Elasticsearch是一个基于Apache Lucene(TM)的开源搜索引擎。无论在开源还是专有领域,Lucene可以被认为是迄今为止最先进、性能最好的、功能最全的搜索引擎库。
特点:
分布式的实时文件存储,每个字段都被索引并可被搜索
分布式的实时分析搜索引擎库(可做不规则查询)
可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级结构化或非结构化数据
Elasticsearch也使用Java开发并使用Lucene作为其核心来实现所有索引和搜索的功能,但是它的目的是通过简单的RESTful API来隐藏Lucene的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。
ES能做什么?
全文检索(全部字段;值--->数据)、模糊查询(搜索)、数据分析(提供分析语法,例如聚合)
数仓--分析处理--hbase/mysql--es--(分析、检索、搜索、javaee前端可视化)
mysql--->Json(脚本)--->ES
Solr、ElasticSearch、 Hermes(腾讯开发;主要用于实时检索分析,处理数据量庞大)3者的区别:
Solr、ES(都可以做全文检索、搜索、分析,基于lucene)
①. 源自搜索引擎,侧重搜索与全文检索。
②. 数据规模从几百万到千万不等,数据量过亿的集群特别少。
有可能存在个别系统数据量过亿,但这并不是普遍现象(就像Oracle的表里的数据规模有可能超过Hive里一样,但需要小型机)。
Hermes
①. 一个基于大索引技术的海量数据实时检索分析平台。侧重数据分析。
②. 数据规模从几亿到万亿不等。最小的表也是千万级别。
在 腾讯17 台TS5机器,就可以处理每天450亿的数据(每条数据1kb左右),数据可以保存一个月之久。
Solr、ES区别
①. Solr 利用 Zookeeper 进行分布式管理,而 Elasticsearch 自身带有分布式协调管理功能;
②. Solr 支持更多格式的数据,而 Elasticsearch 仅支持json文件格式;
③. Solr 官方提供的功能更多,而 Elasticsearch 本身更注重于核心功能,高级功能多有第三方插件提供;
④. Solr 在传统的搜索应用中表现好于 Elasticsearch,但在处理实时搜索应用时效率明显低于 Elasticsearch
Lucene是一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包,但它不是一个完整的全文检索引擎,而是一个全文检索引擎的架构,提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎
搜索引擎产品简介
安装和配置
安装Centos7、建议内存2G以上、安装java1.8环境
设置IP地址
查看自己电脑的网关号

C:UsersAdministrator>ipconfig 以太网适配器 VMware Network Adapter VMnet1: 连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . : 本地链接 IPv6 地址. . . . . . . . : fe80::7d9a:22ee:77c9:3781%18 IPv4 地址 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.174.1 子网掩码 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 默认网关. . . . . . . . . . . . . : 以太网适配器 VMware Network Adapter VMnet8: 连接特定的 DNS 后缀 . . . . . . . : 本地链接 IPv6 地址. . . . . . . . : fe80::29bd:7dab:56c2:ec50%19 IPv4 地址 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.5 子网掩码 . . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0 默认网关. . . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.2
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
DEVICE="ens33" ONBOOT="yes" IPADDR="192.168.1.0" PREFIX="24" GATEWAY="192.168.1.2" DNS1="114.114.114.114" IPV6_PRIVACY="no"
改成自己的网关(GATEWAY)
# 网络重置
service network restart
添加用户
[root@localhost ~]# adduser elk [root@localhost ~]# passwd elk
以下授权步骤可省略
[root@localhost ~]# whereis sudoers sudoers: /etc/sudoers.d /etc/sudoers /usr/share/man/man5/sudoers.5.gz [root@localhost ~]# ls -l /etc/sudoers -r--r-----. 1 root root 3960 Jul 15 2018 /etc/sudoers [root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/sudoers ## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL linuxidc ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software,
[root@localhost ~]# chmod -v u-w /etc/sudoers
[root@localhost ~]# su elk
Java环境安装
解压安装包
[root@localhost jdk1.8]# tar -zxvf jdk-8u171-linux-x64.tar.gz
设置Java环境变量
[root@localhost jdk1.8.0_171]# vi /etc/profile
在文件最后添加
