在views里边,怎么导入局部配置和全局配置
from s18day24 import settings
#这样导入的是仅仅用户自定义的配置
from django.conf import settings
#这样导入的是全局的配置,包含用户自己定义的配置和内部自带的配置
装饰器怎么写:
装饰器有一个模板,
先定义一个函数,内层再定义一个函数,然后直接将函数名返回。
函数里边写功能,最后return返回回去
模板:
def auth(func): def inner (request,*args,**kwargs): response = func (request,*args,**kwargs) return response return inner def auth(func): def inner(request,*args,**kwargs): # 在执行视图函数之前 user_info = request.session.get(settings.USER_SESSION_KEY) if not user_info: return redirect('/login/') # 执行视图函数 response = func(request,*args,**kwargs) return response return inner
中间件:
装饰器对于一个功能来说,能够做到很好的调节,但是对于某些功能来说,例如验证。
如果功能都需要用到它, 改动起来会比较麻烦。所以这时候我们可以利用中间件。
Django的请求周期:
请求过来路由系统,然后做url的匹配,当匹配成功了以后做路由分发执行视图函数,然后执行视图函数取数据等一系列操作,最后将网页字符串返回给用户。
中间件就是在路由系统前面加的一些规则(类)。

django中间件必须知道的图:
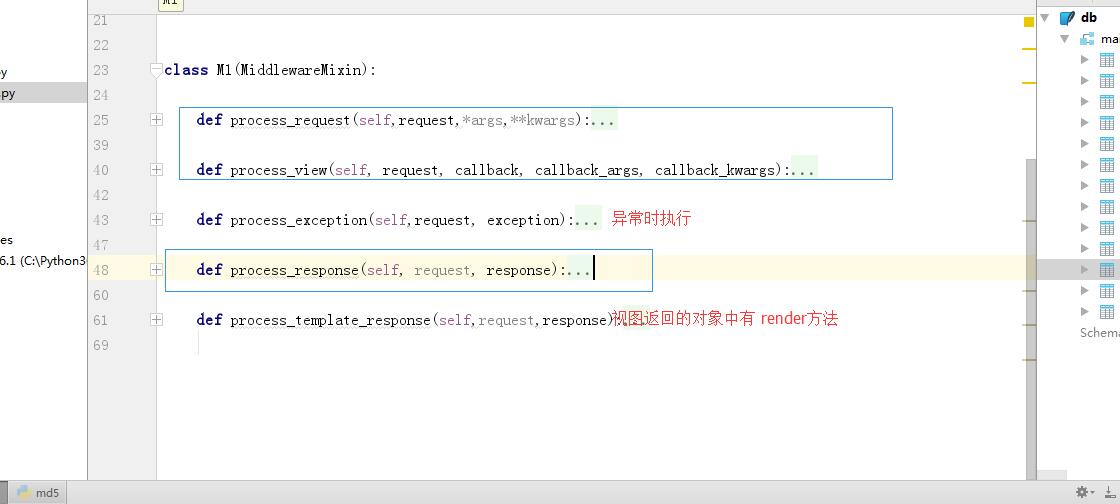
1 process_request: 2 #先正常执行request 3 4 process_views: 5 #先正常执行request,不执行后边的路由系统,然后先执行views,最后执行路由系统 6 7 process_expection: 8 #异常时执行 9 10 process_response: 11 #先正常执行request,然后先执行views,然后执行response,最后执行路由系统 12 13 process_template_response: 14 #视图返回的对象中有render方法
网页有一个模板,写新网页的时候直接继承过来,改想改的内容就可以:
<html> <head> <title></title> <style></style> {% block css %}{% endblock %} </head> <body> {% block body %}{% endblock %} </body> <script></script> {% block body %}{% endblock %} </html> #继承时写上继承哪个网页 {% extends "layout.html" %} #然后后边修改某些模块就可以了
写一个分页的模块:
新建一个目录utils,然后在下面写一个pager.py文件:
""" 分页组件: 使用方法: 视图函数: from utils.pager import Pagination def host(request): all_count = models.Host.objects.all().count() # page_obj = Pagination(request.GET.get('page'),all_count,'/host/') page_obj = Pagination(request.GET.get('page'),all_count,request.path_info) host_list = models.Host.objects.all()[page_obj.start:page_obj.end] return render(request,'host.html',{'host_list':host_list,'page_html': page_obj.page_html()}) HTML: <style> .pager a{ display: inline-block; padding: 3px 5px; margin: 0 3px; border: 1px solid #dddddd; } .pager a.active{ background-color: cadetblue; color: white; } </style> <div class="pager"> {{ page_html}} </div> """ from django.utils.safestring import mark_safe class Pagination(object): def __init__(self,current_page,total_count,base_url, per_page_count=10,max_pager_num=11): """ :param current_page: 用户请求的当前页 :param per_page_count: 每页显示的数据条数 :param total_count: 数据库中查询到的数据总条数 :param max_pager_num: 页面上最多显示的页码 """ self.base_url = base_url total_page_count, div = divmod(total_count, per_page_count) if div: total_page_count += 1 self.total_page_count = total_page_count