动机(Motivate):
在软件开发系统中,客户程序经常会与复杂系统的内部子系统之间产生耦合,而导致客户程序随着子系统的变化而变化。那么如何简化客户程序与子系统之间的交互接口?如何将复杂系统的内部子系统与客户程序之间的依赖解耦?
意图(Intent):
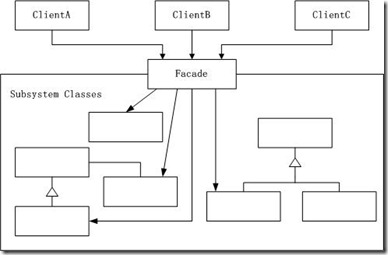
为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。 --------《设计模式》GOF
结构图(Struct):
适用性:
1.为一个复杂子系统提供一个简单接口。
2.提高子系统的独立性。
3.在层次化结构中,可以使用Facade模式定义系统中每一层的入口。
生活中的例子: 
代码实现:
我们平时的开发中其实已经不知不觉的在用Façade模式,现在来考虑这样一个抵押系统,当有一个客户来时,有如下几件事情需要确认:到银行子系统查询他是否有足够多的存款,到信用子系统查询他是否有良好的信用,到贷款子系统查询他有无贷款劣迹。只有这三个子系统都通过时才可进行抵押。我们先不考虑Façade模式,那么客户程序就要直接访问这些子系统,分别进行判断。类结构图下: 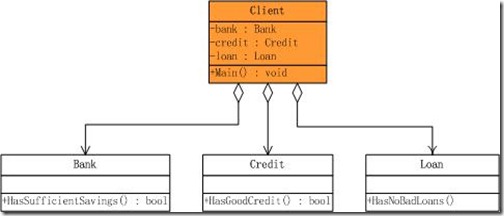
在这个程序中,我们首先要有一个顾客类,它是一个纯数据类,并无任何操作,示意代码:
1 //顾客类
2 public class Customer
3 {
4 private string _name;
5
6 public Customer(string name)
7 {
8 this._name = name;
9 }
10
11 public string Name
12 {
13 get { return _name; }
14 }
15 }
下面这三个类均是子系统类,示意代码:
1 //银行子系统
2 public class Bank
3 {
4 public bool HasSufficientSavings(Customer c, int amount)
5 {
6 Console.WriteLine("Check bank for " + c.Name);
7 return true;
8 }
9 }
10
11 //信用子系统
12 public class Credit
13 {
14 public bool HasGoodCredit(Customer c)
15 {
16 Console.WriteLine("Check credit for " + c.Name);
17 return true;
18 }
19 }
20
21 //贷款子系统
22 public class Loan
23 {
24 public bool HasNoBadLoans(Customer c)
25 {
26 Console.WriteLine("Check loans for " + c.Name);
27 return true;
28 }
29 }
看客户程序的调用:
1 //客户程序
2 public class MainApp
3 {
4 private const int _amount = 12000;
5
6 public static void Main()
7 {
8 Bank bank = new Bank();
9 Loan loan = new Loan();
10 Credit credit = new Credit();
11
12 Customer customer = new Customer("Ann McKinsey");
13
14 bool eligible = true;
15
16 if (!bank.HasSufficientSavings(customer, _amount))
17 {
18 eligible = false;
19 }
20 else if (!loan.HasNoBadLoans(customer))
21 {
22 eligible = false;
23 }
24 else if (!credit.HasGoodCredit(customer))