export JAVA_HOME=/home/elk1/jdk1.8/jdk1.8.0_171 export JRE_HOME=$JAVA_HOME/jre export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/LIB:$JRE_HOME/LIB:$CLASSPATH export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin:$PATH
[root@localhost jdk1.8.0_171]# source /etc/profile [root@localhost jdk1.8.0_171]# java -version java version "1.8.0_171"
ElasticSerach单机安装
[root@localhost elasticserach]# tar -zxvf elasticsearch-6.3.1.tar.gz [root@localhost elasticserach]# cd elasticsearch-6.3.1/bin [root@localhost bin]# ./elasticsearch can not run elasticserach as root [root@localhost bin]# su elk [elk@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch javo.nio.fileAccessDeniedException:/home/elk/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.3.1/config/jvm.options [root@localhost bin]# chown -R elk:elk /home/elk1/elasticsearch ##要在root账户下授权! [elk@localhost config]$ vi jvm.options ##改成2g ## See https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/heap-size.html ## for more information ## ################################################################ # Xms represents the initial size of total heap space # Xmx represents the maximum size of total heap space -Xms2g -Xmx2g [elk@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch [2019-03-23T05:22:00,380][INFO ][o.e.n.Node ] [dbaiLyW] initialized [2019-03-23T05:22:00,380][INFO ][o.e.n.Node ] [dbaiLyW] starting ... 在另外一个窗口: [root@localhost jdk1.8.0_171]# curl 127.0.0.1:9200 { "name" : "dbaiLyW", "cluster_name" : "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid" : "vm5Jpe7OTE-GdV4nUb5q1w", "version" : { "number" : "6.3.1", "build_flavor" : "default", "build_type" : "tar", "build_hash" : "eb782d0", "build_date" : "2018-06-29T21:59:26.107521Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "7.3.1", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" }
#后台启动 [elk@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch -d #关闭程序 [elk@localhost bin]$ ps -ef|grep elastic [elk@localhost bin]$ kill 10097
#设置浏览器访问
[root@localhost bin]systemctl stop firewalld [root@localhost bin]vi config/elasticsearch.yml ##改下地址 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 192.168.1.0
若出现bootstrap checks failed
[root@localhost bin]# vi /etc/security/limits.conf * hard nofile 65536 * soft nofile 131072 * hard nproc 4096 * soft nproc 2048 # End of file 解释说明: nofile - 打开文件的最大数目 noproc - 进程的最大数目 soft 指的是当前系统生效的设置值 hard 表明系统中所能设定的最大值 [root@localhost bin]# vi /etc/sysctl.conf # For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5). vm.max_map_count=655360 fs.file-max=655360 参数解释说明: vm.max_map_count=65530,因此缺省配置下,单个jvm能开启的最大线程数为其一半 file-max是设置 系统所有进程一共可以打开的文件数量
[root@localhost bin]# sysctl -p ##生效配置。
# 测试
Liunx执行: curl 'http://192.168.1.0:9200/?pretty'
浏览器访问:http://192.168.1.0:9200/?pretty
Elasticsearch的交互方式
1、基于HTTP协议,以JSON为数据交互格式的RESTful API(请求方式:GET/POST/PUT/DELETE/HEAD)
