Netty内部的io.netty.util.concurrent.Future<V> 继承自java.util.concurrent.Future<V>,而Promise<V>是前者的一个特殊实现。

(一)jdk中future和netty中future的比较
jdk中future:
// 取消异步操作 boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); // 异步操作是否取消 boolean isCancelled(); // 异步操作是否完成,正常终止、异常、取消都是完成 boolean isDone(); // 阻塞直到取得异步操作结果 V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; // 同上,但最长阻塞时间为timeout V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException,TimeoutException;
jdk中future的特点:
1.无论结果是成功还是失败还是取消,返回的都是isdone();
2.而且我们在异步操作触发和结束的时候比较关心其他的一些操作,在jdk的future中无法进行补充。所以netty对future做了扩展。
netty中future(以下为扩展内容):
// 异步操作完成且正常终止
boolean isSuccess();
// 异步操作是否可以取消
boolean isCancellable();
// 异步操作失败的原因
Throwable cause();
// 添加一个监听者,异步操作完成时回调,类比javascript的回调函数
Future<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
// 增长多个回调方法
Future<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
// 删除回调方法
Future<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
// 删除多个回调方法
Future<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
// 阻塞等待,且若是失败抛出异常
Future<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;
// 同上,区别是不可中断阻塞等待过程
Future<V> syncUninterruptibly();
// 阻塞等待
Future<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
// 同上,区别是不可中断阻塞等待过程
Future<V> awaitUninterruptibly();
V getNow();
netty中future的特点:
1.操作结果分为success,fail,canceled三种;
2.并且通过addlisteners()方法可以添加回调操作,即触发或者完成时需要进行的操作;
3.await()和sync(),可以以阻塞的方式等待异步完成;getnow()可以获得异步操作的结果,如果还未完成则返回Null;
综合以上的分析,给出一张表示future的状态图来增强对future的理解:
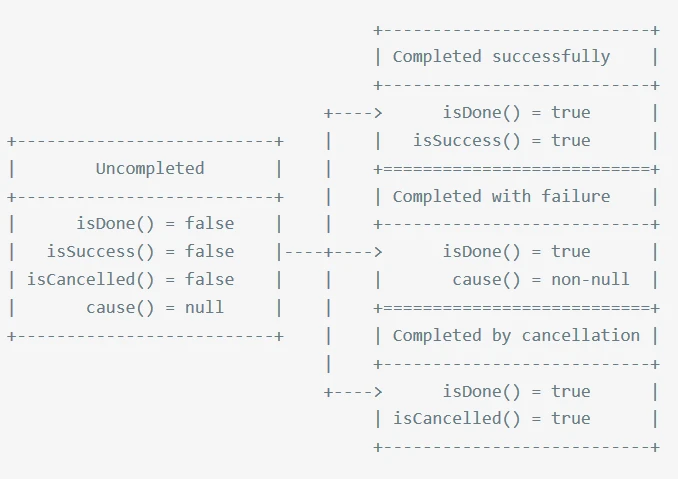
注释:future只有两种状态,unconpleted和conpleted.
