
try { if(resultSet!=null){ resultSet.close(); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(preparedStatement!=null){ preparedStatement.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(connection!=null){ connection.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/erbing/p/5805727.html
一、相关概念
1.什么是JDBC
JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序。
2.数据库驱动
我们安装好数据库之后,我们的应用程序也是不能直接使用数据库的,必须要通过相应的数据库驱动程序,通过驱动程序去和数据库打交道。其实也就是数据库厂商的JDBC接口实现,即对Connection等接口的实现类的jar文件。
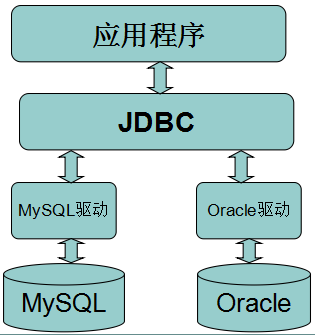
二、常用接口
1.Driver接口
Driver接口由数据库厂家提供,作为java开发人员,只需要使用Driver接口就可以了。在编程中要连接数据库,必须先装载特定厂商的数据库驱动程序,不同的数据库有不同的装载方法。如:
装载MySql驱动:Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
装载Oracle驱动:Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
2.Connection接口
Connection与特定数据库的连接(会话),在连接上下文中执行sql语句并返回结果。DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password)方法建立在JDBC URL中定义的数据库Connection连接上。
连接MySql数据库:Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://host:port/database", "user", "password");
连接Oracle数据库:Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:database", "user", "password");
连接SqlServer数据库:Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver://host:port; DatabaseName=database", "user", "password");
常用方法:
-
- createStatement():创建向数据库发送sql的statement对象。
- prepareStatement(sql) :创建向数据库发送预编译sql的PrepareSatement对象。
- prepareCall(sql):创建执行存储过程的callableStatement对象。
- setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):设置事务是否自动提交。
- commit() :在链接上提交事务。
- rollback() :在此链接上回滚事务。
3.Statement接口
用于执行静态SQL语句并返回它所生成结果的对象。
三种Statement类:
-
- Statement:由createStatement创建,用于发送简单的SQL语句(不带参数)。
- PreparedStatement :继承自Statement接口,由preparedStatement创建,用于发送含有一个或多个参数的SQL语句。PreparedStatement对象比Statement对象的效率更高,并且可以防止SQL注入,所以我们一般都使用PreparedStatement。
- CallableStatement:继承自PreparedStatement接口,由方法prepareCall创建,用于调用存储过程。
常用Statement方法:
-
- execute(String sql):运行语句,返回是否有结果集
- executeQuery(String sql):运行select语句,返回ResultSet结果集。
- executeUpdate(String sql):运行insert/update/delete操作,返回更新的行数。
- addBatch(String sql) :把多条sql语句放到一个批处理中。
- executeBatch():向数据库发送一批sql语句执行。
4.ResultSet接口
ResultSet提供检索不同类型字段的方法,常用的有:
-
- getString(int index)、getString(String columnName):获得在数据库里是varchar、char等类型的数据对象。
- getFloat(int index)、getFloat(String columnName):获得在数据库里是Float类型的数据对象。
- getDate(int index)、getDate(String columnName):获得在数据库里是Date类型的数据。
- getBoolean(int index)、getBoolean(String columnName):获得在数据库里是Boolean类型的数据。
- getObject(int index)、getObject(String columnName):获取在数据库里任意类型的数据。
ResultSet还提供了对结果集进行滚动的方法:
-
- next():移动到下一行
- Previous():移动到前一行
- absolute(int row):移动到指定行
- beforeFirst():移动resultSet的最前面。
- afterLast() :移动到resultSet的最后面。
使用后依次关闭对象及连接:ResultSet → Statement → Connection
三、使用JDBC的步骤
加载JDBC驱动程序 → 建立数据库连接Connection → 创建执行SQL的语句Statement → 处理执行结果ResultSet → 释放资源
1.注册驱动 (只做一次)
方式一:Class.forName(“com.MySQL.jdbc.Driver”);
推荐这种方式,不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
方式二:DriverManager.registerDriver(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver);
会造成DriverManager中产生两个一样的驱动,并会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
2.建立连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
URL用于标识数据库的位置,通过URL地址告诉JDBC程序连接哪个数据库,URL的写法为:
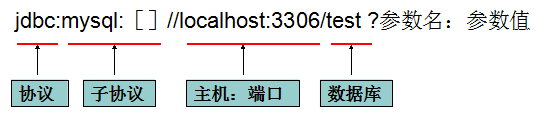
其他参数如:useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
3.创建执行SQL语句的statement
//存在sql注入风险,statement

