=abs(a[b[x].next].d-a[x].d);
else k=INF;
if(i!=1) ans+=min(j,k);
else ans+=a[x].d;
del(x);
r[i]=0;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
第三种方法:splay树
提根操作!左右旋操作,这个不好写也不好记
注意如果发现已经有这个数的话,就不要再计算前驱和后继了,肯定加的是0
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100100;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//第三种做法 平衡树 splay
int root,tot;
struct tree{
int key;
int son[2]; //son[0]左儿子,son[1]右儿子
int fa;
}T[maxn];
void newnode(int &r,int w,int fa){
r=++tot;
T[r].key=w;
T[r].fa=fa;
T[r].son[0]=T[r].son[1]=0;
}
void rotat(int r,int kind){ //旋转,kind为1是右旋,为0是左旋
int y=T[r].fa;
T[y].son[!kind]=T[r].son[kind];
T[T[r].son[kind]].fa=y;
if(T[y].fa)
T[T[y].fa].son[T[T[y].fa].son[1]==y]=r;
T[r].fa=T[y].fa;
T[r].son[kind]=y;
T[y].fa=r;
}
void splay(int r,int goal){ //Splay调整,将结点r调整到goal下面(以r为根节点)
int y;
while(T[r].fa!=goal){
y=T[r].fa;
if(T[y].fa==goal) rotat(r,T[y].son[0]==r); //如果是左子树就右旋 右子树就左旋
//如果现在的爸爸的爸爸就是目标的话,就旋转
else{
int kind=T[T[y].fa].son[0]==y;
if(T[y].son[kind]==r){
rotat(r,!kind);
rotat(r,kind);
}
else{
rotat(y,kind);
rotat(r,kind);
}
}
}
if(goal==0) root=r; //更新根节点
}
bool inser(int w){
int r=root;
while(T[r].son[w>T[r].key]){
if(T[r].key==w){ //如果w已经在树中
splay(r,0); //移到树根
return false; //返回0,不用继续插入了
}
r=T[r].son[w>T[r].key]; //如果大的话,就插入右子树(1),小的话就插入左子树(0)
}
newnode(T[r].son[w>T[r].key],w,r); //插在r相应的子树里面 void newnode(int &r,int w,int fa)
splay(T[r].son[w>T[r].key],0);
//移动到树根
return true;
}
int get_pre(int r){ //在左子树中找到最大的值(找前驱)
int temp=T[r].son[0];
if(temp==0) return INF;
while(T[temp].son[1]) //在左子树的右子树里面寻找
temp=T[temp].son[1];
return T[r].key-T[temp].key;
}
int get_next(int r){ //在右子树中找到最小的值(找后继)
int temp=T[r].son[1];
if(temp==0) return INF;
while(T[temp].son[0])
temp=T[temp].son[0];
return T[temp].key-T[r].key;
}
int main(){
int n,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
int ans=0;
scanf("%d",&x);
ans=x;
newnode(root,x,0);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
if(!inser(x)) continue;
ans+=min(get_pre(root),get_next(root));
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
第四种方法:treap树
每次取出新读入数据的前驱与后继,与该数据差值较小的就是。(注意若已有同一个数据,特判ans+=0)
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100010;
inline void qread(int &x) {
x = 0;
char ch = getchar();
int flag = 0;
