【Problem:1-Two Sum】
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
【Example】
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
【Solution】
1)-----------Submission Status :Time Limit Exceeded
Time complexity:O(n^2)2).
【Python】
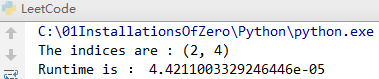
import time class Solution(object): def twoSum(self,nums,target): for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i+1,len(nums)): if nums[i]+nums[j]==target: return i,j start = time.clock() test=Solution() nums=[1,2,3,4,5,55,26,25,36,211,200,300,258,459] target=8 print("The indices are :",test.twoSum(nums,target)) end = time.clock() c=end-start print("Runtime is :",c)
可是 Java 的这个,Time complexity 也是O(n^2)2 ,却可以 AC??
【Java】
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) { if (nums[j] == target - nums[i]) { return new int[] { i, j }; } } } throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution"); }
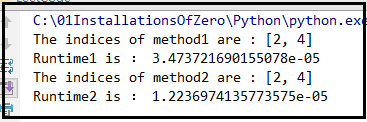
2)两个方法做个对比:(Python 语言)
#---- class Solution(object): # Method 1 : O(n_2) def twoSum1(self,nums,target): for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i+1,len(nums)): if nums[i]+nums[j]==target: return i,j # Method 2 : O(n) def twoSum2(self, nums, target): if len(nums) <= 1: return False buff_dict = {} for i in range(len(nums)): if nums[i] in buff_dict: return [buff_dict[nums[i]], i] else: buff_dict[target - nums[i]] = i test=Solution() nums=[1,2,3,4,5,55,26,25,36] target=8 start1 = time.clock() print("The indices of method1 are :",test.twoSum2(nums,target)) end1 = time.clock() t1=end1-start1 print("Runtime1 is :",t1) start2 = time.clock() print("The indices of method2 are :",test.twoSum2(nums,target)) end2 = time.clock() t2=end2-start2 print("Runtime2 is :",t2)
结果是:
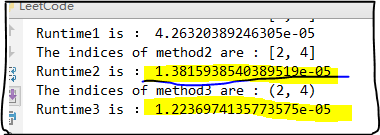
3)外加一个方法3 ,会比法2好些?(亦可AC)
#---- class Solution(object): # Method 1 : O(n_2) def twoSum1(self,nums,target): for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i+1,len(nums)): if nums[i]+nums[j]==target: return i,j # Method 2 : O(n) def twoSum2(self, nums, target): if len(nums) <= 1: return False buff_dict = {} for i in range(len(nums)): if nums[i] in buff_dict: return [buff_dict[nums[i]], i] else: buff_dict[target - nums[i]] = i def twoSum3(self, num, target): tmp_num = {} for i in range(len(num)): if target - num[i] in tmp_num: # here do not need to deal with the condition i = target-i return (tmp_num[target-num[i]], i) else: tmp_num[num[i]] = i return (-1, -1) test=Solution() nums=[1,2,3,4,5,55,26,25,36] target=8 start1 = time.clock() print("The indices of method1 are :",test.twoSum2(nums,target)) end1 = time.clock() t1=end1-start1 print("Runtime1 is :",t1) start2 = time.clock() print("The indices of method2 are :",test.twoSum2(nums,target)) end2 = time.clock() t2=end2-start2 print("Runtime2 is :",t2) start3 = time.clock() print("The indices of method3 are :",test.twoSum3(nums,target)) end3 = time.clock() t3=end3-start3 print("Runtime3 is :",t3)
结果是: