一、
1.特点
(1)merge-sort : to sort an array, divide it into two halves, sort the two halves (recursively), and then merge the results. As you will see, one of mergesort’s most attractive properties is that it guarantees to sort any array of N items in time proportional to N log N. Its prime disadvantage is that it uses extra space proportional to N.
(2)
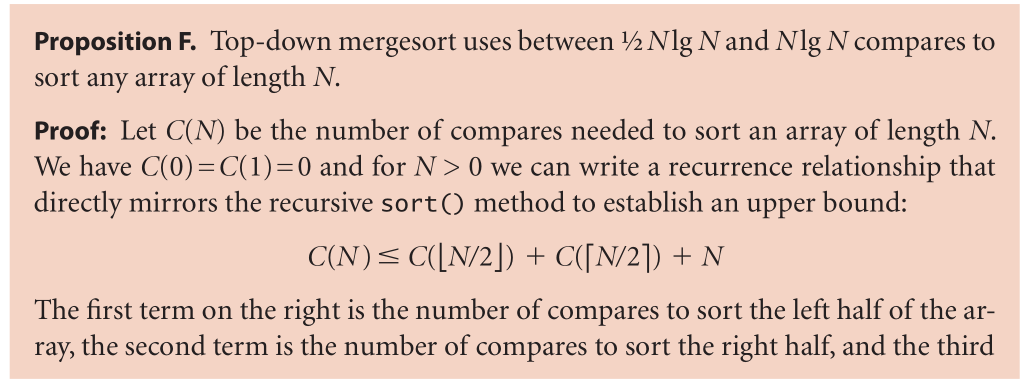
(3)

(4)
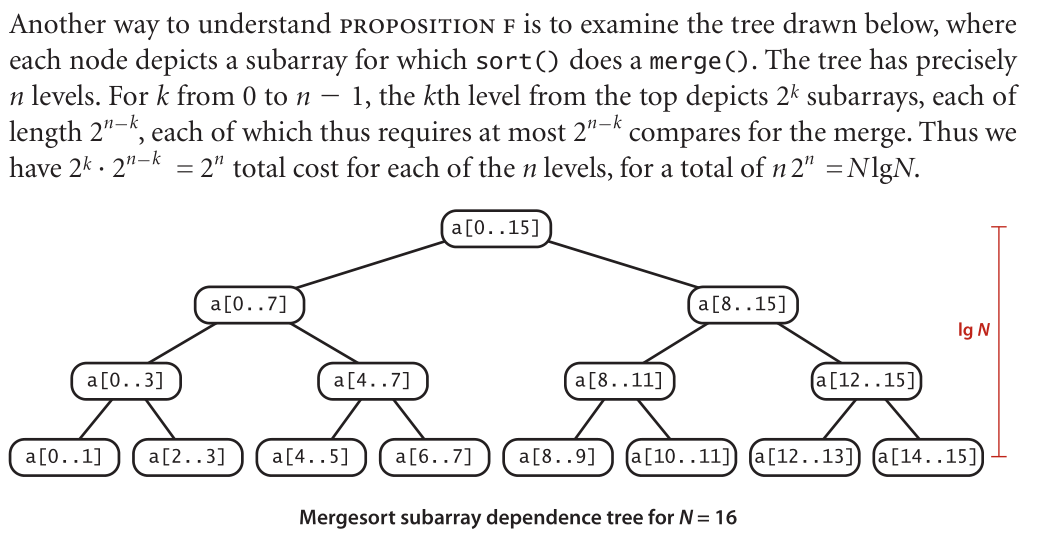
(5)

2.缺点
■ Mergesort is not optimal with respect to space usage.
■ The worst case may not be likely in practice.
■ Operations other than compares (such as array accesses) may be important.
■ One can sort certain data without using any compares.
Thus, we shall be considering several other sorting methods in this book.