completedfuture表示已经完成异步操做,该类在异步操做结束时建立,用户使用addlistener()方法提供异步操做方法。
(二)abstractfuture
abstractfuture类实现future接口,在其中主要实现了get()方法,以阻塞的方式来取得异步操作的结果,其功能与jdk中future的get()方法类似。
abstractfuture源码:
@Override public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { //阻塞直到异步任务完成 await(); Throwable cause = cause(); if (cause == null) { //获得异步操作结果 return getNow(); } //操作失败则抛出异常 if (cause instanceof CancellationException) { throw (CancellationException) cause; } throw new ExecutionException(cause);
}
该类中get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 实现方式与get()大致相同。
(三)completefuture
completedfuture表示已经完成异步操作,该类在异步操作结束时创建,用户使用addlistener()方法提供异步操作方法。
completefuture的状态:
@Override public boolean isDone() { return true; }
completefuture表示已经完成异步操作,所以isdone()方法返回true;并且sync()方法和await()方法会立即返回。
@Override public Future<V> sync() throws InterruptedException { return this; }
触发操作的执行者(eventexecutor)
private final EventExecutor executor; protected CompleteFuture(EventExecutor executor) { this.executor = executor; } protected EventExecutor executor() { return executor; }
completefuture中维护了一个eventexecutor实例,用来执行listener中的任务。
触发操作的执行过程:
第一步addlistener():
#completefuture类 public Future<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener) { if (listener == null) { throw new NullPointerException("listener"); } DefaultPromise.notifyListener(executor(), this, listener); return this;
调用addlistener()方法后,DefaultPromise会调用静态方法notifyListener(),来执行listener中的操作。
#DefaultPromise类 protected static void notifyListener( EventExecutor eventExecutor, final Future<?> future, final GenericFutureListener<?> listener) { //省略 …… notifyListenerWithStackOverFlowProtection(eventExecutor, future, listener); }
然后再看看notifyListenerWithStackOverFlowProtection()
#DefaultPromise类 private static void notifyListenerWithStackOverFlowProtection(final EventExecutor executor, final Future<?> future, final GenericFutureListener<?> listener) { if (executor.inEventLoop()) { //省略,这段代码表示在本线程中执行 …… } //在外部触发,则将其封装成runnable任务 safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { notifyListener0(future, listener); } }); }
接下来的safeexecute()和notifylistener0()就很简单了,
#DefaultPromise类 private static void safeExecute(EventExecutor executor, Runnable task) { try { //将任务添加到任务队列中等待执行 executor.execute(task); } //省略 …… } private static void notifyListener0(Future future, GenericFutureListener l) { try { //可以清楚的看到,执行到了listener中的operationcomplete(future)方法 l.operationComplete(future); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("An exception was thrown by " + l.getClass().getName() + ".operationComplete()", t); } }
completefuture类总结:
1.conpletefuture中保存了eventexecutor的信息,用来执行listener中的任务。
2.调用了future的addlistener()方法后,将listener中的操作封装成runnble任务扔到eventexecutor中的任务队列中等待执行
3.completefuture表示已经完成异步操作,状态是isdone。
(四)channelfuture
这是一个继承future的接口,顾名思义,该接口与通道操作有关,所以在channelfuture接口中,除了覆盖future的功能外,只提供了一个channel()抽象方法。
Channel channel();
(五)completechannelfuture
completechannelfuture类实现channelfuture接口,继承completefuture类。
abstract class CompleteChannelFuture extends CompleteFuture<Void> implements ChannelFuture
异步操作结果的获取
尖括号中的泛型表示返回结果的类型,此处是void,表示不关心返回的结果。
@Override public Void getNow() { return null; }
getnow()方法的返回结果为null,结合前面对abstractfuture类中get()方法的分析,可以得知在completechannelfuture跟get相关的方法返回的结果都是null.
completechannelfuture的初始化
类中的channel字段:
private final Channel channel;
类的初始化:
protected CompleteChannelFuture(Channel channel, EventExecutor executor) { super(executor); if (channel == null) { throw new NullPointerException("channel"); } this.channel = channel; }
eventexecutor的管理:
@Override protected EventExecutor executor() { EventExecutor e = super.executor(); if (e == null) { return channel().eventLoop(); } else { return e; } }
如果父类中eventexecutor不为空,则返回父类中的eventexecutor,否则返回channel中保存的eventexecutor。
completechannelfuture中的addlistener()和await(),sync()等方法的特点和completefuture类相似。
(六)Succeededchannelfuture/FailedChannelFuture
这两个类继承自completechannelfuture,一个表示的状态是success,另一个表示操作失败。
#FailedChannelFuture @Override public Throwable cause() { return cause; } #Succeededchannelfuture @Override public boolean isSuccess() { return true; }
参考:
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012979865
https://blog.csdn.net/moneywenxue/article/details/116905669