django rest_framework框架的封装特点
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.exceptions import APIException
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination
from rest_framework.settings import APISettings
from rest_framework.parsers import JSONParser
from rest_framework.filters import OrderingFilter
APIView的请求生命周期
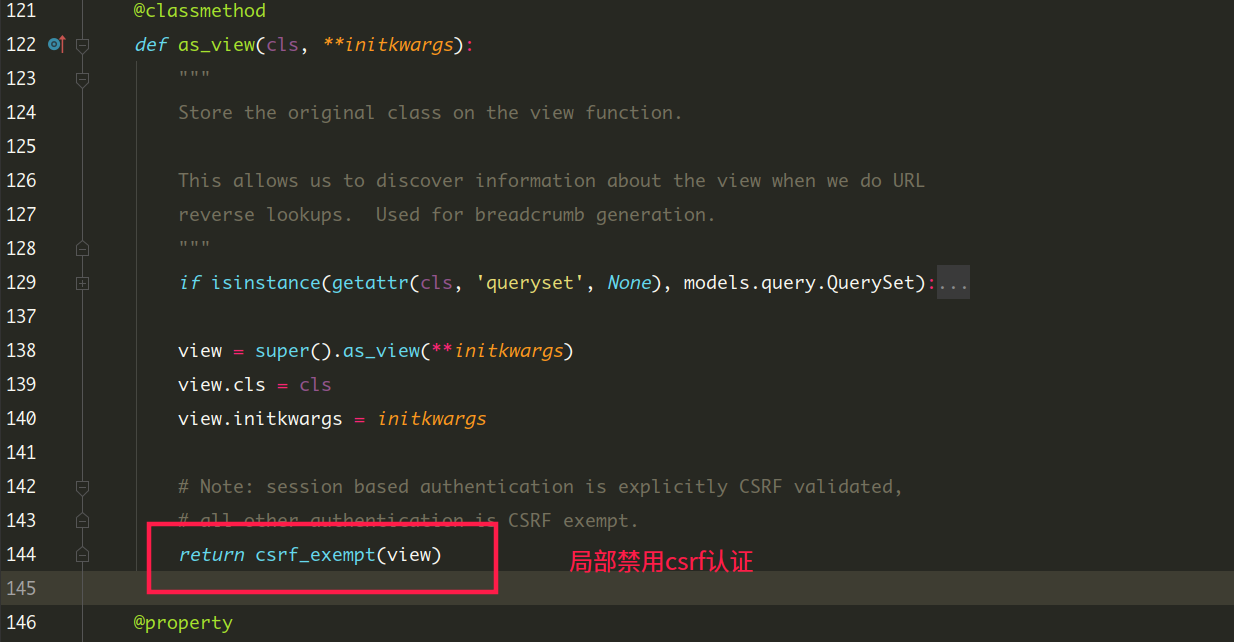