# 状态查看命令 语法:ip:post/_cat/[args](?v|?format=json&pretty) (?v表示显示字段说明,?format=json&pretty表示显示成json格式) 1、查看所有索引 GET _cat/indices?v 2、查看es集群状态 GET _cat/health?v
http://192.168.1.0:9200/_cat 在浏览器中输入可以看到它的一些命令
http://192.168.1.0:9200/_cat/health 查看健康状态;
2、Elasticsearch官方提供了多种程序语言的客户端—java,Javascript,.NET,PHP,Perl,Python,以及 Ruby——还有很多由社区提供的客户端和插件
Elasticsearch操作工具(用浏览器测试手动只能完成GET,其他的需要借助工具完成PUT/POST等)
- 浏览器(postman)
- Linux命令行
- Kibana的Dev Tools
安装配置Kibana
[elk@localhost soft]$ tar -zxvf kibana-6.3.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /home/elk/kibana/
[elk@localhost config]$ vi kibana.yml # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "192.168.1.0" ###SentOS6中配置了 ”0.0.0.0” # The URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries. elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.1.0:9200" # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. kibana.index: ".kibana" ##把它打开,创建index索引 ###SentOS6并没有配置它
[elk@localhost ~]$ cd kibana/kibana-6.3.1-linux-x86_64/bin/ [elk@localhost bin]$ ./kibana 在浏览器中访问: http://192.168.1.0:5601/
创建文档语句
PUT atguigu/doc/0 { "name":"zhangsan", "age":10 }
默认情况下,返回结果是按相关性倒序排列的。
_index:文档所在索引名称;
_type:文档所在类型名称;
_id:文档唯一id
_score:每个文档都有相关性评分,_score 的评分越高,相关性越高
_uid:组合id,由_type和_id组成(6.x后,_type不再起作用,同_id)
_source:文档的原始Json数据,包括每个字段的内容
_all:将所有字段内容整合起来,默认禁用(用于对所有字段内容检索)
{ "_index": "kris", //index索引名称 "_type": "doc", //type类型 "_id": "3", "_score": 0.2876821, "_source": { "test2": "haha helo", "first_name": "Douglas", "last_name": "Fir", "age": 35, "about": "I like to build cabinets", "interests": [ "forestry" ] } }
version乐观锁---控制版本号;每次更新数据时,version数值会不一样;
Elasticsearch数据存储方式
数据的插入用PUT,用文档的方式进行数据的存储;
1)面向文档
Elasticsearch是面向文档(document oriented)的,这意味着它可以存储整个对象或文档(document)。然而它不仅仅是存储,还会索引(index)每个文档的内容使之可以被搜索。在Elasticsearch中,你可以对文档(而非成行成列的数据)进行索引、搜索、排序、过滤。这种理解数据的方式与以往完全不同,这也是Elasticsearch能够执行复杂的全文搜索的原因之一。
面向对象(表)是基于二维表(行列excel)的存储模型-如mysql,操作数据时把它当做一个对象,创建封装对象;写sql语句,查询等
面向对象:表 id name age 1 kris 22 2 alex 18 面向文档:单条 ---------------------- 1 kris 22 ; -------------------------------- 2 alex 18; ----------------------------
面向文档(单条)是一条一条的,多个文档在一块,以单条数据位单位;json字符串,可直接进行操作如.split(“ ”);遍历等
2)JSON
ELasticsearch使用Javascript对象符号(JavaScript Object Notation),也就是JSON,作为文档序列化格式。JSON现在已经被大多语言所支持,而且已经成为NoSQL领域的标准格式。它简洁、简单且容易阅读。更方便的堆数据进行操作;更方便的分词,全文检索、搜索等
以下使用JSON文档来表示一个用户对象:

{ "email": "john@smith.com", "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "info": { "bio": "Eco-warrior and defender of the weak", "age": 25, "interests": [ "dolphins", "whales" ] }, "join_date": "2014/05/01" }
存储结构
5.x
index--->①库database type -->②表 table field-->③字段column document-->row一行数据;存储数据的基本单元;
6.0之后
一个index中只能有一个type,
一个type中有多个文档,
一个document中有多个field字段
index可以看作一个表:index( index:_doc默认的 )
7.x,type就被取消了
 ES6.0之后就不能运行有type2了!!
ES6.0之后就不能运行有type2了!!