25 {
26 eligible = false;
27 }
28
29 Console.WriteLine("
" + customer.Name + " has been " + (eligible ? "Approved" : "Rejected"));
30 Console.ReadLine();
31 }
32 }
可以看到,在不用Façade模式的情况下,客户程序与三个子系统都发生了耦合,这种耦合使得客户程序依赖于子系统,当子系统化时,客户程序也将面临很多变化的挑战。一个合情合理的设计就是为这些子系统创建一个统一的接口,这个接口简化了客户程序的判断操作。看一下引入Façade模式后的类结构图: 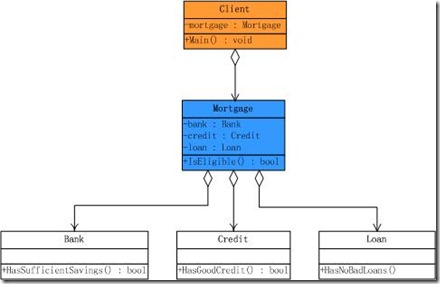 变
变
外观类Mortage的实现如下:
1 /外观类
2 public class Mortgage
3 {
4 private Bank bank = new Bank();
5 private Loan loan = new Loan();
6 private Credit credit = new Credit();
7
8 public bool IsEligible(Customer cust, int amount)
9 {
10 Console.WriteLine("{0} applies for {1:C} loan
",
11 cust.Name, amount);
12
13 bool eligible = true;
14
15 if (!bank.HasSufficientSavings(cust, amount))
16 {
17 eligible = false;
18 }
19 else if (!loan.HasNoBadLoans(cust))
20 {
21 eligible = false;
22 }
23 else if (!credit.HasGoodCredit(cust))
24 {
25 eligible = false;
26 }
27
28 return eligible;
29 }
30 }
顾客类和子系统类的实现仍然如下:
1 //银行子系统
2 public class Bank
3 {
4 public bool HasSufficientSavings(Customer c, int amount)
5 {
6 Console.WriteLine("Check bank for " + c.Name);
7 return true;
8 }
9 }
10
11 //信用证子系统
12 public class Credit
13 {
14 public bool HasGoodCredit(Customer c)
15 {
16 Console.WriteLine("Check credit for " + c.Name);
17 return true;
18 }
19 }
20
21 //贷款子系统
22 public class Loan
23 {
24 public bool HasNoBadLoans(Customer c)
25 {
26 Console.WriteLine("Check loans for " + c.Name);
27 return true;
28 }
29 }
30
31 //顾客类
32 public class Customer
33 {
34 private string name;
35
36 public Customer(string name)
37 {
38 this.name = name;
39 }
40
41 public string Name
42 {
43 get { return name; }
44 }
45 }
而此时客户程序的实现:
1 //客户程序类
2 public class MainApp
3 {
4 public static void Main()
5 {
6 //外观
7 Mortgage mortgage = new Mortgage();
8
9 Customer customer = new Customer("Ann McKinsey");
