2.3 实现属于我们自己的向量
Vector.py
-
class Vector:
-
def __init__(self, lst):
-
self._values = lst
-
#return len
-
def __len__(self):
-
return len(self._values)
-
#return index th item
-
def __getitem__(self, index):
-
return self._values[index]
-
#direct use call this method
-
def __repr__(self):
-
return "Vector({})".format(self._values)
-
#print call this method
-
def __str__(self):
-
return "({})".format(", ".join(str(e) for e in self._values))
-
-
main_vector.py
-
import sys
-
import numpy
-
import scipy
-
from playLA.Vector import Vector
-
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
vec = Vector([5, 2])
-
print(vec)
-
print(len(vec))
-
print("vec[0] = {}, vec[1] = {}".format(vec[0], vec[1]))
2.5 实现向量的基本运算
Vector.py
-
class Vector:
-
def __init__(self, lst):
-
self._values = lst
-
#return len
-
def __len__(self):
-
return len(self._values)
-
#return index th item
-
def __getitem__(self, index):
-
return self._values[index]
-
#direct use call this method
-
def __repr__(self):
-
return "Vector({})".format(self._values)
-
#print call this method
-
def __str__(self):
-
return "({})".format(", ".join(str(e) for e in self._values))
-
#vector add method
-
def __add__(self, another):
-
assert len(self) == len(another),"lenth not same"
-
# return Vector([a + b for a, b in zip(self._values, another._values)])
-
return Vector([a + b for a, b in zip(self, another)])
-
#迭代器 设计_values其实是私有成员变量,不想别人访问,所以使用迭代器
-
#单双下划线开头体现在继承上,如果类内内部使用的变量使用单下划线
-
def __iter__(self):
-
return self._values.__iter__()
-
#sub
-
def __sub__(self, another):
-
# return Vector([a + b for a, b in zip(self._values, another._values)])
-
return Vector([a - b for a, b in zip(self, another)])
-
#self * k
-
def __mul__(self, k):
-
return Vector([k * e for e in self])
-
# k * self
-
def __rmul__(self, k):
-
return Vector([k * e for e in self])
-
#取正
-
def __pos__(self):
-
return 1 * self
-
#取反
-
def __neg__(self):
-
return -1 * self
main_vector.py
-
import sys
-
import numpy
-
import scipy
-
from playLA.Vector import Vector
-
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
vec = Vector([5, 2])
-
print(vec)
-
print(len(vec))
-
print("vec[0] = {}, vec[1] = {}".format(vec[0], vec[1]))
-
vec2 = Vector([3, 1])
-
print("{} + {} = {}".format(vec, vec2, vec + vec2))
-
print("{} - {} = {}".format(vec, vec2, vec - vec2))
-
print("{} * {} = {}".format(vec, 3, vec * 3))
-
print("{} * {} = {}".format(3, vec, vec * 3))
-
print("-{} = {}".format(vec, -vec))
-
print("+{} = {}".format(vec, +vec))
2.8 实现0向量
Vector.py
-
-
def zero(cls, dim):
-
return cls([0] * dim)
main_vector.py
-
zero2 = Vector.zero(2)
-
print(zero2)
-
print("{} + {} = {}".format(vec, zero2, vec + zero2))
3.2实现向量规范
Vector.py
-
# self / k
-
def __truediv__(self, k):
-
return Vector((1 / k) * self)
-
#模
-
def norm(self):
-
return math.sqrt(sum(e**2 for e in self))
-
#归一化
-
def normalize(self):
-
if self.norm() < EPSILON:
-
raise ZeroDivisionError("Normalize error! norm is zero.")
-
return Vector(self._values)/self.norm()
main_vector.py
-
print("normalize vec is ({})".format(vec.normalize()))
-
print(vec.normalize().norm())
-
try :
-
zero2.normalize()
-
except ZeroDivisionError:
-
print("cant normalize zero vector {}".format(zero2))
3.3 向量的点乘

3.5实现向量的点乘操作
Vector.py
-
def dot(self, another):
-
assert len(self) == len(another), "Error in dot product. Length of vectors must be same."
-
return sum(a * b for a, b in zip(self, another))
main_vector.py
print(vec.dot(vec2))3.6向量点乘的应用