try: current_page = int(current_page) except Exception as e: current_page = 1 if current_page > total_page_count: current_page = total_page_count self.current_page = current_page self.per_page_count = per_page_count self.total_count = total_count self.max_pager_num = max_pager_num self.half_max_pager_num = int(max_pager_num/2) @property def start(self): return (self.current_page - 1) * self.per_page_count @property def end(self): return self.current_page * self.per_page_count def page_html(self): page_html_list = [] if self.current_page <= 1: prev = "<a href='#'>上一页</a>" else: prev = "<a href='%s?page=%s'>上一页</a>" % (self.base_url,self.current_page - 1,) page_html_list.append(prev) max_pager_num = 11 half_max_pager_num = int(max_pager_num / 2) # 数据总页数 < 页面上最大显示的页码个数 if self.total_page_count <= max_pager_num: page_start = 1 page_end = self.total_page_count else: # 数据比较多,已经超过11个页码 # 如果当前页 <=5,显示 1-11 if self.current_page <= half_max_pager_num: page_start = 1 page_end = max_pager_num else: # 当前页 >=6 if (self.current_page + 5) > self.total_page_count: page_end = self.total_page_count # page_start = current_page - 5 page_start = self.total_page_count - max_pager_num + 1 else: page_start = self.current_page - half_max_pager_num # 当前页 - 5 page_end = self.current_page + half_max_pager_num # 当前页 + 5 for i in range(page_start, page_end + 1): if self.current_page == i: tag = "<a class='active' href='%s?page=%s'>%s</a>" % (self.base_url,i, i,) else: tag = "<a href='%s?page=%s'>%s</a>" % (self.base_url,i, i,) page_html_list.append(tag) # 下一页 if self.current_page >= self.total_page_count: nex = "<a href='#'>下一页</a>" else: nex = "<a href='%s?page=%s'>下一页</a>" % (self.base_url,self.current_page + 1,) page_html_list.append(nex) return mark_safe("".join(page_html_list))
然后在views视图中写入函数:
def host(request): all_count = models.Host.objects.all().order_by('-id').count() # page_obj = Pagination(request.GET.get('page'),all_count,'/host/') page_obj = Pagination(request.GET.get('page'),all_count,request.path_info) host_list = models.Host.objects.all().order_by('-id')[page_obj.start:page_obj.end] return render(request,'host.html',{'host_list':host_list,'page_html': page_obj.page_html()})
前面的models里是这样定义的:
class Host(models.Model): hostname = models.CharField(verbose_name='主机名',max_length=32) ip = models.CharField(max_length=32)# ip = models.GenericIPAddressField(protocol='both') port = models.IntegerField() user = models.ForeignKey(to='UserInfo',default=1) dp = models.ManyToManyField(to="Department")