while(ch <'0' || ch >'9') {
if(ch =='-') flag = 1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >='0'&& ch <='9') x = 10 * x + ch - 48, ch = getchar();
if(flag) x = -x;
}
int rt = 0, tpn, v[maxn], l[maxn], r[maxn], R[maxn], sz[maxn], vn[maxn];
inline void update(int x) {
sz[x] = sz[l[x]] + sz[r[x]] + vn[x];
}
inline void zig(int &x) {
int t = l[x];
l[x] = r[t];
r[t] = x;
update(x);
update(t);
x = t;
}
inline void zag(int &x) {
int t = r[x];
r[x] = l[t];
l[t] = x;
update(x);
update(t);
x = t;
}
void insert(int &x, int w) {
if(!x) {
x = ++tpn;
v[x] = w;
R[x] = rand();
sz[x] = vn[x] = 1;
return ;
}
if(w < v[x]) insert(l[x], w);
else if(w > v[x]) insert(r[x], w);
else vn[x]++;
update(x);
if(l[x] && R[l[x]] < R[x]) zig(x);
if(r[x] && R[r[x]] < R[x]) zag(x);
}
void pop(int &x, int w) {
if(w < v[x]) pop(l[x], w);
else if(w > v[x]) pop(r[x], w);
else {
if(vn[x] > 1) vn[x]--;
else if(!l[x] || !r[x]) x = l[x] | r[x];
else if(R[l[x]] < R[r[x]]) zig(x), pop(x, w);
else zag(x), pop(x, w);
}
update(x);
}
int ask(int x, int w){
if(!x) return -1;
if(w < v[x]) return ask(l[x], w);
if(w > v[x]) return ask(r[x], w);
return x;
}
int findk(int x, int k){
if(k >= sz[l[x]] + 1 && k <= sz[l[x]] + vn[x]) return v[x];
if(k <= sz[l[x]]) return findk(l[x], k);
return findk(r[x], k - sz[x] - vn[x]);
}
int findpre(int x, int w){
int res = -0x3f3f3f3f;
while(x){
if(w <= v[x]) x = l[x];
else res = v[x], x = r[x];
}
return res;
}
int findnxt(int x, int w){
int res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
while(x){
if(w < v[x]) res = v[x], x = l[x];
else x = r[x];
}
return res;
}
int main(void) {
srand(11535);
int n, ans;
qread(n);
qread(ans);
insert(rt, ans);
for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i){
int x;
qread(x);
int l = findpre(rt, x), r = findnxt(rt, x);
if(ask(rt, x) != -1) {insert(rt, x); continue;}
insert(rt, x);
ans += min(x - l, r - x);
}
printf("%d
", ans);
}
还有第五种方法是线段树、第六种替罪羊树(不知道没写了)
1566:宠物收养所
这道题和前面一道很相似,都是需要计算相差最小的前驱和后继,适合使用treap或者splay这样的数据结构
这个跟 营业额统计 那题差不多,多了个标记。标记一下当前这个树里的是人还是狗。判断一下当前操作的与树里的是不是同种生物,然后相应做出处理就好了。
首先是treap的做法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=80005;
const int mod=1000000;
const int inf=1e9;
int n,ans,a,b,R,sum,num[N];
int ch[N][2],size[N],val[N],rd[N];
void rotate(int &q,int d)
{