3.7numpy中向量的基本使用
main_numpy_vector.py
-
import numpy as np
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
print(np.__version__)
-
-
lst = [1, 2, 3]
-
lst[0] = "LA"
-
print(lst)
-
#numpy中只能存储一种数据
-
vec = np.array([1, 2, 3])
-
print(vec)
-
# vec[0] = "LA"
-
# vec[0] = 666
-
print(vec)
-
print(np.zeros(5))
-
print(np.ones(5))
-
print(np.full(5, 666))
-
-
print(vec)
-
print("size = ", vec.size)
-
print("size = ", len(vec))
-
print(vec[0])
-
print(vec[-1])
-
print(vec[0:2])
-
print(type(vec[0:2]))
-
#点乘
-
vec2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
-
print("{} + {} = {}".format(vec, vec2, vec + vec2))
-
print("{} - {} = {}".format(vec, vec2, vec - vec2))
-
print("{} * {} = {}".format(2, vec, 2 * vec))
-
print("{} * {} = {}".format(vec, 2, vec * 2))
-
print("{} * {} = {}".format(vec, vec2, vec * vec2))
-
print("{}.dot({})= {}".format(vec, vec2, vec.dot(vec2)))
-
#求模
-
print(np.linalg.norm(vec))
-
print(vec/ np.linalg.norm(vec))
-
print(np.linalg.norm(vec/ np.linalg.norm(vec)))
-
#为什么输出nan
-
zero3 = np.zeros(3)
-
print(zero3 /np.linalg.norm(zero3))
4矩阵
4.2实现矩阵
Matrix.py
-
from .Vector import Vector
-
class Matrix:
-
#list2d二维数组
-
def __init__(self, list2d):
-
self._values = [row[:] for row in list2d]
-
def __repr__(self):
-
return "Matrix({})".format(self._values)
-
__str__ = __repr__
-
def shape(self):
-
return len(self._values),len(self._values[0])
-
def row_num(self):
-
return self.shape()[0]
-
def col_num(self):
-
return self.shape()[1]
-
def size(self):
-
r, c = self.shape()
-
return r * c
-
__len__ = row_num
-
def __getitem__(self, pos):
-
r, c =pos
-
return self._values[r][c]
-
#第index个行向量
-
def row_vector(self, index):
-
return Vector(self._values[index])
-
def col_vector(self, index):
-
return Vector([row[index] for row in self._values])
main_matrix.py
-
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
matrix = Matrix([[1, 2],[3, 4]])
-
print(matrix)
-
print("matrix.shape = {}".format(matrix.shape()))
-
print("matrix.size = {}".format(matrix.size()))
-
print("matrix.len = {}".format(len(matrix)))
-
print("matrix[0][0]= {}".format(matrix[0, 0]))
-
print("{}".format(matrix.row_vector(0)))
-
print("{}".format(matrix.col_vector(0)))
4.4 实现矩阵的基本计算
Matrix.py
-
def __add__(self, another):
-
assert self.shape() == another.shape(),"ERROR in shape"
-
return Matrix([[a + b for a, b in zip(self.row_vector(i), another.row_vector(i))]for i in range(self.row_num())])
-
def __sub__(self, another):
-
assert self.shape() == another.shape(),"ERROR in shape"
-
return Matrix([[a - b for a, b in zip(self.row_vector(i), another.row_vector(i))]for i in range(self.row_num())])
-
def __mul__(self, k):
-
return Matrix([[e*k for e in self.row_vector(i)] for i in range(self.row_num())])
-
def __rmul__(self, k):
-
return self * k
-
#数量除法
-
def __truediv__(self, k):
-
return (1/k) * self
-
def __pos__(self):
-
return 1 * self
-
def __neg__(self):
-
return -1 * self
-
-
def zero(cls, r, c):
-
return cls([[0]*c for _ in range(r)])
main_matrix.py
-
matrix2 = Matrix([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
-
print("add: {}".format(matrix + matrix2))
-
print("sub: {}".format(matrix - matrix2))
-
print("mul: {}".format(matrix * 2))
-
print("rmul: {}".format(2 * matrix))
-
print("zero_2_3:{}".format(Matrix.zero(2, 3)))
4.8实现矩阵乘法
Matrix.py
main_matrix.py
Matrix.py
-
def dot(self, another):
-
if isinstance(another, Vector):
-
assert self.col_num() == len(another), "error in shape"
-
return Vector([self.row_vector(i).dot(another) for i in range(self.row_num())])
-
if isinstance(another, Matrix):
-
assert self.col_num() == another.row_num(),"error in shape"
-
return Matrix([self.row_vector(i).dot(another.col_vector(j)) for j in range(another.col_num())] for i in range(self.row_num()))
main_matrix.py
-
T = Matrix([[1.5, 0], [0, 2]])
-
p = Vector([5, 3])
-
print("T.dot(p)= {}".format(T.dot(p)))
-
P = Matrix([[0, 4, 5], [0, 0, 3]])
-
print("T.dot(P)={}".format(T.dot(P)))
4.11 实现矩阵转置和Numpy中的矩阵
main_numpy_matrix.py
-
import numpy as np
-
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
#创建矩阵
-
A = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
-
print(A)
-
#矩阵属性
-
print(A.shape)
-
print(A.T)
-
#获取矩阵元素
-
print(A[1, 1])
-
print(A[0])
-
print(A[:, 0])
-
print(A[1, :])
-
#矩阵的基本运算
-
B = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
-
print(A + B)
-
print(A - B)
-
print(10 * A)
-
print(A * 10)
-
print(A * B)
-
print(A.dot(B))
-
-
5 矩阵进阶
5.3 矩阵变换

