题目如下:
Given a binary tree
rootand an integertarget, delete all the leaf nodes with valuetarget.Note that once you delete a leaf node with value
target, if it's parent node becomes a leaf node and has the valuetarget, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you can't).Example 1:
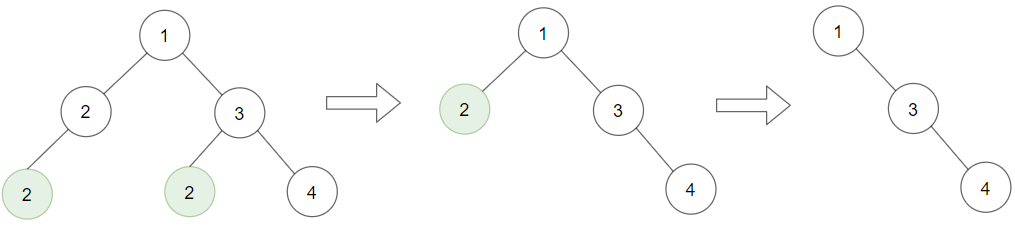
Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 Output: [1,null,3,null,4] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed (Picture in left). After removing, new nodes become leaf nodes with value (target = 2) (Picture in center).Example 2:
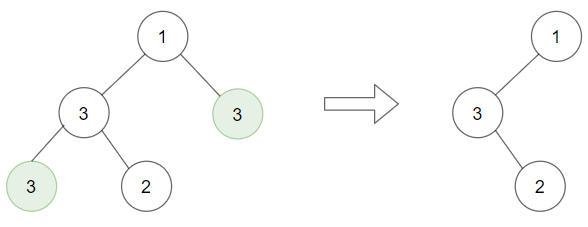
Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 Output: [1,3,null,null,2]Example 3:
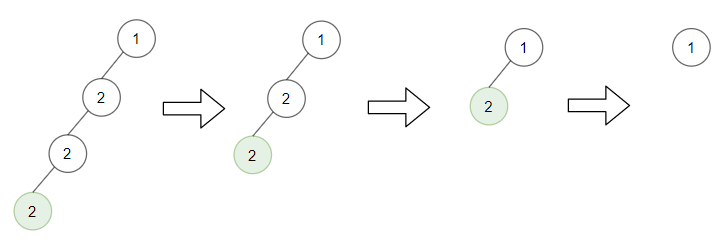
Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 Output: [1] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed at each step.Example 4:
Input: root = [1,1,1], target = 1 Output: []Example 5:
Input: root = [1,2,3], target = 1 Output: [1,2,3]Constraints:
1 <= target <= 1000- Each tree has at most
3000nodes.- Each node's value is between
[1, 1000].
解题思路:最直接的方法就是循环做删除特定值的叶子节点的操作,只能没有符合条件的叶子节点为止。
代码如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution(object): def recursive(self,node,parent,target,direction): if node.left is None and node.right is None and node.val == target: self.flag = True if direction == 'L': parent.left = None else: parent.right = None if node.left != None: self.recursive(node.left,node,target,'L') if node.right != None: self.recursive(node.right,node,target,'R') def removeLeafNodes(self, root, target): """ :type root: TreeNode :type target: int :rtype: TreeNode """ while True: self.flag = False if root.left == None and root.right == None and root.val == target: return None node = root self.recursive(node,None,target,'') if self.flag == False: break return root