public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } testDelete(); } public static void testDelete() throws SQLException{ Connection connection=getConnection(); Statement statement=createStatement(connection); String id="2"; //存在sql注入的危险 //如果用户传入的id为“5 or 1=1”,那么将删除表中的所有记录 String sql="delete from t_blog where id="+id; statement.execute(sql); } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl,user,pwd); } public static Statement createStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { return connection.createStatement(); }
//不存在sql诸如风险,PreparedStatement

public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } testPreparedStatement(); } public static void testPreparedStatement() throws SQLException { Connection connection = getConnection(); int id = 1; String sql = "delete from t_blog where id=?"; //PreparedStatement 有效的防止sql注入(SQL语句在程序运行前已经进行了预编译,当运行时动态地把参数传给PreprareStatement时, //即使参数里有敏感字符如 or '1=1'也数据库会作为一个参数一个字段的属性值来处理而不会作为一个SQL指令) PreparedStatement preparedStatement = createPreparedStatement(connection, sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);//占位符顺序从1开始 int clomSize = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println("影响的数据库行数=》" + clomSize); } public static PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection connection, String sql) throws SQLException { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, pwd); }
//处理结果

public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } testResult(); } public static void testResult() throws SQLException{ Connection connection = getConnection(); int id=2; String sql="select * from t_blog where id>=?"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement=createPreparedStatement(connection,sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1,id); ResultSet resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()){ int rid=resultSet.getInt(1); String name=resultSet.getString(2); String context=resultSet.getString(3); Date date=resultSet.getDate(4); System.out.println("读取的记录=>"+rid+"-"+name+"-"+context+"-"+ DateFormatUtils.format(date,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); } } public static PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection connection, String sql) throws SQLException { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, pwd); }
//释放资源

try { if(resultSet!=null){ resultSet.close(); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(preparedStatement!=null){ preparedStatement.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(connection!=null){ connection.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
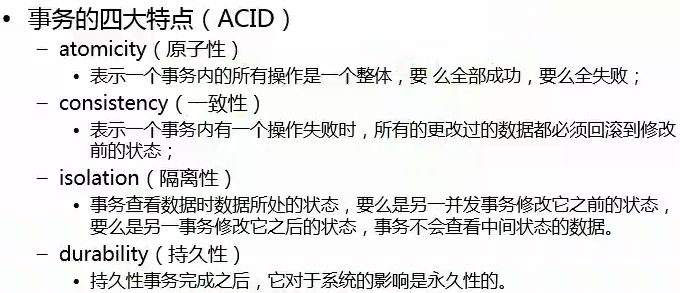
四、事务(ACID特点、隔离级别、提交commit、回滚rollback)


1.批处理Batch


public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } testBatch(); } public static void testBatch() throws SQLException { Connection connection = getConnection(); Statement statement=connection.createStatement(); for(int i=4;i<104;i++){ String sql="insert into t_blog (id,name,context,createDateTime) values ('"+i+"','tst3数据库','jdbc学习3','2018-01-01 12:00:00') "; statement.addBatch(sql); } statement.executeBatch(); statement.close(); connection.close(); }
