python高级特性
1、集合的推导式
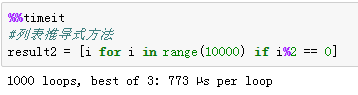
- 列表推导式,使用一句表达式构造一个新列表,可包含过滤、转换等操作。
语法:[exp for item in collection if codition]
if codition - 可选

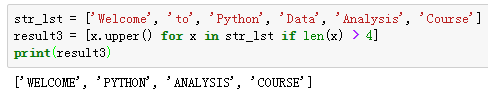
- 字典推导式,使用一句表达式构造一个新列表,可包含过滤、转换等操作。
语法:{key_exp:value_exp for item in collection if codition}

- 集合推导式
语法:{exp for item in collection if codition}

- 嵌套列表推导式

2、多函数模式
函数列表,python中一切皆对象。
# 处理字符串
str_lst = ['$1.123', ' $1123.454', '$899.12312']
def remove_space(str):
"""
remove space
"""
str_no_space = str.replace(' ', '')
return str_no_space
def remove_dollar(str):
"""
remove $
"""
if '$' in str:
return str.replace('$', '')
else:
return str
def clean_str_lst(str_lst, operations):
"""
clean string list
"""
result = []
for item in str_lst:
for op in operations:
item = op(item)
result.append(item)
return result
clean_operations = [remove_space, remove_dollar]
result = clean_str_lst(str_lst, clean_operations)
print result
执行结果:['1.123', '1123.454', '899.12312']
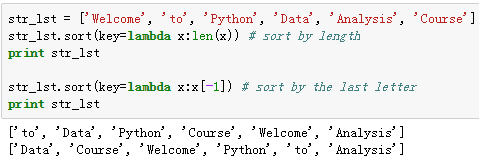
3、匿名函数lambda
- 没有函数名
- 单条语句组成
- 语句执行的结果就是返回值
- 可用作sort的key函数
python高阶函数
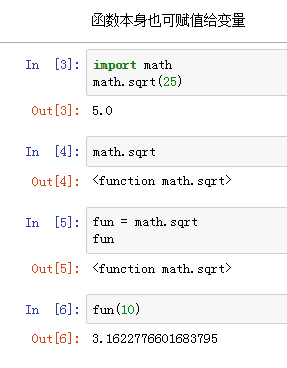
1、函数式编程
- 函数本身可以赋值给变量,赋值后变量为函数;
- 允许将函数本身作为参数传入另一个函数;
- 允许返回一个函数。

2、map/reduce函数
- map(fun, lst),将传入的函数变量func作用到lst变量的每个元素中,并将结果组成新的列表返回

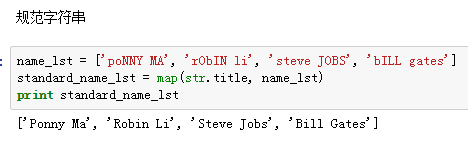
- reduce(func(x,y),lst),其中func必须有两个参数。每次func计算的结果继续和序列的下一个元素做累积计算。
lst = [a1, a2 ,a3, ......, an]
reduce(func(x,y), lst) = func(func(func(a1, a2), a3), ......, an)

3、filter函数
- 筛选序列
- filter(func, lst),将func作用于lst的每个元素,然后根据返回值是True或False判断是保留还是丢弃该元素。
