Given a non-empty binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Input:
3
/
9 20
/
15 7
Output: [3, 14.5, 11]
Explanation:
The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Note:
- The range of node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
这个题主要想总结一下bfs算法:
广度优先遍历:类似于树的层序遍历。将根放入队列,一层层遍历,将根弹出后,将左右孩子加入队列。
1、树的广度优先遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> bfs(TreeNode root){ ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>(); if(root==null) return list; Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode treeNode=queue.poll(); if(treeNode.left!=null) queue.add(treeNode.left); if(treeNode.right!=null) queue.add(treeNode.right); list.add(treeNode.val); } return list; } }
2、图的广度优先遍历
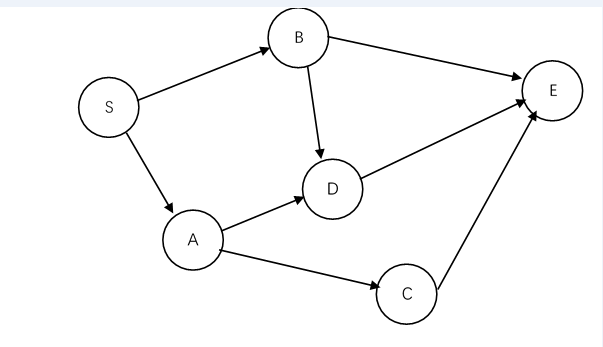
以s为顶点的邻接表为:
S -> A -> B
A -> C -> D
B -> E
class Solution {
static HashMap<Character,LinkedList<Character>> graph;//输入的邻接表
static HashMap<Character,Integer> dirt;//距离集合
public static void bfs(HashMap<Character,LinkedList<Character>> graph,
HashMap<Character,Integer> dirt,char start){
Queue<Character> queue=new LinkedList<Character>();
queue.add(start);//把起点加入队列
dirt.put(start,0);//记录每个节点距离顶点的距离
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
char top=queue.poll();//取出队列顶的元素
int d=dirt.get(top)+1;
for(Character c:graph.get(top)){
if(!dirt.containsKey(c)){
dirt.put(c,d);
queue.add(c);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// s顶点的邻接表
LinkedList<Character> list_s = new LinkedList<Character>();
list_s.add('A');
list_s.add('B');
LinkedList<Character> list_a = new LinkedList<Character>();
list_a.add('C');
list_a.add('D');
LinkedList<Character> list_b = new LinkedList<Character>();
list_b.add('D');
list_b.add('E');
LinkedList<Character> list_c = new LinkedList<Character>();
list_c.add('E');
LinkedList<Character> list_d = new LinkedList<Character>();
list_c.add('E');
//构造图
graph = new HashMap<Character, LinkedList<Character>>();
graph.put('S', list_s);
graph.put('A', list_a);
graph.put('B', list_b);
graph.put('C', list_c);
graph.put('D', list_d);
graph.put('E', new LinkedList<Character>());
//调用
dirt = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
bfs(graph, dirt, 'S');
}
}
3、本题解法:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) { List<Double> result =new ArrayList<>(); if(root==null) return result; Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int cur=queue.size(); double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<cur;i++){ TreeNode treeNode=queue.poll(); sum+=treeNode.val; if(treeNode.left!=null) queue.add(treeNode.left); if(treeNode.right!=null) queue.add(treeNode.right); } result.add(sum/cur); } return result; } }