3.介绍

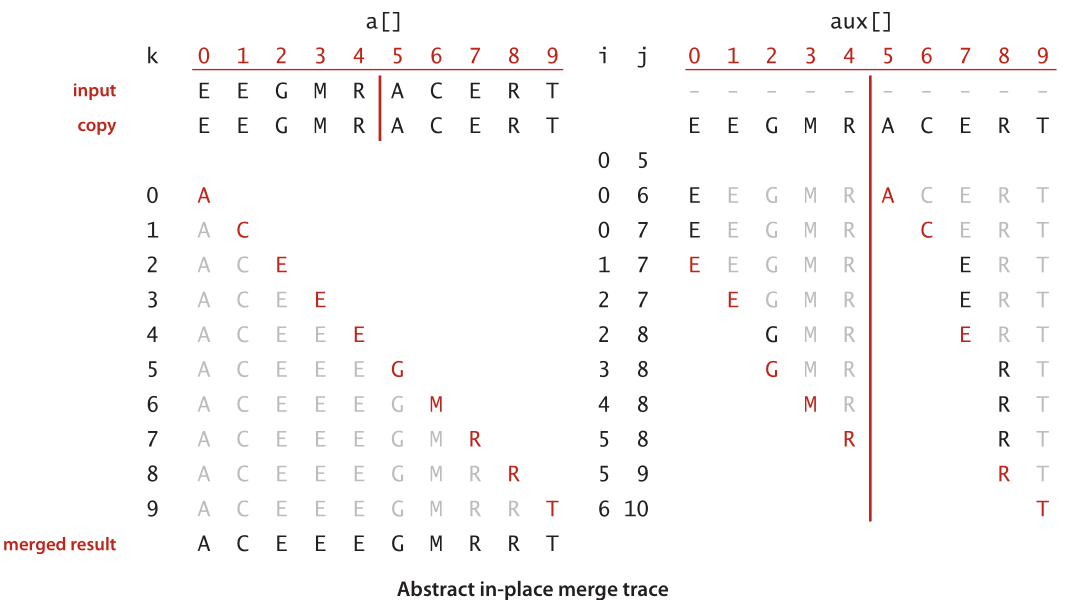


二、
1.代码
1 package algorithms.mergesort22; 2 3 import algorithms.util.StdIn; 4 import algorithms.util.StdOut; 5 6 /****************************************************************************** 7 * Compilation: javac Merge.java 8 * Execution: java Merge < input.txt 9 * Dependencies: StdOut.java StdIn.java 10 * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/tiny.txt 11 * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/words3.txt 12 * 13 * Sorts a sequence of strings from standard input using mergesort. 14 * 15 * % more tiny.txt 16 * S O R T E X A M P L E 17 * 18 * % java Merge < tiny.txt 19 * A E E L M O P R S T X [ one string per line ] 20 * 21 * % more words3.txt 22 * bed bug dad yes zoo ... all bad yet 23 * 24 * % java Merge < words3.txt 25 * all bad bed bug dad ... yes yet zoo [ one string per line ] 26 * 27 ******************************************************************************/ 28 29 /** 30 * The <tt>Merge</tt> class provides static methods for sorting an 31 * array using mergesort. 32 * <p> 33 * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort">Section 2.2</a> of 34 * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. 35 * For an optimized version, see {@link MergeX}. 36 * 37 * @author Robert Sedgewick 38 * @author Kevin Wayne 39 */ 40 public class Merge { 41 42 // This class should not be instantiated. 43 private Merge() { } 44 45 // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 ..hi] using aux[lo .. hi] 46 private static void merge(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { 47 // precondition: a[lo .. mid] and a[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays 48 assert isSorted(a, lo, mid); 49 assert isSorted(a, mid+1, hi); 50 51 // copy to aux[] 52 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 53 aux[k] = a[k]; 54 } 55 56 // merge back to a[] 57 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 58 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 59 if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; 60 else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; 61 else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++]; 62 else a[k] = aux[i++]; 63 } 64 65 // postcondition: a[lo .. hi] is sorted 66 assert isSorted(a, lo, hi); 67 } 68 69 // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi] 70 private static void sort(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int hi) { 71 if (hi <= lo) return; 72 int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; 73 sort(a, aux, lo, mid); 74 sort(a, aux, mid + 1, hi); 75 merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi); 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order. 80 * @param a the array to be sorted 81 */ 82 public static void sort(Comparable[] a) { 83 Comparable[] aux = new Comparable[a.length]; 84 sort(a, aux, 0, a.length-1); 85 assert isSorted(a); 86 } 87 88 89 /*************************************************************************** 90 * Helper sorting functions. 91 ***************************************************************************/ 92 93 // is v < w ? 94 private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) { 95 return v.compareTo(w) < 0; 96 } 97 98 // exchange a[i] and a[j] 99 private static void exch(Object[] a, int i, int j) { 100 Object swap = a[i]; 101 a[i] = a[j]; 102 a[j] = swap; 103 } 104 105 106 /*************************************************************************** 107 * Check if array is sorted - useful for debugging. 108 ***************************************************************************/ 109 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) { 110 return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1); 111 } 112 113 private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) { 114 for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++) 115 if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false; 116 return true; 117 } 118 119 120 /*************************************************************************** 121 * Index mergesort. 122 ***************************************************************************/ 123 // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 .. hi] using aux[lo .. hi] 124 private static void merge(Comparable[] a, int[] index, int[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { 125 126 // copy to aux[] 127 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 128 aux[k] = index[k]; 129 } 130 131 // merge back to a[] 132 int i = lo, j = mid+1; 133 for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { 134 if (i > mid) index[k] = aux[j++]; 135 else if (j > hi) index[k] = aux[i++]; 136 else if (less(a[aux[j]], a[aux[i]])) index[k] = aux[j++]; 137 else index[k] = aux[i++]; 138 } 139 } 140 141 /** 142 * Returns a permutation that gives the elements in the array in ascending order. 