10 bool eligable = mortgage.IsEligible(customer, 125000);
11
12 Console.WriteLine("
" + customer.Name +
13 " has been " + (eligable ? "Approved" : "Rejected"));
14 Console.ReadLine();
15 }
16 }
可以看到引入Façade模式后,客户程序只与Mortgage发生依赖,也就是Mortgage屏蔽了子系统之间的复杂的操作,达到了解耦内部子系统与客户程序之间的依赖。
.NET架构中的Façade模式
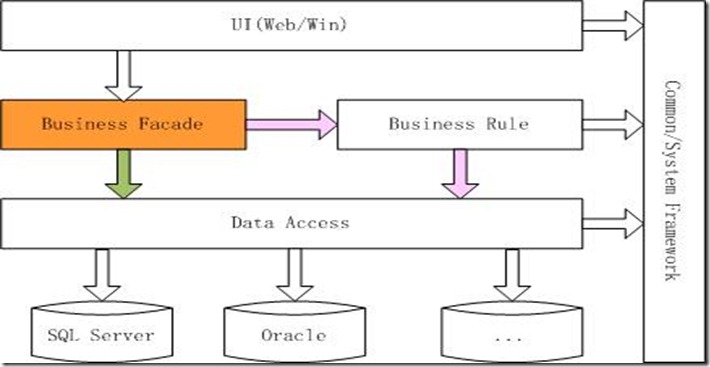
Façade模式在实际开发中最多的运用当属开发N层架构的应用程序了,一个典型的N层结构如下:
在这个架构中,总共分为四个逻辑层,分别为:用户层UI,业务外观层Business Façade,业务规则层Business Rule,数据访问层Data Access。其中Business Façade层的职责如下:
l 从“用户”层接收用户输入
l 如果请求需要对数据进行只读访问,则可能使用“数据访问”层
l 将请求传递到“业务规则”层
l 将响应从“业务规则”层返回到“用户”层
l 在对“业务规则”层的调用之间维护临时状态
对这一架构最好的体现就是Duwamish示例了。在该应用程序中,有部分操作只是简单的从数据库根据条件提取数据,不需要经过任何处理,而直接将数据显示到网页上,比如查询某类别的图书列表。而另外一些操作,比如计算定单中图书的总价并根据顾客的级别计算回扣等等,这部分往往有许多不同的功能的类,操作起来也比较复杂。如果采用传统的三层结构,这些商业逻辑一般是会放在中间层,那么对内部的这些大量种类繁多,使用方法也各异的不同的类的调用任务,就完全落到了表示层。这样势必会增加表示层的代码量,将表示层的任务复杂化,和表示层只负责接受用户的输入并返回结果的任务不太相称,并增加了层与层之间的耦合程度。于是就引入了一个Façade层,让这个Facade来负责管理系统内部类的调用,并为表示层提供了一个单一而简单的接口。看一下Duwamish结构图: 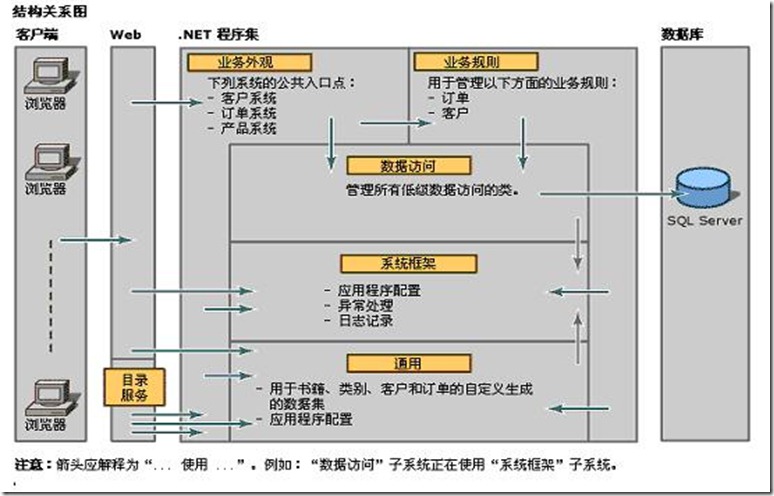
从图中可以看到,UI层将请求发送给业务外观层,业务外观层对请求进行初步的处理,判断是否需要调用业务规则层,还是直接调用数据访问层获取数据。最后由数据访问层访问数据库并按照来时的步骤返回结果到UI层,来看具体的代码实现。
在获取商品目录的时候,Web UI调用业务外观层:
1 productSystem = new ProductSystem();
2 categorySet = productSystem.GetCategories(categoryID);
业务外观层直接调用了数据访问层:
1 public CategoryData GetCategories(int categoryId)
2 {
3 //
4 // Check preconditions
5 //
6 ApplicationAssert.CheckCondition(categoryId >= 0,"Invalid Category Id",ApplicationAssert.LineNumber);
7 //
8 // Retrieve the data
9 //
10 using (Categories accessCategories = new Categories())
11 {
12 return accessCategories.GetCategories(categoryId);
13 }
14
15 }
在添加订单时,UI调用业务外观层:
1 public void AddOrder()
2 {
3 ApplicationAssert.CheckCondition(cartOrderData != null, "Order requires data", ApplicationAssert.LineNumber);
4
5 //Write trace log.