在Es6.0之后,一个index中只运行有1个type,弱化了表的概念;(有可能把type取消掉,完全的面向文档)
名词解释 索引 index 一个索引就是一个拥有几分相似特征的文档的集合。比如说,你可以有一个客户数据的索引,另一个产品目录的索引,还有一个订单数据的索引。一个索引由一个名字来标识(必须全部是小写字母的),并且当我们要对对应于这个索引中的文档进行索引、搜索、更新和删除的时候,都要使用到这个名字。在一个集群中,可以定义任意多的索引。 类型 type 在一个索引中,你可以定义一种或多种类型。一个类型是你的索引的一个逻辑上的分类/分区,其语义完全由你来定。通常,会为具有一组共同字段的文档定义一个类型。比如说,我们假设你运营一个博客平台并且将你所有的数据存储到一个索引中。在这个索引中,你可以为用户数据定义一个类型,为博客数据定义另一个类型,当然,也可以为评论数据定义另一个类型。 字段Field 相当于是数据表的字段,对文档数据根据不同属性进行的分类标识 document 一个document相当于mysql中的一条 一个文档是一个可被索引的基础信息单元。比如,你可以拥有某一个客户的文档,某一个产品的一个文档,当然,也可以拥有某个订单的一个文档。文档以JSON(Javascript Object Notation)格式来表示,而JSON是一个到处存在的互联网数据交互格式。在一个index/type里面,你可以存储任意多的文档。注意,尽管一个文档,物理上存在于一个索引之中,文档必须被索引/赋予一个索引的type。
GET 索引 _mapping 是查看字段的结构类型,ES可以自动推断出来,但这种是很不讲究的;
ES文本字段类型有:text(分词,占据很大资源,用空间换取时间;text还有一个局限性就是分词字段是不能聚合的,groupBy后边的字段,如果有这种字段就要设置成不分词)
和keyword(不分词,比如订单状态、手机号等);本质上这两个都是加索引的,只是一个分词一个不分词;
要不要索引:与mysql正好相反,ES只要是插入默认都是会加索引的;过滤、聚合、搜索、匹配、排序等这些字段是需要索引,有些字段是不需要索引的,如电话脱敏的不需要索引;加索引也是会浪费很大空间,如果不加索引得加上: “index”:false
Elasticsearch检索 URI查询没有请求体
GET/my_*/_search 可匹配所有的月份
2019-03-xx
2019-04-xx
检索文档
Mysql : select * from user where id = 1;
ES : GET /kris/doc/1 ;可以把/kris/doc理解为表名user,检索id=1的;
简单检索
Mysql : select * from user;
ES : GET /kris/doc/_search GET /megacorp/employee/_search
全文检索
ES : GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=haha (查询字段中带有haha的数据,q相当于关键字,haha为值); 指定字段查询q=user:kris或q=kris;
查询出所有文档字段值为haha的文档;
q="want to"组合查询,没有""是单个和组合都会查询到
GET /my_index/_search?q=alfred&df=user&sort=age:asc&from=4&size=10&timeout=1s #from, size是用于分页;
q : 指定查询的语句,例如q=aa或q=user:aa df:q中不指定字段默认查询的字段,如果不指定,es会查询所有字段 Sort:排序,asc升序,desc降序 timeout:指定超时时间,默认不超时 from,size:用于分页;from从第 页查询 size页
搜索
ES : GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=hello (只要字段中包含hello,不管前边后边有什么值都可以查询到)
查询出所有文档字段值分词后包含hello的文档;mysql中的模糊查询(会影响性能,索引就不能使用了;)不规则匹配查询;搜索;
Elasticsearch搜索原理(内部运行机制)
search: 关键字;对关键字分词;
分词-->在资源库(比如百度,对分词在资源库中进行批评)中做一个全文搜索;
在资源库中也会有一个分词(每个字段都会进行分词);
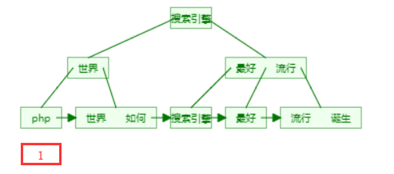
倒排索引:(值---关键字(文档id的集合等)去匹配倒排索引---->数据文档(得到每一个具体的文档的ID));用值去找文档ID即倒排索引;
分词: k1: v1, k1: v1,v2, k1: v3 倒排索引:每个词对应的id会形成 索引 v1:1, 2 v2:2 (只有第二个中有这个值) v3:3
正排索引和倒排索引:
l 正排索引
记录文档Id到文档内容、单词的关联关系
l 倒排索引
记录单词到文档id的关联关系,包含:
单词词典(Term DicTionary):记录所有文档的单词,一般比较大;通过某个字--->数据
倒排索引(Posting List):记录单词倒排列表的关联信息
如搜索硅谷Term Dictionary 硅谷
Posting List
DocId TF Position Offset 1 1 0 <0,2> 3 1 0 <0,2>
DocId:文档id,文档的原始信息
TF:单词频率,记录该词在文档中出现的次数,用于后续相关性算分(评分,想把搜索内容靠前些,即可把评分高点就会靠前了;)
Position:位置(文档),记录Field分词后,单词所在的位置,从0开始;北京 是 最 漂亮 的,北京在0位;
Offset:偏移量,记录单词在文档中开始和结束位置,用于高亮显示等
分词后(通过B+Tree)就可以高效查询;
内存结构--B+Tree