int k=ch[q][d];
ch[q][d]=ch[k][d^1];
ch[k][d^1]=q;
size[k]=size[q];
size[q]=size[ch[q][0]]+size[ch[q][1]]+1;
q=k;
}
void ins(int &q,int x)
{
if(!q)
{
q=++sum;
size[q]=1;val[q]=x;
rd[q]=rand(); return;
}
size[q]++;
if(val[q]<x)
{
ins(ch[q][1],x);
if(rd[q]>rd[ch[q][1]]) rotate(q,1);
}
else
{
ins(ch[q][0],x);
if(rd[q]>rd[ch[q][0]]) rotate(q,0);
}
}
void del(int &q,int x)
{
if(!q) return;
if(val[q]==x)
{
if(ch[q][0]==0||ch[q][1]==0) q=ch[q][0]+ch[q][1];
else if(rd[ch[q][0]]<rd[ch[q][1]]) rotate(q,0),del(q,x);
else rotate(q,1),del(q,x);
}
else
{
size[q]--;
if(val[q]>x) del(ch[q][0],x);
else del(ch[q][1],x);
}
}
int qq(int q,int x)
{
if(!q) return -inf;
if(val[q]>x) return qq(ch[q][0],x);
else return max(val[q],qq(ch[q][1],x));
}
int hq(int q,int x)
{
if(!q) return inf;
if(val[q]<x) return hq(ch[q][1],x);
else return min(val[q],hq(ch[q][0],x));
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);int c=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(c==a) ins(R,b);
else if(size[R]){
int hhh=qq(R,b),ggg=hq(R,b);
if(b-hhh<=ggg-b) ans=(ans+b-hhh)%mod,del(R,hhh);
else ans=(ans+ggg-b)%mod,del(R,ggg);
}
else c=a,ins(R,b);
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
第二种方法:splay树
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 200000
#define MOD 1000000
int tot;
inline int read()
{
register int x=0,t=1;
register char ch=getchar();
while(ch!='-'&&(ch<'0'||ch>'9'))ch=getchar();
if(ch=='-'){t=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-48;ch=getchar();}
return x*t;
}
struct Node
{
int ch[2];
int val;
int ff;
}t[MAX];
int root;
inline void rotate(int x)
{
int y=t[x].ff;
int z=t[y].ff;
int k=(x==t[y].ch[1]);
t[z].ch[y==t[z].ch[1]]=x;
t[x].ff=z;
t[y].ch[k]=t[x].ch[k^1];
t[t[x].ch[k^1]].ff=y;
t[x].ch[k^1]=y;
t[y].ff=x;
}
inline void splay(int x,int goal)
{
//if(x==0)return;
while(t[x].ff!=goal)
{
int y=t[x].ff;
int z=t[y].ff;
if(z!=goal)
(t[z].ch[0]==y)^(t[y].ch[0]==x)?rotate(x):rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
if(goal==0)root=x;
}
inline void insert(int x)
{
int u=root,ff=0;
while(u&&t[u].val!=x)
{
ff=u;
u=t[u].ch[t[u].val<x];
}
if(u);
else
{
u=++tot;
if(ff)t[ff].ch[t[ff].val<x]=u;
t[u].ff=ff;
t[u].ch[0]=t[u].ch[1]=0;
t[u].val=x;
}
splay(u,0);
}
inline void find(int x)
{
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
