第二次实验主要内容是函数重载,快速排序及其模板实现,简单的user类实现。
实验结论:
一、函数重载编程练习
/*编写重载函数add(),实现对int型,double型和Complex型数据的加法。在main函数中定义不同类型数据,调用测试。*/
代码如下:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct Complex//Complex结构体定义 5 { 6 double real; 7 double imaginary; 8 }e,f; 9 10 int add(int , int); 11 12 double add(double , double); 13 14 Complex add(Complex,Complex); 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 int a,b; 19 double c,d; 20 21 cin>>a>>b;//int 型输入 22 cout<<add(a,b)<<endl; 23 cin>>c>>d;//double 型输入 24 cout<<add(c,d)<<endl; 25 cin>>e.real>>e.imaginary>>f.real>>f.imaginary;//Complex 型输入 26 cout<<add(e,f).real<<"+"<<add(e,f).imaginary<<"i"<<endl; 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 int add(int a,int b) 31 { 32 return a+b; 33 } 34 double add(double a,double b) 35 { 36 return a+b; 37 } 38 Complex add(Complex a,Complex b) 39 { 40 struct Complex c; 41 c.real=a.real+b.real; 42 c.imaginary=a.imaginary+b.imaginary; 43 return c; 44 }
运行截图:
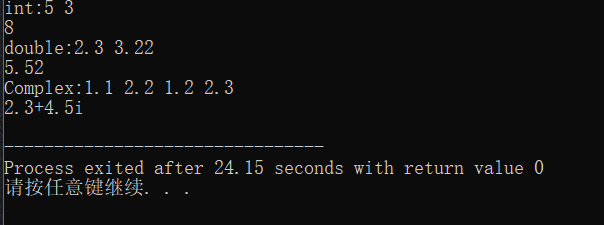
二、函数模板编程练习
/*编写实现快速排序函数模板,并在main()函数中定义不同数据类型,调用测试。*/
这里我个人有一些关于快速排序简单的想法。快速排序是在实践中最快的已知排序算法,其平均运行时间是O(N log N)。
此算法之所以特别快是由于非常精炼和高度优化的内部循环。它的最坏情形的性能为O(N2),这个是在极端情况下会出现的情况,下面会有一点介绍。
假设我们将要对数组S进行排序,其基本算法可以由以下简单的四步组成:
1、若S中的元素个数是0或1,则返回。
2、取S中的任意元素v,称之为枢纽元(pivot)。
3、将S中除去v剩下的元素分为两个不相交的集合,S1,S2。
4、返回quick_sort(S1)后,继随v,继而quick_sort(S2)。
关于枢纽元的选取:通常情况下,我们的选择是将第一个元素用作枢纽元。如果输入是随机的,那么影响不是太大。但是如果输入是预排序或者是反序的,
那么以第一个元素为枢纽元就会产生一个恶劣的结果,因为所有的元素不是被分到了S1,就是被分到了S2,甚至这种情况可能发生在所有的递归中。
所以为了安全起见,我们更加倾向于随机选取枢纽元。
三数中值分割法:枢纽元最理想的结果是数组数值大小的中值,但是这很难找到,因此一般的做法是使用左端右端和中心位置上的三个元素的中值作为枢纽元。
显然,使用三数中值分割可以消除预排序的坏情况,并且可以一定程度减少排序的时间。
其它值得思考的问题:a.如果出现相同大小元素,在进行交叉排序的过程中,交叉是否会越界? b.对于处理数组元素个数并不是很多的情况下,快速排序是不是一定最有效?