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BPlusTree.html
每个文档字段都有自己的倒排索引
比如:北京 是 最 漂亮 的

每个值都会通过算法计算出一个值,那句话中某个值去搜索,它会先去顶点,如果比这个值(最)大就看左边(是),比它大就在左边(北京);
通过北京这个词就可以看到倒排索引,id、TF、Position、Offset等; B+Tree每个单元最多2个
它的所有数据都保存在最后一层的节点上,每两个节点之间会有一个链表(一个指向);可以递归获取这个值;
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/ComparisonSort.html
分词
分词是指将文本转换成一系列单词(term or token)的过程,也可以叫做文本分析,在es里面称为Analysis
分词的机制
过滤
Character Filter 对原始文本进行处理 例:去除html标签、特殊字符等
Tokenizer 将原始文本进行分词 例:培训机构-->培训,机构
Token Filters 分词后的关键字进行加工 例:转小写、删除语气词、近义词和同义词等
l 分词API 分词器依赖索引
1)、直接指定测试(指定分词器)
POST _analyze { "analyzer":"standard", "text": "we are family" } 与倒排索引相对应: { "tokens": [ { "token": "we", "start_offset": 0, ###we,前闭后开的区间[ ) "end_offset": 2, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "are", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 6, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 1 }, { "token": "family", "start_offset": 7, "end_offset": 13, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 2 } ] }
2)、针对索引的字段进行分词测试(利用该字段的分词器);主要用于测试
GET /kris/doc/_search?q=like 可以搜索出来;--> PUT创建时就已经按照一定规则分词了,
默认的分词器
POST atguigu/_analyze { "field": "name", "text":"hello world" }
POST atguigu/_analyze { "field": "about", ##about可检测出默认的分词器 "text":"we are family" "text":"we are fam?ily" 会把? 两边的分成2部分; }

{ "tokens": [ { "token": "we", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 2, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "are", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 6, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 1 }, { "token": "family", "start_offset": 7, "end_offset": 13, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 2 } ] }
3)、自定义分词器
request: POST _analyze { "tokenizer": "standard", "filter": ["lowercase"], "text":"Hello WORLD" } response: { "tokens": [ { "token": "hello", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 5, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "world", "start_offset": 6, "end_offset": 11, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 1 } ] }
Elasticsearch自带的分词器
分词器(Analyzer) 特点 Standard(es默认) 支持多语言,按词切分并做小写处理 Simple 按照非字母切分,小写处理 Whitespace 按照空格来切分 Stop 去除语气助词,如the、an、的、这等 Keyword 不分词 Pattern 正则分词,默认w+,即非字词符号做分割符 Language 常见语言的分词器(30+)
中文分词
官方默认的中文分词器就是逐字拆解。显然不符合中文的搜索习惯。
为了更好的根据中文的语义环境搜索,需要把词进行拆解。
目前很多大厂都自己开发了词库,但是工作量巨大。省心一些的办法就是利用第三方开源分词器,达到基本满意的效果。
IK 实现中英文单词切分 自定义词库
不要直接下源码(下载与ES相当于的版本),不然还要打包编译,在release中下载,选择相匹配的版本;
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/tag/v6.3.1
解压,将压缩包解压到/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.3.1/plugins/ik 下,在plugins目录下创建ik目录; 最后要记得分发到其他机器!!!!!
