一、在树莓派中安装opencv库
安装依赖
pip3 install --upgrade setuptools
pip3 install numpy Matplotlib
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev libtiff5-dev libjasper-dev libpng12-dev
sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libv4l-dev
sudo apt-get install libxvidcore-dev libx264-dev
sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev libgtk-3-dev
sudo apt-get install libatlas-base-dev
sudo apt install libqt4-test
sudo apt install libqtgui4
pip3安装opencv以及opencv
pip3 install opencv-python
pip3 install opencv-contrib-python
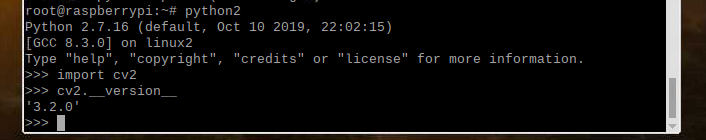
检测安装
二、使用opencv和python控制树莓派的摄像头
相关代码
from picamera.array import PiRGBArray
from picamera import PiCamera
import time
import cv2
camera = PiCamera()
rawCapture = PiRGBArray(camera)
time.sleep(2)
camera.capture(rawCapture, format="bgr")
image = rawCapture.array
cv2.imshow("Image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
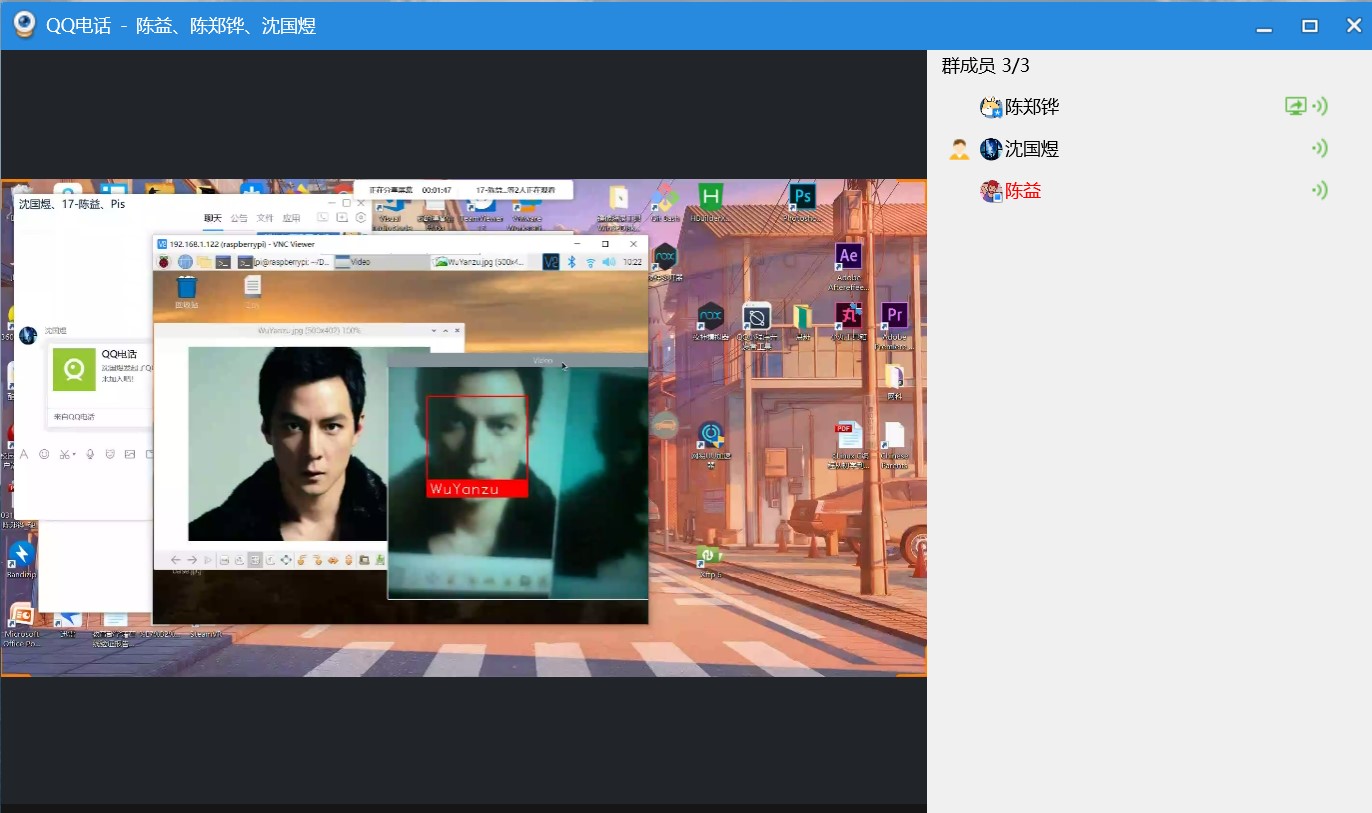
三、利用树莓派的摄像头实现人脸识别
1.facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py
facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py
import face_recognition
import picamera
import numpy as np
camera = picamera.PiCamera()
camera.resolution = (320, 240)
output = np.empty((240, 320, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
print("Loading known face image(s)")
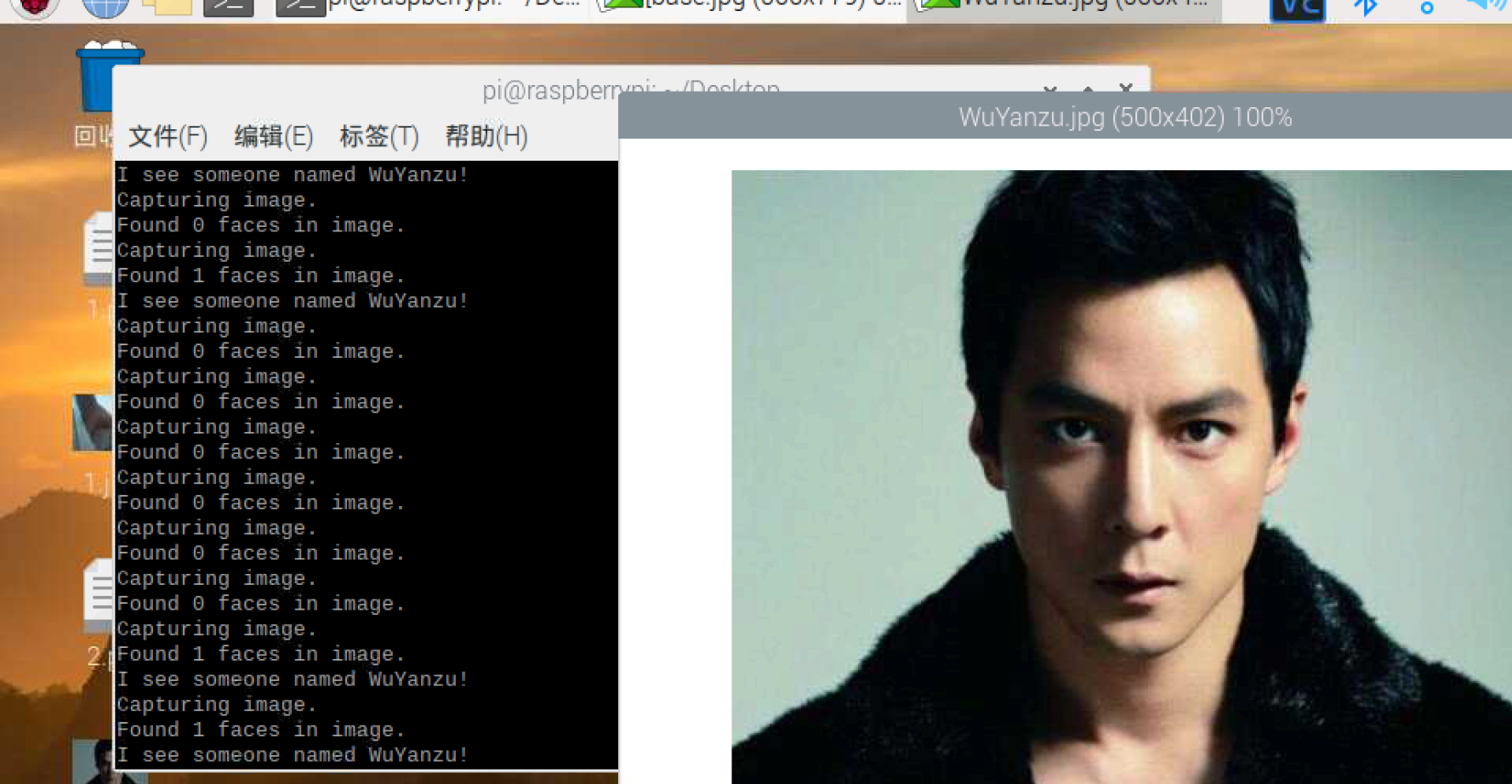
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("WuYanzu.jpg")
obama_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
while True:
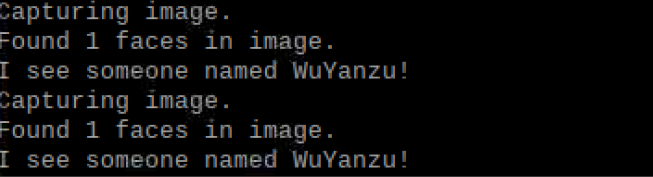
print("Capturing image.")