限于目前的能力,以上的只是自己暂时的思考,具体在代码中还未能很好的实现。
代码如下:
#include "pch.h"//编译器需要的引用 #include<iostream> #include<algorithm>//swap函数引用 using namespace std; #define N 100 void swap(int &A, int &B)//定义swap函数 { int c = A; A = B; B = c; } void swap(double &A, double &B)//swap函数重载 { double c = A; A = B; B = c; } template <class T>//实现三数中值分割 int Median3(T A[], int left, int right) { int center = (left + right)/2;//找到中间值,作为枢纽元 if (A[left] > A[center]) swap(A[left], A[center]); if (A[left] > A[right]) swap(A[left], A[right]); if (A[center] > A[right]) swap(A[center], A[right]); swap(A[center],A[right-1]); return A[right - 1]; } template <class T>//快速排序主程序 void quick_sort(const T A[], int left, int right) { int i, j; T pivot; pivot = Median3(A, left, right); i = left; j = right - 1; for (;;) { while (A[++i] < pivot) {} while (A[--j] > pivot) {} if (i < j) swap(A[i],A[j]); else//i和j已经交错,所以不再交换 break; } swap(A[i],A[right - 1]); quick_sort(A, left, i - 1);//数组分割成两部分之后的递归部分 quick_sort(A, i + 1, right); } int main() { int b[N],n; double a[N]; cout << "请输入参与排序的数字个数:n=" ; cin >> n; cout << endl << "a[]="; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i]; cout << endl << "b[]="; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >>b[i]; quick_sort(a, 0, n-1); quick_sort(b, 0, n-1); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << "排序后a[]="<<a[i]<<ends; cout << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << "排序后b[]=" << b[i] << ends; return 0; }
运行截图:
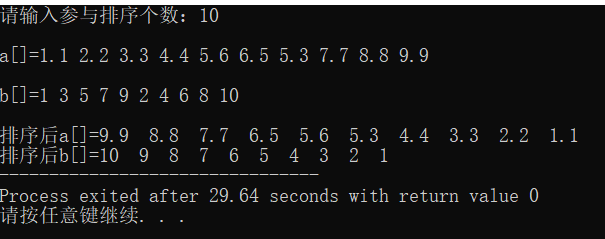
三、类的定义、实现和使用编程
/*设计并实现一个用户类user,并在主函数中使用和测试这个类,具体要求如下:
1、每一个用户有用户名(name),密码(password)和邮箱(email)三个属性
2、支持设置用户信息setinfo()。允许设置信息时密码默认值为6个1,联系邮箱默认为空串
3、支持打印用户信息printinfo()。打印用户名,密码,联系邮箱。其中密码以6个*方式显示
4、支持修改密码changepassword()。在修改密码前,要求先输入旧密码,确认无误后,才允许修改。如果输入旧密码时
连续三次输入错误,则提示用户稍后再试,并退出暂时修改密码程序
5、在main函数中创建user类实例,测试user类的各项操作(设置用户信息,修改密码,打印用户信息)
6、(选做)对user类进行完善。
代码如下:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 //user类的声明 5 class user{ 6 public: 7 void setinfo(string name ,string password="111111" ,string email="");//带有默认形参值 8 void changepassword(); 9 void printfinfo(); 10 private: 11 string name; 12 string password; 13 string email; 14 }; 15 //user类的实现 16 void user::setinfo(string name0, string password0, string email0) { 17 name = name0; 18 password = password0; 19 email = email0; 20 } 21 //成员函数changepassword的实现 22 void user::changepassword() 23 { 24 string password1; 25 int c = 3; 26 cout << "please enter the old password firstly,if it is right ,you can change password then" << endl; 27 cin >> password1; 28 while (password1 != "111111"&&c > 1) 29 { 30 c--; 31 cout << "old password is not corrent,you have " << c << " time(s) to try it again" << endl; 32 cin >> password1; 33 } 34 if (c <= 1) 35 cout << "you have no time to try, please try it next day!" << endl; 36 else 37 { 38 cout << "you changed your password successfully! please remember it" << endl; 39 password = password1; 40 } 41 } 42 //成员函数printinfo的实现 43 void user::printfinfo() 44 { 45 cout << "name: "<< name << endl; 46 cout << "password: " << "******" << endl; 47 cout << "email: " << email << endl; 48 } 49 //主函数中对user类进行测试 50 int main() 51 { 52 cout << "...testing 1..." << endl; 53 user user1; 54 user1.setinfo("shenqidetao"); 55 user1.printfinfo(); 56 user1.changepassword(); 57 user1.printfinfo(); 58 cout << endl; 59 cout << "...testing 2..." << endl; 60 user user2; 61 user2.setinfo("arboter", "520521", "abc123@11.com"); 62 user2.printfinfo(); 63 return 0; 64 }
运行结果截图:

实验总结与体会
1、在编写快速排序函数模板的时候,尝试写一个效率更高的算法,但是在代码实现的时候,除了几个bug。
主要是处在swap函数调用的地方。个人感觉debug虽然很烦,但是在过程中遇到的一些没有见过的error,总会
给个人的能力带来提升,也会帮助自己查找学习过程中的语法漏洞,即使补缺。
2、对于user类的编写,是第一次,但是能够很明显的感觉到面向对象与结构化编程的区别。
个人感受先列出几点:
a、面向对象编程中对于数据的public,private和prevent的区分,使得数据的安全型提高。
b、提高了程序的复用性。
c、emmmm,一言难尽,感觉还挺爽的。
作者:爱因斯坦PLUS。2019-03-22 23:21:35
实验一评阅地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/rcloud/p/10561804.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jackyayue/p/10545013.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/Tiger-Hu22/p/10547198.html