重新启动ElasticSearch,即可加载IK分词器
IK提供了两个分词算法ik_smart 和 ik_max_word,其中 ik_smart 为最少切分,粗粒度分词器; ik_max_word为最细粒度划分,细粒度分词器;
用kibana进行测试:
1)最小切分: ik_smart分词器;
POST _analyze //或者使用GET _analyze{ ...} { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "text":"php是世界上最好的语言" }

{ "tokens": [ { "token": "php", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 3, "type": "ENGLISH", "position": 0 }, { "token": "是", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 1 }, { "token": "世界上", "start_offset": 4, "end_offset": 7, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 2 }, { "token": "最好", "start_offset": 7, "end_offset": 9, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 3 }, { "token": "的", "start_offset": 9, "end_offset": 10, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 4 }, { "token": "语言", "start_offset": 10, "end_offset": 12, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 5 } ] }
2)最细切分 把词分的更细 ik_max_word分词器
POST _analyze //或者使用GET _analyze{ ...} { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text":"php是世界上最好的语言" }

{ "tokens": [ { "token": "php", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 3, "type": "ENGLISH", "position": 0 }, { "token": "是", "start_offset": 3, "end_offset": 4, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 1 }, { "token": "世界上", "start_offset": 4, "end_offset": 7, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 2 }, { "token": "世界", "start_offset": 4, "end_offset": 6, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 3 }, { "token": "上", "start_offset": 6, "end_offset": 7, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 4 }, { "token": "最好", "start_offset": 7, "end_offset": 9, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 5 }, { "token": "的", "start_offset": 9, "end_offset": 10, "type": "CN_CHAR", "position": 6 }, { "token": "语言", "start_offset": 10, "end_offset": 12, "type": "CN_WORD", "position": 7 } ] }
世界上又分成了 世界 上,有重复的;
自定义词库:
由于第三方分词器预存的词库有限,远远赶不上层出不穷的新词。
比如:
GET _analyze { "text": "荣耀10青春版 幻彩渐变 2400万AI自拍 全网通版4GB+64GB 渐变蓝 移动联通电信4G全面屏手机 双卡双待" , "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }
实际执行的话,会发现

比如 双卡双待 这种词并没有识别成为一个关键词,而是逐字拆开的。
那么这种情况下,如果想一直保持词汇能够同步更新就需要,维护一个能够自主维护的词库。
搭建自定义的词库的几种方法:关键看这个文件===>>
[kris@hadoop101 config]$ vim /elasticsearch-6.6.0/plugins/ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd"> <properties> <comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment> <!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 --> <entry key="ext_dict"></entry> <!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典--> <entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry> <!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 --> <!-- <entry key="remote_ext_dict">words_location</entry> --> <!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典--> <!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> --> </properties>
一种办法可以自己添加个文本文件放到服务器中的某个位置,然后把位置路径写在本地位置,
但是这样如果需要管理分词的运营人员,要登录linux服务器进行修改非常不方便。尤其是es的集群环境,每个服务器都要改,更麻烦。
另一种办法可以自己添加词库,作为网络服务发布出来。整个ES集群可以共享使用。
搭建分词服务模块---SpringBoot外部服务

controller:

@RestController public class DictController { @GetMapping("dict") public String dict(){ StringBuilder dict=new StringBuilder(); //此处应该查询数据库 获得分词列表 dict.append("蓝瘦香菇 "); dict.append("双卡双待 "); response.addHeader("Last-Modified",new Date().toString()); return dict.toString(); } }
修改词库配置:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 -->
<entry key="ext_dict"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典-->
<entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 -->
<entry key="remote_ext_dict">http://192.168.11.1:8090/dict</entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典-->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>
更新现有词库:
POST gmall_sale_detail/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed
文档操作
创建
文档通过其_index、_type、_id唯一确定
PUT /{index}/{type}/{id}
{
"field": "value",
...