while(t[u].ch[x>t[u].val]&&x!=t[u].val)
u=t[u].ch[x>t[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
inline int Next(int x,int f)
{
find(x);
int u=root;
if(t[u].val>=x&&f)return u;
if(t[u].val<=x&&!f)return u;
u=t[u].ch[f];
while(t[u].ch[f^1])u=t[u].ch[f^1];
return u;
}
inline int Next_une(int x,int f)
{
find(x);
int u=root;
if(t[u].val>x&&f)return u;
if(t[u].val<x&&!f)return u;
u=t[u].ch[f];
while(t[u].ch[f^1])u=t[u].ch[f^1];
return u;
}
inline void Delete(int x)
{
int lt=Next_une(x,0);
int nt=Next_une(x,1);
splay(lt,0);splay(nt,lt);
t[nt].ch[0]=0;
}
int main()
{
int n=read();
int cnt=0,ans=0;
insert(+214748364);
insert(-214748364);
while(n--)
{
int k=read(),x=read();
if(x==1)
x=1;
if(cnt==0)//空树
insert(x);
if(cnt>0)//宠物树
{
if(k==0)insert(x);
else//新来顾客
{
int a1=t[Next(x,0)].val;//前驱
int a2=t[Next(x,1)].val;//后继
if(abs(a1-x)<=abs(a2-x))
{
ans+=abs(a1-x);
Delete(a1);
}
else
{
(ans+=abs(a2-x))%=MOD;
Delete(a2);
}
}
}
if(cnt<0)//顾客树
{
if(k==1)insert(x);
else//新来宠物
{
int a1=t[Next(x,0)].val;
int a2=t[Next(x,1)].val;
if(abs(a1-x)<=abs(a2-x))
{
(ans+=abs(a1-x))%=MOD;
Delete(a1);
}
else
{
(ans+=abs(a2-x))%=MOD;
Delete(a2);
}
}
}
cnt=cnt+(k==0?1:-1);
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
1567:郁闷的出纳员
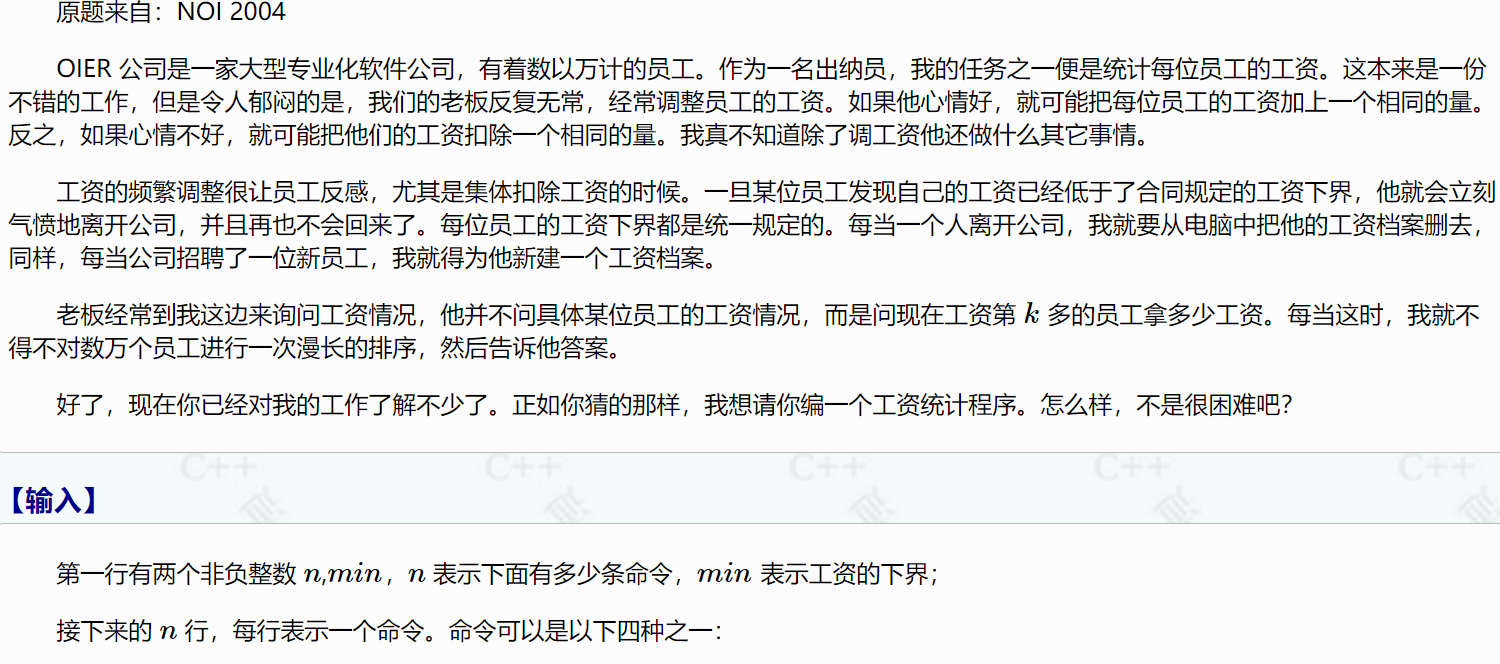
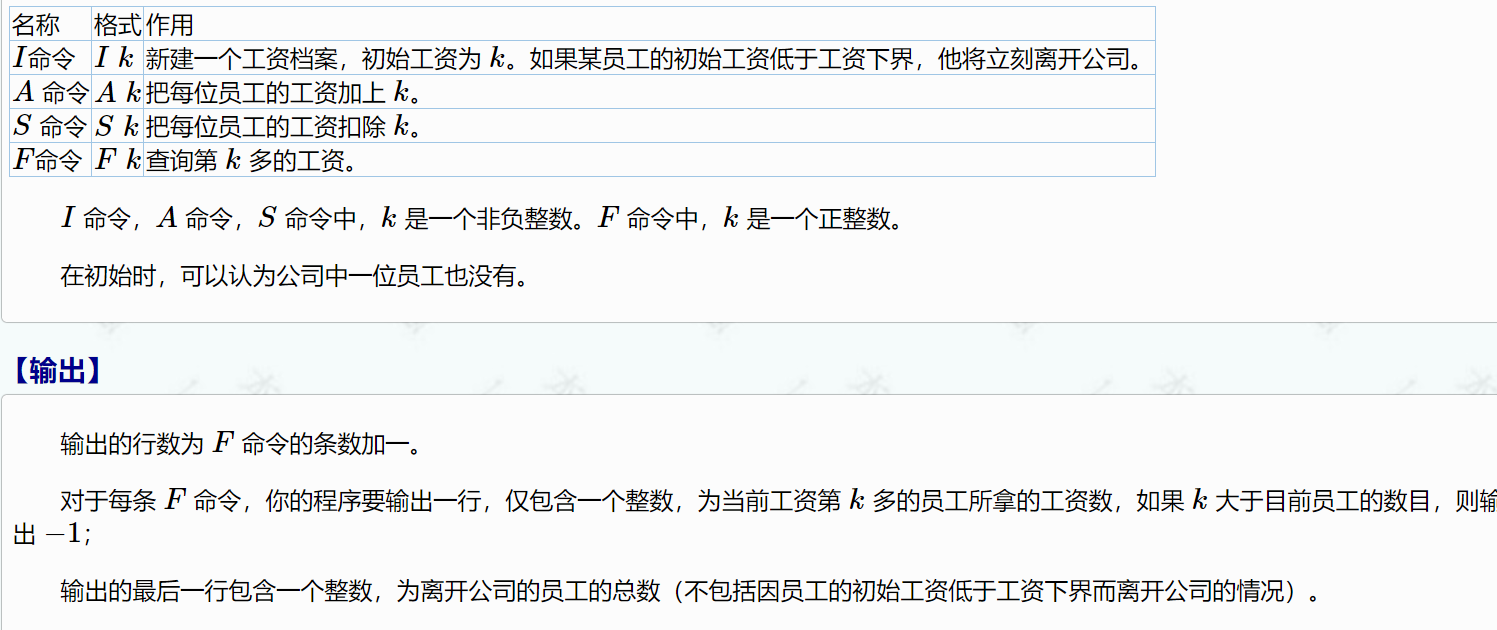
其实看题目就能够明白:需要做的事有增加或减少每一个节点的值,增加节点、删除节点,查询排名为第k的人的值
节点的值是会动态改变,还可能动态删除的,而重点是这道题想问当前工资第k多的员工所拿的工资数
先写一个最简单的vector https://www.sogou.com/link?url=hedJjaC291P3yGwc7N55kLSc2ls_Ks2xYJXKjZDwcU0p1wk5xGC9fwNZoNd2gwAGIeZ8aQ291kY.
/*
vector通过lower_bound和insert操作能够维护一个有序递减/递增的线性表
insert复杂度虽然是O(n),实际表现却非常快(可以看做sqrt(n)),配合lower_bound能够做到许多事情
在这道题中,我们重载了lower_bound的<运算符,维护一个单调递减的序列
ps
erase的复杂度为O(n),因为是区间删除,我们要避免用erase操作,注意到删除的区间是序列中最小的一段区间,考虑用O(1)的pop_back
pop_back的复杂度是O(1),元素总数不超过100000,故删除操作总复杂度为O(N)
查询元素总数时,我们也不用STL的size()(单次复杂度O(N)),而是手动维护一个siz变量
但是我对delta偏移的用法还不是很懂
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6+10;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int n,m;
int k;
vector<int> q;
bool cmp(int a,int b) {
return a>b;
}
int delta=0; //用这个记录偏移 就是增加或者减小的工资
int main(){
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
char op;
int size=0,ans=0; //手动维护集合大小
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf(" %c",&op);