6 ApplicationLog.WriteTrace("Duwamish7.Web.Cart.AddOrder:
CustomerId: " +
7 cartOrderData.Tables[OrderData.CUSTOMER_TABLE].Rows[0][OrderData.PKID_FIELD].ToString());
8 cartOrderData = (new OrderSystem()).AddOrder(cartOrderData);
9 }
业务外观层调用业务规则层:
1 public OrderData AddOrder(OrderData order)
2 {
3 //
4 // Check preconditions
5 //
6 ApplicationAssert.CheckCondition(order != null, "Order is required", ApplicationAssert.LineNumber);
7
8 (new BusinessRules.Order()).InsertOrder(order);
9 return order;
10 }
业务规则层进行复杂的逻辑处理后,再调用数据访问层:
1 public OrderData AddOrder(OrderData order)
2 {
3 //
4 // Check preconditions
5 //
6 ApplicationAssert.CheckCondition(order != null, "Order is required", ApplicationAssert.LineNumber);
7
8 (new BusinessRules.Order()).InsertOrder(order);
9 return order;
10 }
11
12
13 业务规则层进行复杂的逻辑处理后,再调用数据访问层:
14 public bool InsertOrder(OrderData order)
15 {
16 //
17 // Assume it's good
18 //
19 bool isValid = true;
20 //
21 // Validate order summary
22 //
23 DataRow summaryRow = order.Tables[OrderData.ORDER_SUMMARY_TABLE].Rows[0];
24
25 summaryRow.ClearErrors();
26
27 if (CalculateShipping(order) != (Decimal)(summaryRow[OrderData.SHIPPING_HANDLING_FIELD]))
28 {
29 summaryRow.SetColumnError(OrderData.SHIPPING_HANDLING_FIELD, OrderData.INVALID_FIELD);
30 isValid = false;
31 }
32
33 if (CalculateTax(order) != (Decimal)(summaryRow[OrderData.TAX_FIELD]))
34 {
35 summaryRow.SetColumnError(OrderData.TAX_FIELD, OrderData.INVALID_FIELD);
36 isValid = false;
37 }
38 //
39 // Validate shipping info
40 //
41 isValid &= IsValidField(order, OrderData.SHIPPING_ADDRESS_TABLE, OrderData.SHIP_TO_NAME_FIELD, 40);
42 //
43 // Validate payment info
44 //
45 DataRow paymentRow = order.Tables[OrderData.PAYMENT_TABLE].Rows[0];
46
47 paymentRow.ClearErrors();
48
49 isValid &= IsValidField(paymentRow, OrderData.CREDIT_CARD_TYPE_FIELD, 40);
50 isValid &= IsValidField(paymentRow, OrderData.CREDIT_CARD_NUMBER_FIELD, 32);
51 isValid &= IsValidField(paymentRow, OrderData.EXPIRATION_DATE_FIELD, 30);
52 isValid &= IsValidField(paymentRow, OrderData.NAME_ON_CARD_FIELD, 40);
53 isValid &= IsValidField(paymentRow, OrderData.BILLING_ADDRESS_FIELD, 255);
54 //
55 // Validate the order items and recalculate the subtotal
56 //
57 DataRowCollection itemRows = order.Tables[OrderData.ORDER_ITEMS_TABLE].Rows;
58
59 Decimal subTotal = 0;
60
61 foreach (DataRow itemRow in itemRows)
62 {
63 itemRow.ClearErrors();
64
65 subTotal += (Decimal)(itemRow[OrderData.EXTENDED_FIELD]);
66
67 if ((Decimal)(itemRow[OrderData.PRICE_FIELD]) <= 0)
68 {
69 itemRow.SetColumnError(OrderData.PRICE_FIELD, OrderData.INVALID_FIELD);
70 isValid = false;
71 }
72
73 if ((short)(itemRow[OrderData.QUANTITY_FIELD]) <= 0)
74 {
75 itemRow.SetColumnError(OrderData.QUANTITY_FIELD, OrderData.INVALID_FIELD);
76 isValid = false;
77 }
78 }
79 //
80 // Verify the subtotal
81 //
82 if (subTotal != (Decimal)(summaryRow[OrderData.SUB_TOTAL_FIELD]))
83 {
84 summaryRow.SetColumnError(OrderData.SUB_TOTAL_FIELD, OrderData.INVALID_FIELD);
85 isValid = false;
86 }
87
88 if ( isValid )
89 {
90 using (DataAccess.Orders ordersDataAccess = new DataAccess.Orders())
91 {
92 return (ordersDataAccess.InsertOrderDetail(order)) > 0;
93 }
94 }
95 else
96 return false;
97 }
Facade模式的个要点:
从客户程序的角度来看,Facade模式不仅简化了整个组件系统的接口,同时对于组件内部与外部客户程序来说,从某种程度上也达到了一种“解耦”的效果----内部子系统的任何变化不会影响到Facade接口的变化。
Facade设计模式更注重从架构的层次去看整个系统,而不是单个类的层次。Facdae很多时候更是一种架构
设计模式。
注意区分Facade模式、Adapter模式、Bridge模式与Decorator模式。Facade模式注重简化接口,Adapter模式注重转换接口,Bridge模式注重分离接口(抽象)与其实现,Decorator模式注重稳定接口的前提下为对象扩展功能