main_matrix_transformation.py
-
import math
-
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
-
from playLA.Vector import Vector
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
points = [[0, 0], [0, 5], [3, 5], [3, 4], [1, 4],
-
[1, 3], [2, 3], [2, 2], [1, 2], [1, 0]]
-
x = [point[0] for point in points]
-
y = [point[1] for point in points]
-
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
-
plt.xlim(-10, 10)
-
plt.ylim(-10, 10)
-
plt.plot(x, y)
-
# plt.show()
-
P = Matrix(points)
-
# T = Matrix([[2, 0], [0, 1.5]])#x扩大2倍,y扩大1.5倍
-
# T = Matrix([[1, 0], [0, -1]])#关于X轴对称
-
# T = Matrix([[-1, 0], [0, 1]])#关于X轴对称
-
# T = Matrix([[-1, 0], [0, -1]])#关于原点对称
-
# T = Matrix([[1, 0.5], [0, 1]])
-
# T = Matrix([[1, 0], [0.5, 1]])
-
theta = math.pi / 3
-
#旋转theta角度
-
T = Matrix([[math.cos(theta), math.sin(theta)], [-math.sin(theta), math.cos(theta)]])
-
P2 = T.dot(P.T())
-
plt.plot([P2.col_vector(i)[0] for i in range(P2.col_num())],[P2.col_vector(i)[1] for i in range(P2.col_num())])
-
plt.show()
5.6实现单位矩阵和numpy中的逆矩阵



Matrix.py
-
#单位矩阵
-
-
def identity(cls, n):
-
m = [[0]*n for _ in range(n)]
-
for i in range(n):
-
m[i][i] = 1
-
return cls(m)
main_matrix.py
-
I = Matrix.identity(2)
-
print(I)
-
print("A.dot(I) = {}".format(matrix.dot(I)))
-
print("I.dot(A) = {}".format(I.dot(matrix)))
main_numpy_matrix.py
-
#numpy中的逆矩阵
-
invA = np.linalg.inv(A)
-
print(invA)
-
print(A.dot(invA))
-
print(invA.dot(A))
-
-
C = np.array([[1,2]])
-
print(np.linalg.inv(C))
5.8用矩阵表示空间


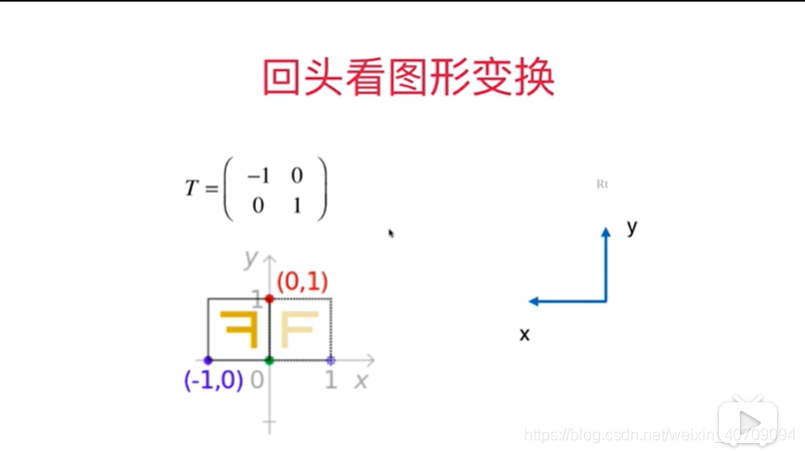
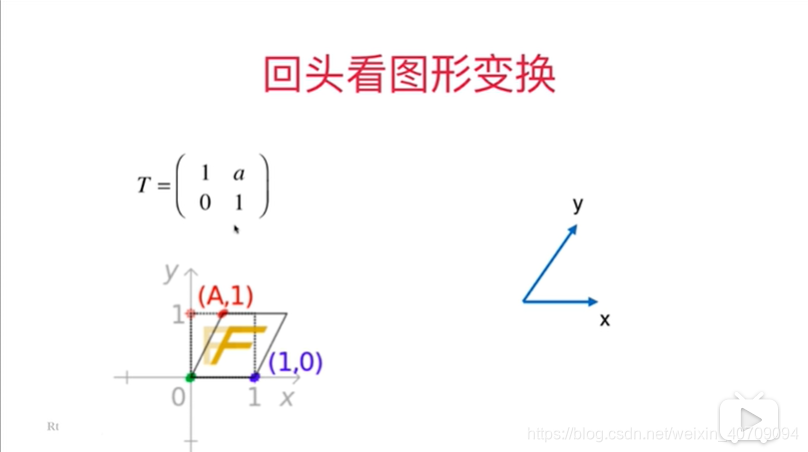


x轴就是(0,1)y轴就是(-1,0)
6 线性系统
6.4实现高斯-约旦消元法
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40709094/article/details/105602775