# Grab a single frame of video from the RPi camera as a numpy array
camera.capture(output, format="rgb")
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(output)
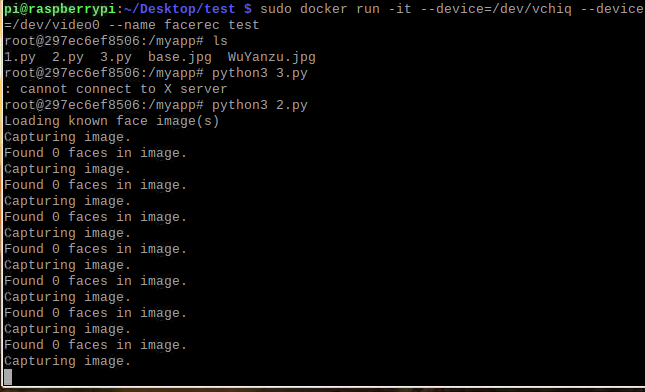
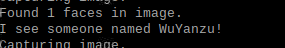
print("Found {} faces in image.".format(len(face_locations)))
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(output, face_locations)
# Loop over each face found in the frame to see if it's someone we know.
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
match = face_recognition.compare_faces([obama_face_encoding], face_encoding)
name = "<Unknown Person>"
if match[0]:
name = "WuYanzu"
print("I see someone named {}!".format(name))
相同路径放一张对比图片,图片名称WuYanzu.jpg
2.facerec_from_webcam_faster.py
facerec_from_webcam_faster.py
import face_recognition
import cv2
import numpy as np
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
wu_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("base.jpg")
wu_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(wu_image)[0]
# Create arrays of known face encodings and their names
known_face_encodings = [
wu_face_encoding,
]
known_face_names = [
"WuYanzu",
]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
# Grab a single frame of video
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