}
id不指定就会自动生成一个20位的_id;
更新即直接修改值去PUT,version会发生变化;在响应中,我们可以看到Elasticsearch把_version增加
局部更新:
PUT /website/blog/123 { "title": "My first blog entry", "text": "I am starting to get the hang of this...", "date": "2014/01/02" } GET website/blog/123 ## 局部更新 POST /website/blog/123/_update { "doc" : { "title" : "--My first blog--", "date": "2018/08/10" } }
pretty--格式化:
在任意的查询字符串中增加pretty参数,类似于上面的例子。会让Elasticsearch美化输出(pretty-print)JSON响应以便更加容易阅读。_source字段不会被美化,它的样子与我们输入的一致。
GET请求返回的响应内容包括{"found": true}。这意味着文档已经找到。如果我们请求一个不存在的文档,依旧会得到一个JSON,不过found值变成了false。
此外,HTTP响应状态码也会变成'404 Not Found'代替'200 OK'。我们可以在curl后加-i参数得到响应头:
curl -i -XGET http://localhost:9200/website/blog/124?pretty
[elk@localhost config]$ curl -i -XGET http://192.168.1.101:9200/website/blog/123 HTTP/1.1 200 OK content-type: application/json; charset=UTF-8 content-length: 183 {"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123","_version":3,"found":true,"_source":{"title":"--My first blog--","text":"I am starting to get the hang of this...","date":"2018/08/10"}}[elk@localhost config]$ [elk@localhost config]$ curl -i -XGET http://192.168.1.101:9200/website/blog/123?pretty HTTP/1.1 200 OK content-type: application/json; charset=UTF-8 content-length: 239 { "_index" : "website", "_type" : "blog", "_id" : "123", "_version" : 3, "found" : true, "_source" : { "title" : "--My first blog--", "text" : "I am starting to get the hang of this...", "date" : "2018/08/10" } }
检索文档的一部分
GET /website/blog/123?_source=title,text
_source字段现在只包含我们请求的字段,而且过滤了date字段;
GET /website/blog/123_source 只想得到_source字段而不要其他的元数据
删除文档
删除文档的语法模式与之前基本一致,只不过要使用DELETE方法:
DELETE /website/blog/123
批量插入(从mysql中) | (每个json中不能有换行),先建立索引+doc,使用_bulk
POST test_search_index/doc/_bulk {"index":{"_id":1}} {"username":"alfred way","job":"java engineer","age":18,"birth":"1991-12-15","isMarried":false} {"index":{"_id":2}} {"username":"alfred","job":"java senior engineer and java specialist","age":28,"birth":"1980-05-07","isMarried":true} {"index":{"_id":3}} {"username":"lee","job":"java and ruby engineer","age":22,"birth":"1985-08-07","isMarried":false} {"index":{"_id":4}} {"username":"lee junior way","job":"ruby engineer","age":23,"birth":"1986-08-07","isMarried":false}

{ "took": 28, "errors": false, "items": [ { "index": { "_index": "test_search_index", "_type": "doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 3, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 2, "_primary_term": 1, "status": 200 } }, { "index": { "_index": "test_search_index", "_type": "doc", "_id": "2", "_version": 3, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 2, "_primary_term": 1, "status": 200 } }, { "index": { "_index": "test_search_index", "_type": "doc", "_id": "3", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 0, "_primary_term": 1, "status": 201 } }, { "index": { "_index": "test_search_index", "_type": "doc", "_id": "4", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 3, "_primary_term": 1, "status": 201 } } ] }