scanf("%d",&k);
switch(op){
case 'I':{
if(k>=m){
q.insert(lower_bound(q.begin(),q.end(),k-delta,cmp),k-delta); //为什么插入的是k-delta
size++;
}
break;
}
case 'A':
delta+=k;break;
case 'S':{
delta-=k;
int it=upper_bound(q.begin(),q.end(),m-delta,cmp)-q.begin(); //为什么比较的是m-delta
while(size!=it) {
q.pop_back();
ans++;
size--;
}
break;
}
case 'F':{
if(size<k) printf("-1
");
else printf("%d
",q[k-1]+delta);
break;
}
}
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}
第二种方法:splay
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 100009
using namespace std;
struct splay{
int l, r, fa, size, v, time;
}node[maxn];
int root = 0, cnt = 0, change = 0, p = 0, n, small;
inline void update(int x){node[x].size = node[node[x].l].size + node[node[x].r].size + node[x].time;}
void zig(int x){
int F = node[x].fa, G = node[F].fa;
if (G){
if (node[G].l == F) node[G].l = x;
else node[G].r = x;
}
node[x].fa = G;
node[F].l = node[x].r;
if (node[x].r) node[node[x].r].fa = F;
node[F].fa = x;
node[x].r = F;
}
void zag(int x){
int F = node[x].fa, G = node[F].fa;
if (G){
if (node[G].l == F) node[G].l = x;
else node[G].r = x;
}
node[x].fa = G;
node[F].r = node[x].l;
if (node[x].l) node[node[x].l].fa = F;
node[F].fa = x;
node[x].l = F;
}
void Splay(int x, int s = 0){
while (node[x].fa != s){
int F = node[x].fa, G = node[F].fa;
if (G == s){
if (node[F].l == x) zig(x); else zag(x);
update(F);
break;
}
else{
if (node[F].l == x){
if (node[G].l == F){zig(F); zig(x);}
else{zig(x);zag(x);}
}
else{
if (node[G].r == F){zag(F); zag(x);}
else{zag(x); zig(x);}
}
update(G);
update(F);
}
}
update(x);
if (!s) root = x;
}
int find(int x){
int p = root;
while (p && node[p].v != x){
if (x > node[p].v) p = node[p].r; else p = node[p].l;
}
if (p) Splay(p);
return p;
}
void insert(int x){
if (!root){node[++cnt] = (splay){0, 0, 0, 1, x, 1}; root = cnt; return;}
int p = root, p2;
while (p){
if (x == node[p].v) {++node[p].time;update(p); Splay(p);break;}
else if (x > node[p].v) p2 = node[p].r;
else p2 = node[p].l;
if (!p2){
node[++cnt] = (splay){0, 0, p, 1, x, 1};
if (x > node[p].v) node[p].r = cnt;
else node[p].l = cnt;
update(p);
Splay(cnt);
break;
}
p = p2;
}
}
int getKth(int k){
int p = root;
while (k){
int size = node[node[p].l].size, time = node[p].time;
