1.Map接口
public interface Map<K,V>
将键映射到值的对象。一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
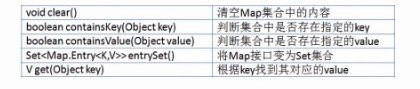
2.HashMap、Hashtable、TreeMap
public class HashMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。(除了非同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap 类与 Hashtable 大致相同。)此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
public class MapDemo { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 hashMap(); } /** * 是二叉树数据结构的实现(红黑树--平衡二叉树) */ public static void treeMap(){ TreeMap<String,String> map=new TreeMap<String,String>(); map.put("1", "hah"); } /** * 线程安全,同步的,效率低,与HashMap相似,初始容量为11,每次扩充2倍+1 */ public static void hashtable(){ Hashtable<String, String> table=new Hashtable<String,String>(); } /** * 使用哈希表(数组+链表)实现,键不能重复,如果相同就会覆盖原来的对象 * 默认创建一个长度为16的数组,加载因子为0.75(当数组满75%的容量后,表示需要重新扩充,又叫哈希表重新散列) * 哈希表保存对象时,会根据key对象的hashcode值对HashMap的容量求余,决定该对象要存在数组的哪个位置, * 如果该位置有对象那么这些对象以链表的结构存储 * 线程不安全,效率高 * 每次扩充2倍 */ public static void hashMap(){ Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String,String>(); map.put("1","小明"); System.out.println("1".hashCode()%16); map.put("2","小花"); System.out.println("2".hashCode()%16); map.put("3","小刚"); System.out.println("3".hashCode()%16); System.out.println("----------"); System.out.println(map.size()); //取值 System.out.println(map.get("1")); System.out.println(map.get("2")); System.out.println(map.containsKey(1)); } }
3.Map集合的输出
在Collection接口中,可以使用iterator()方法为Iterator接口实例化,并且进行输出操作,但是在Map接口中并没有此方法的定义,所以Map接口本身是不能直接使用iterator进行输出的。
hashcode深入分析:两个hashcode值不同,则两个对象一定不同;两个对象不同,hashcode值可能相同;程序员要做的是任何情况下输出同一个对象的hashcode值都应该相同

public class MapIterator { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 iterator(); stack(); queue(); } public static void iterator(){ HashMap<String,Student> map=new HashMap<String,Student>(); map.put("jack", new Student("jack",2)); map.put("tom", new Student("tom",3)); map.put("honey", new Student("honey",4)); //遍历 Set<String> keys=map.keySet(); Iterator<String> i=keys.iterator(); while(i.hasNext()){ String key=i.next(); Student s=map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"-->"+s); } } /** * 堆栈 */ public static void stack(){ Stack<String> s=new Stack<String>(); s.push("xiaoming");//压栈,入栈 s.push("xiaohua"); String str=s.pop();//出栈 System.out.println(str); } /** * 队列 */ public static void queue(){ Queue<String> q=new LinkedList<String>(); q.add("xiaogang"); q.add("xiaobin"); //移除队列的头 String str=q.poll(); System.out.println(str); } }
4.对象一对多关系可以使用HashSet实现
public class Person { private String name; private Set<Book> books=new HashSet<Book>(); public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Set<Book> getBooks() { return books; } public void setBooks(Set<Book> books) { this.books = books; } }
public class Book { private String name; private Person person; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Person getPerson() { return person; } public void setPerson(Person person) { this.person = person; } }