Mapping
实际上每个type中的字段是什么数据类型,由mapping定义。
但是如果没有设定mapping系统会自动,根据一条数据的格式来推断出应该的数据格式。
查看mapping: GET movie_index/_mapping/movie ES会推断出应该的数据格式比如: true/false → boolean 1020 → long 20.1 → double “2018-02-01” → date “hello world” → text +keyword 默认只有text会进行分词,keyword是不会分词的字符串。 mapping除了自动定义,还可以手动定义,但是只能对新加的、没有数据的字段进行定义。一旦有了数据就无法再做修改了。 注意:虽然每个Field的数据放在不同的type下,但是同一个名字的Field在一个index下只能有一种mapping定义。
作用:
定义数据库中的表的结构的定义,通过mapping来控制索引存储数据的设置
- 定义Index下的字段名(Field Name)
- 定义字段的类型,比如数值型、字符串型、布尔型等
- 定义倒排索引相关的配置,比如documentId、记录position、打分等
获取索引mapping; 不进行配置时,自动创建的mapping
请求: GET /kris/_mapping
响应: key-word是分词类型

{ "kris": { "mappings": { "doc": { "properties": { "age": { "type": "long" }, "birth": { "type": "date" }, "isMarried": { "type": "boolean" }, "job": { "type": "text", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } }, "username": { "type": "text", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } } } } } } }
自定义mapping
请求:

GET my_index/_mapping DELETE my_index PUT my_index { "mappings":{ "doc":{ "dynamic":"false", "properties":{ "title":{ "type":"text" }, "name":{ "type":"keyword" }, "age":{ "type":"integer" } } } } } POST my_index/doc { "title":"class1", "name":"smile", "age":19 } #"title1":"ssm", #"title2":"bbb" GET my_index/_search
Dynamic Mapping
es依靠json文档字段类型来实现自动识别字段类型,支持的类型
mapping中的字段类型一旦设定后,禁止修改
原因:Lucene实现的倒排索引生成后不允许修改(提高效率)
如果要修改字段的类型,需要从新建立索引,然后做reindex操作
dynamic设置
- true:允许自动新增字段(默认的配置)
- False:不允许自动新增字段,但是文档可以正常写入,无法对字段进行查询操作
- strict:文档不能写入(如果写入会报错)
dynamic 默认为true,可以增加数据类型,约束性变小
dynamic=false 可以正常写入,可增加新的字段类型,不能更改,不会报错
dynamic="strict", 不能增加新的字段类型,会报错;可以对字段的值进行更改;
Index属性
Index属性,控制当前字段是否索引,默认为true,即记录索引,false不记录,即不可以搜索,比如:手机号、身份证号等敏感信息,不希望被检索
基于中文分词搭建索引
1、建立mapping
PUT movie_chn { "mappings": { "movie":{ "properties": { "id":{ "type": "long" }, "name":{ "type": "text" , "analyzer": "ik_smart" }, "doubanScore":{ "type": "double" }, "actorList":{ "properties": { "id":{ "type":"long" }, "name":{ "type":"keyword" } } } } } } } 插入数据 PUT /movie_chn/movie/1 { "id":1, "name":"红海行动", "doubanScore":8.5, "actorList":[ {"id":1,"name":"张译"}, {"id":2,"name":"海清"}, {"id":3,"name":"张涵予"} ] } PUT /movie_chn/movie/2 { "id":2, "name":"湄公河行动", "doubanScore":8.0, "actorList":[ {"id":3,"name":"张涵予"} ] } PUT /movie_chn/movie/3 { "id":3, "name":"红海事件", "doubanScore":5.0, "actorList":[ {"id":4,"name":"张晨"} ] } 查询测试 GET /movie_chn/movie/_search { "query": { "match": { "name": "红海战役" } } } GET /movie_chn/movie/_search { "query": { "term": { "actorList.name": "张译" } } }