if (size + time < k) {p = node[p].r; k -= size + time;}
else if (size >= k) p = node[p].l;
else return node[p].v;
}
}
void del(){
int p = root, p2 = root, ch = small - change;
while(p){
if (node[p].v < ch) p = node[p].r;
else{p2 = p; p = node[p].l;}
}
if (node[p2].v < ch) {root = 0;return;}
Splay(p2);
node[p2].l = 0;
update(p2);
}
int read(){
char c;
while (c = getchar(), c < '0' || c > '9');
int x = c - '0';
while (c = getchar(), c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0';
return x;
}
int main(){
char c; int x;
node[0] = (splay){0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
n = read(); small = read();
while(n--){
while (c = getchar(), !(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'));
x = read();
switch(c){
case 'I':if (x >= small) {++p;insert(x - change);};break;
case 'A':change += x;break;
case 'S':change -= x; del();break;
case 'F':if (x > node[root].size) printf("-1
");
else printf("%d
", getKth(node[root].size - x + 1) + change);break;
}
}
printf("%d
", p - node[root].size);
return 0;
}
1568:普通平衡树
这是一道模板题。
您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作:
1、插入 xx 数;
2、删除 xx 数(若有多个相同的数,因只删除一个);
3、查询 xx 数的排名(若有多个相同的数,因输出最小的排名);
4、查询排名为 xx 的数;
5、求 xx 的前趋(前趋定义为小于 xx,且最大的数);
6、求 xx 的后继(后继定义为大于 xx,且最小的数)。
treap的模板
https://www.cnblogs.com/Y-Knightqin/p/12252930.html
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 100010
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
//https://www.cnblogs.com/Y-Knightqin/p/12252930.html
int key[maxn],cnt[maxn],ran[maxn],siz[maxn],son[maxn][2],op,n,num=0,x,root=0;
void pushup(int x)
{
siz[x]=siz[son[x][0]]+siz[son[x][1]]+cnt[x];
}
void rotate(int &x,int op)
{
int p=son[x][!op];
son[x][!op]=son[p][op];
son[p][op]=x;
pushup(x);
pushup(p);
x=p;
}
void insert(int &k,int x)
{
if (k==0)
{
k=++num;
cnt[k]=1;
key[k]=x;
ran[k]=rand();
siz[k]=1;
return;
}
else if (key[k]==x)
{
cnt[k]++;
siz[k]++;
return;
}
int op=(x>key[k]);
insert(son[k][op],x);
if (ran[son[k][op]]<ran[k]) rotate(k,!op);
pushup(k);
}
void _delete(int &k,int x)
{
if (k==0) return;
if (x!=key[k])
{
int op=(x>key[k]);
_delete(son[k][op],x);
pushup(k);
return;
}
if (cnt[k]>1)
{
cnt[k]--;
siz[k]--;
pushup(k);
return;
}
if (!son[k][0]&&son[k][1])
{
rotate(k,0);
_delete(son[k][0],x);
}
