一、聚集索引介绍
1.什么是聚集索引?
InnoDB’s clustered indexes actually store a B-Tree index and the rows together in the same structure.

2.为什么一张表只能一个聚集索引?
When a table has a clustered index, its rows are actually stored in the index’s leaf pages.The term “clustered” refers to the fact that rows with adjacent key values are stored close to each other. You can have only one clustered index per table, because you can’t store the rows in two places at once. (However, covering indexes let you emulate mul-
tiple clustered indexes; more on this later.)
3.聚集索引的优点
• You can keep related data close together. For example, when implementing a mailbox, you can cluster by user_id , so you can retrieve all of a single user’s messages by fetching only a few pages from disk. If you didn’t use clustering, each message might require its own disk I/O.
• Data access is fast. A clustered index holds both the index and the data together in one B-Tree, so retrieving rows from a clustered index is normally faster than a comparable lookup in a nonclustered index.
• Queries that use covering indexes can use the primary key values contained at the leaf node.
4.聚集索引的缺点
• Clustering gives the largest improvement for I/O-bound workloads. If the data fits in memory the order in which it’s accessed doesn’t really matter, so clustering doesn’t give much benefit.
• Insert speeds depend heavily on insertion order. Inserting rows in primary key order is the fastest way to load data into an InnoDB table. It might be a good idea to reorganize the table with OPTIMIZE TABLE after loading a lot of data if you didn’t load the rows in primary key order.
• Updating the clustered index columns is expensive, because it forces InnoDB to move each updated row to a new location.
• Tables built upon clustered indexes are subject to page splits when new rows are inserted, or when a row’s primary key is updated such that the row must be moved.A page split happens when a row’s key value dictates that the row must be placed into a page that is full of data. The storage engine must split the page into two to
accommodate the row. Page splits can cause a table to use more space on disk.
• Clustered tables can be slower for full table scans, especially if rows are less densely packed or stored nonsequentially because of page splits.
• Secondary (nonclustered) indexes can be larger than you might expect, because their leaf nodes contain the primary key columns of the referenced rows.
• Secondary index accesses require two index lookups instead of one.
二、聚集索引(用innodb)与非聚集索引(用MyISAM)的区别
表结构
1 CREATE TABLE layout_test ( 2 col1 int NOT NULL, 3 col2 int NOT NULL, 4 PRIMARY KEY(col1), 5 KEY(col2) 6 );
1.MyISAM的结构



In fact, in MyISAM, there is no structural difference between a primary key and any other index. A primary key is simply a unique, nonnullable index named PRIMARY .
2.Innodb的结构

At first glance, that might not look very different from Figure 5-5. But look again, and notice that this illustration shows the whole table, not just the index. Because the clustered index “is” the table in InnoDB, there’s no separate row storage as there is for MyISAM.
Each leaf node in the clustered index contains the primary key value, the transaction ID, and rollback pointer InnoDB uses for transactional and MVCC purposes, and the rest of the columns (in this case, col2 ). If the primary key is on a column prefix, InnoDB includes the full column value with the rest of the columns.
Also in contrast to MyISAM, secondary indexes are very different from clustered indexes in InnoDB. Instead of storing “row pointers,” InnoDB’s secondary index leaf nodes contain the primary key values, which serve as the “pointers” to the rows. This strategy reduces the work needed to maintain secondary indexes when rows move or
when there’s a data page split. Using the row’s primary key values as the pointer makes the index larger, but it means InnoDB can move a row without updating pointers to it.


区别总结:
(1)第一个重大区别是InnoDB的数据文件本身就是索引文件。从上文知道,MyISAM索引文件和数据文件是分离的,索引文件仅保存数据记录的地址。而在InnoDB中,表数据文件本身就是按B+Tree组织的一个索引结构,这棵树的叶节点data域保存了完整的数据记录。这个索引的key是数据表的主键,因此InnoDB表数据文件本身就是主索引。
(2)第二个与MyISAM索引的不同是InnoDB的辅助索引data域存储相应记录主键的值而不是地址。换句话说,InnoDB的所有辅助索引都引用主键作为data域。所以辅助索引搜索需要检索两遍索引:首先检索辅助索引获得主键,然后用主键到主索引中检索获得记录。
(3)聚集索引一个表只能有一个,而非聚集索引一个表可以存在多个(因为前者的叶子结点就包含数据,而后者是指针)
(4)聚集索引存储记录是物理上连续存在,而非聚集索引是逻辑上的连续,物理存储并不连续(不知道对不对)
三、用聚集索引时,primary key是否连续的影响
1.

Notice that not only does it take longer to insert the rows with the UUID primary key,but the resulting indexes are quite a bit bigger. Some of that is due to the larger primary key, but some of it is undoubtedly due to page splits and resultant fragmentation as well.
2.主键是否连续为什么会有差别?
连续主键的插入
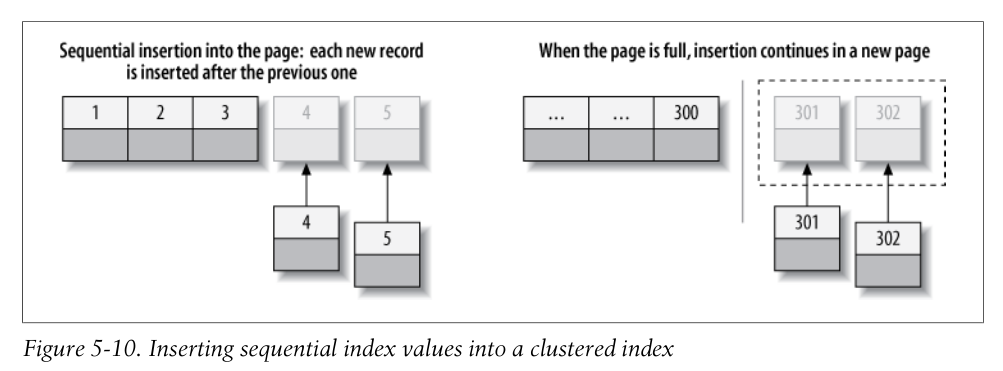
不连续主键的插入

插入不连续主键的缺点:
• The destination page might have been flushed to disk and removed from the caches,or might not have ever been placed into the caches, in which case InnoDB will have to find it and read it from the disk before it can insert the new row. This causes a lot of random I/O.
• When insertions are done out of order, InnoDB has to split pages frequently to make room for new rows. This requires moving around a lot of data, and modifying at least three pages instead of one.
• Pages become sparsely and irregularly filled because of splitting, so the final data is fragmented.