# Only process every other frame of video to save time
if process_this_frame:
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
# # If a match was found in known_face_encodings, just use the first one.
# if True in matches:
# first_match_index = matches.index(True)
# name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
# Or instead, use the known face with the smallest distance to the new face
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
# Display the results
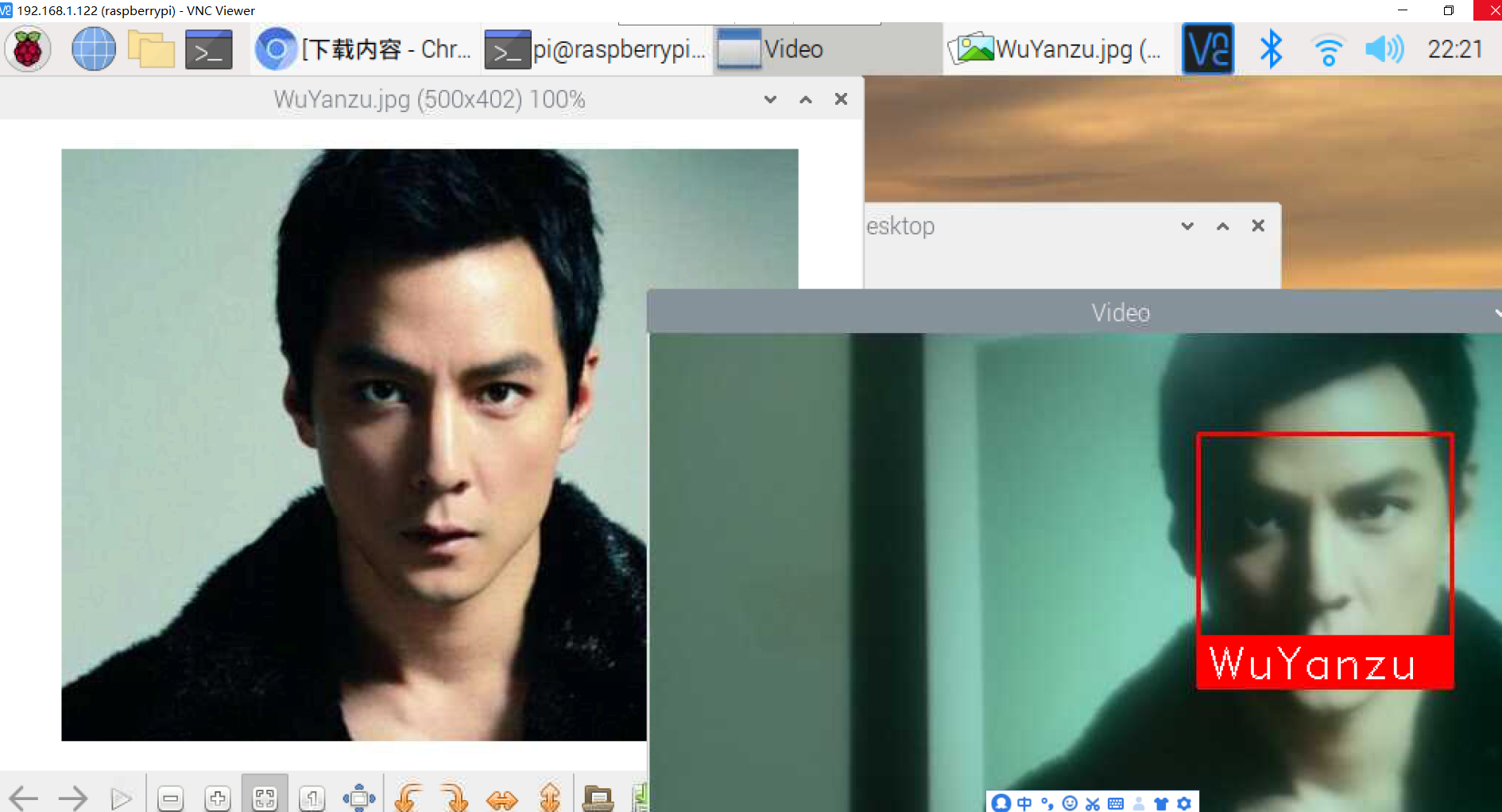
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
# Draw a box around the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Draw a label with a name below the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# Display the resulting image
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
# Hit 'q' on the keyboard to quit!
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release handle to the webcam
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
学习过的图片
四、结合微服务的进阶任务
1.安装docker
下载安装脚本
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh

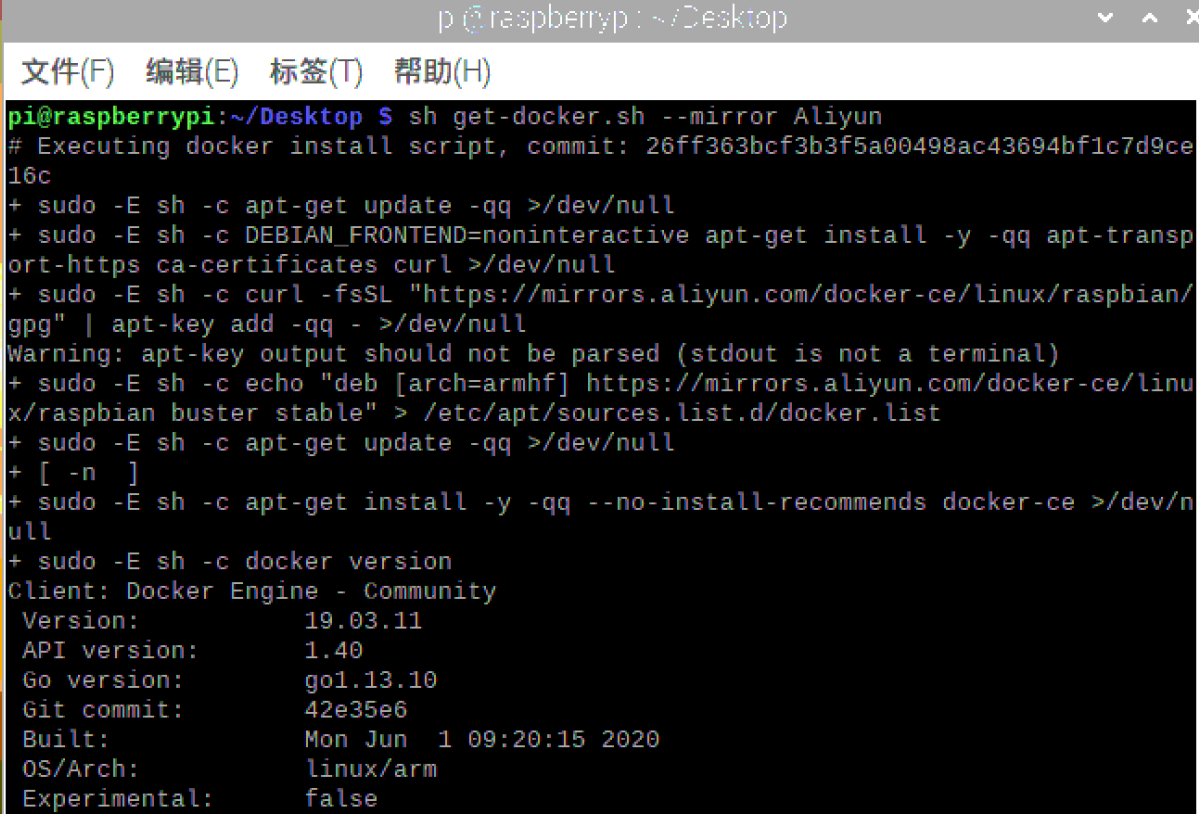
执行安装脚本(阿里云镜像)
sh get-docker.sh --mirror Aliyun
将当前用户加入docker用户组
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER

查看docker版本
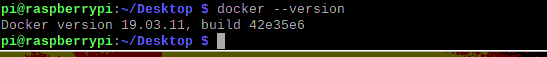
2.配置docker镜像加速
编辑配置文件

restart docker
service docker restart
3.定制opencv镜像
拉取镜像
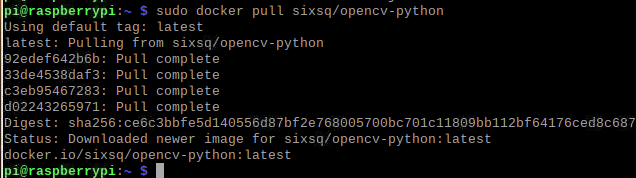
运行此镜像
docker run -it sixsq/opencv-python /bin/bash

在容器中,安装 "picamera[array]" dlib face_recognition
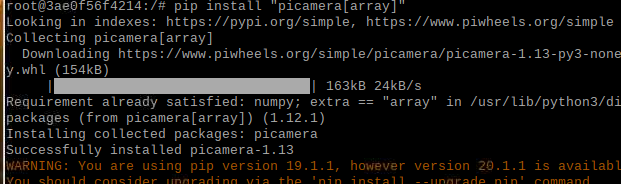
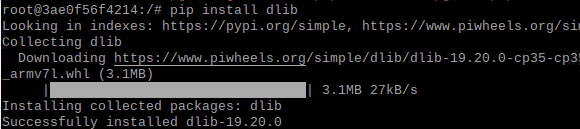

退出容器 commit
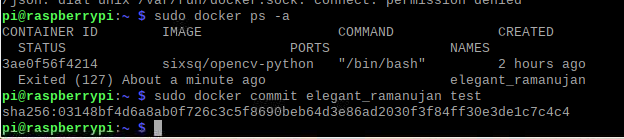
编写Dockerfile
FROM test
MAINTAINER 555
RUN mkdir /myapp
WORKDIR /myapp
COPY myapp .
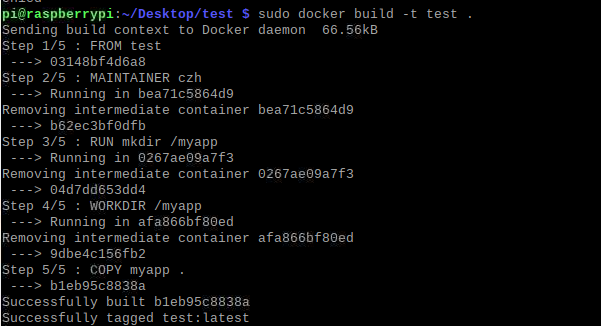
build
docker build -t test .
4.运行容器执行facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py
docker run -it --device=/dev/vchiq --device=/dev/video0 --name facerec myopencv
python3 facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py #2.py
五、记录遇到的问题和解决方法,提供小组成员名单、分工、各自贡献以及在线协作的图片
1.遇到的问题和解决方法
- 问题1:pip install 人脸识别包的时候,速度过慢,网络不稳定就导致重新下载
- 解决方法:从网上下载whl文件、本地安装
- 问题2:最新的OpenCV4不支持Pi
- 解决方法:卸载重新安装OpenCV3
pip3 uninstall opencv-python
pip3 install opencv-python==3.4.6.27
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40868987/article/details/103764696
2.组成员名单、分工、各自贡献以及在线协作的图片
| 学号 | 姓名 | 分工 |
|---|---|---|
| 031702642 | 沈国煜 | OpenCV安装,资料收集,撰写博客 |
| 031702635 | 陈郑铧 | OpenCV安装,人脸识别,微服务,硬件的操作 |
| 031702637 | 陈益 | OpenCV安装,资料收集,修改博客 |