143 * @param a the array 144 * @return a permutation <tt>p[]</tt> such that <tt>a[p[0]]</tt>, <tt>a[p[1]]</tt>, 145 * ..., <tt>a[p[N-1]]</tt> are in ascending order 146 */ 147 public static int[] indexSort(Comparable[] a) { 148 int N = a.length; 149 int[] index = new int[N]; 150 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 151 index[i] = i; 152 153 int[] aux = new int[N]; 154 sort(a, index, aux, 0, N-1); 155 return index; 156 } 157 158 // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi] 159 private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int[] index, int[] aux, int lo, int hi) { 160 if (hi <= lo) return; 161 int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; 162 sort(a, index, aux, lo, mid); 163 sort(a, index, aux, mid + 1, hi); 164 merge(a, index, aux, lo, mid, hi); 165 } 166 167 // print array to standard output 168 private static void show(Comparable[] a) { 169 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { 170 StdOut.println(a[i]); 171 } 172 } 173 174 /** 175 * Reads in a sequence of strings from standard input; mergesorts them; 176 * and prints them to standard output in ascending order. 177 */ 178 public static void main(String[] args) { 179 //String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings(); 180 Integer[] a = {3,1,2,5,4}; 181 Merge.sort(a); 182 show(a); 183 } 184 }
2.可视化
package algorithms.mergesort22; import algorithms.util.StdDraw; import algorithms.util.StdRandom; /****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac MergeBars.java * Execution: java MergeBars M N * Dependencies: StdDraw.java * * Sort N random real numbers between 0 and 1 (with M disintct values) * using mergesort with cutoff to insertion sort. * * Visualize the results by ploting bars with heights proportional * to the values. * * % java MergeBars 1000 96 * * Comments * -------- * - suggest removing the 10% default StdDraw border * - if image is too large, it may not display properly but you can * still save it to a file * ******************************************************************************/ public class MergeBars { private static final int VERTICAL = 70; private static final int CUTOFF = 12; private static int numberOfRows; private static int row = 0; // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 .. hi] using aux[lo .. hi] public static void merge(double[] a, double[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { // copy to aux[] for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { aux[k] = a[k]; } // merge back to a[] int i = lo, j = mid+1; for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++]; else a[k] = aux[i++]; } } // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi] private static void sort(double[] a, double[] aux, int lo, int hi) { int N = hi - lo + 1; if (N <= CUTOFF) { insertionSort(a, lo, hi); show(a, lo, hi); return; } if (hi <= lo) return; int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; sort(a, aux, lo, mid); sort(a, aux, mid + 1, hi); merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi); show(a, lo, hi); } public static void sort(double[] a) { double[] aux = new double[a.length]; sort(a, aux, 0, a.length-1); } // sort from a[lo] to a[hi] using insertion sort private static void insertionSort(double[] a, int lo, int hi) { for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--) exch(a, j, j-1); } private static boolean less(double v, double w) { return v < w; } private static void exch(double[] a, int i, int j) { double t = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = t; } // draw one row of trace private static void show(double[] a, int lo, int hi) { double y = numberOfRows - row - 1; for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) { if (k < lo) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.LIGHT_GRAY); else if (k > hi) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.LIGHT_GRAY); else StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLACK); StdDraw.filledRectangle(k, y + a[k]*.25, .25, a[k]*.25); } row++; } public static void main(String[] args) { int M = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); int N = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); if (args.length == 3) { long seed = Long.parseLong(args[2]); StdRandom.setSeed(seed); } double[] a = new double[N]; double[] b = new double[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { a[i] = (1 + StdRandom.uniform(M)) / (double) M; b[i] = a[i]; } // precompute the number of rows StdDraw.show(0); numberOfRows = 0; sort(b); numberOfRows = row; row = 0; StdDraw.clear(); StdDraw.setCanvasSize(800, numberOfRows*VERTICAL); StdDraw.show(0); StdDraw.square(.5, .5, .5); StdDraw.setXscale(-1, N); StdDraw.setYscale(-0.5, numberOfRows); StdDraw.show(0); sort(a); StdDraw.show(0); } }