else if (son[k][0] && !son[k][1])
{
rotate(k,1);
_delete(son[k][1],x);
}
else if (!son[k][0] && !son[k][1])
{
cnt[k]--;
siz[k]--;
if (cnt[k]==0) k=0;
}
else
{
int op=(ran[son[k][0]]>ran[son[k][1]]);
rotate(k,!op);
_delete(son[k][!op],x);
}
pushup(k);
}
int rank(int k,int x)
{
if (k==0) return 0;
if (key[k]==x) return siz[son[k][0]]+1;
if (key[k]>x) return rank(son[k][0],x);
return siz[son[k][0]]+cnt[k]+rank(son[k][1],x);
}
int find(int k,int x)
{
if (k==0) return 0;
if (siz[son[k][0]]>=x) return find (son[k][0],x);
else if (siz[son[k][0]]+cnt[k]<x) return find (son[k][1],x-siz[son[k][0]]-cnt[k]);
else return key[k];
}
int lowerbound(int k,int x)
{
if (k==0) return -inf;
if (key[k]>=x) return lowerbound(son[k][0],x);
else return max(key[k],lowerbound(son[k][1],x));
}
int upperbound(int k,int x)
{
if (k==0) return inf;
if (key[k]<=x) return upperbound(son[k][1],x);
else return min(key[k],upperbound(son[k][0],x));
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
while (n--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&op,&x);
switch(op)
{
case 1:insert(root,x);break;
case 2:_delete(root,x);break;
case 3:printf("%d
",rank(root,x));break;
case 4:printf("%d
",find(root,x));break;
case 5:printf("%d
",lowerbound(root,x));break;
case 6:printf("%d
",upperbound(root,x));break;
}
}
return 0;
}
里面还写了一个懒人版treap,用vector实现的
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin)
#define mp make_pair
#define ri register int
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int maxn = 4e5+5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 998244353;
inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return s*w;}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;}
vector<int>v;
int t,opt,x;
int main()
{
t=read();
while(t--)
{
opt=read(),x=read();
if(opt==1) v.insert(lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x),x);
if(opt==2) v.erase (lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x));
if(opt==3) printf("%d
",lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x)-v.begin()+1);
if(opt==4) printf("%d
",v[x-1]);
if(opt==5) printf("%d
",v[lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x)-v.begin()-1]);
if(opt==6) printf("%d
",v[upper_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x)-v.begin()]);
}
return 0;
}