- APIView类继承View类,重写了as_view和dispach方法
- 重写的as_view方法,主体还是View的as_view,只是在返回视图view函数地址时,局部禁用csrf认证
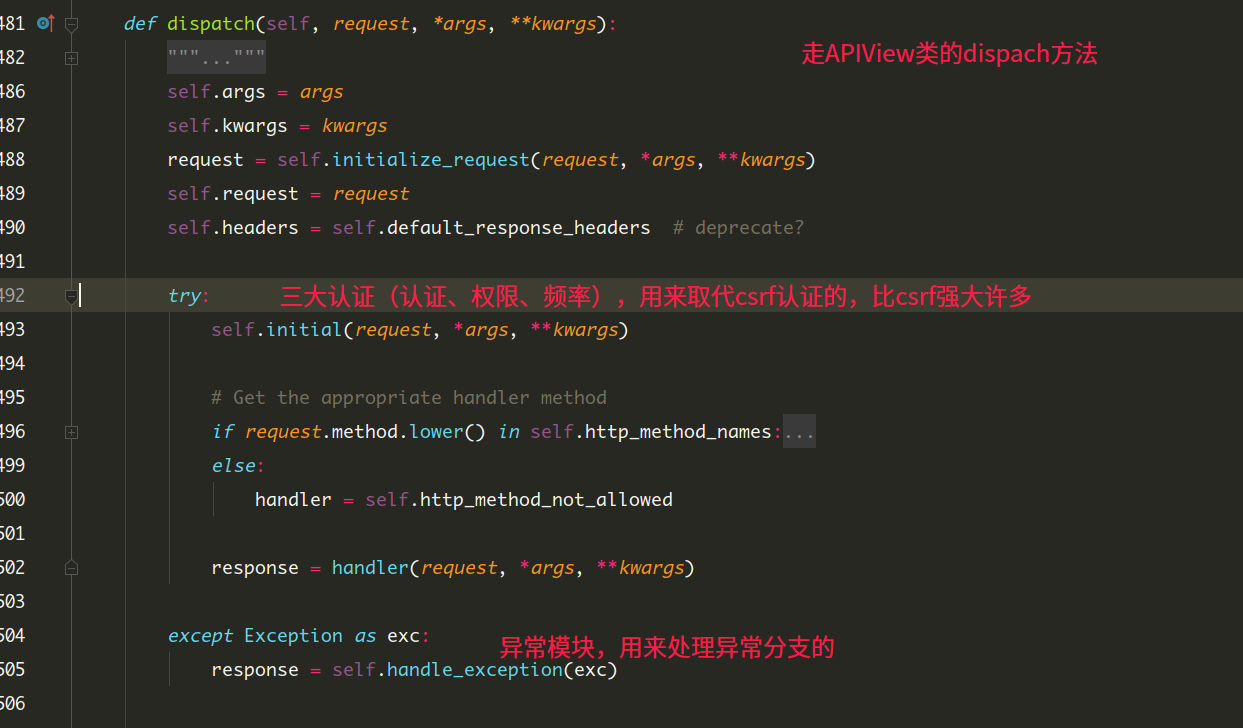
- 重写的dispach方法中:
- 在执行请求逻辑前:请求模块二次封装request,解析模块 解析三种数据包格式。
- 在执行请求逻辑中:异常模块 执行出现任何异常交给异常模块处理
- 在执行请求逻辑后:响应模块二次封装response, 渲染模块处理数据的渲染(响应的数据能JSON化和页面两种渲染)
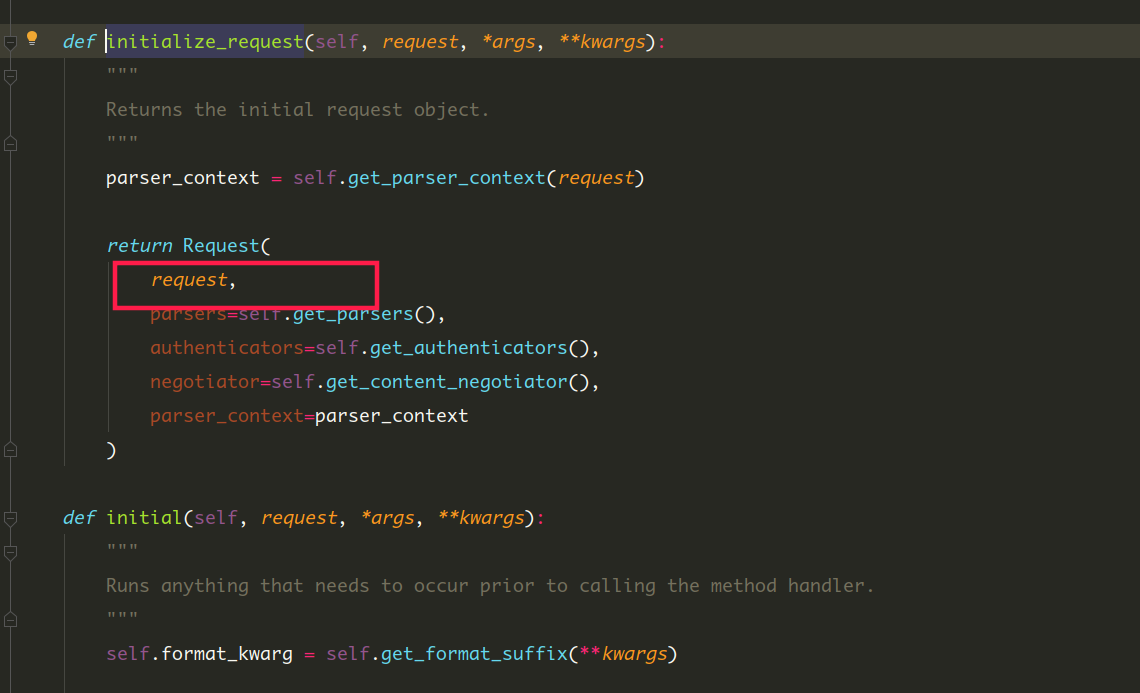
请求模块
-
将wsgi的request对象转化为drf 的Request类的对象
-
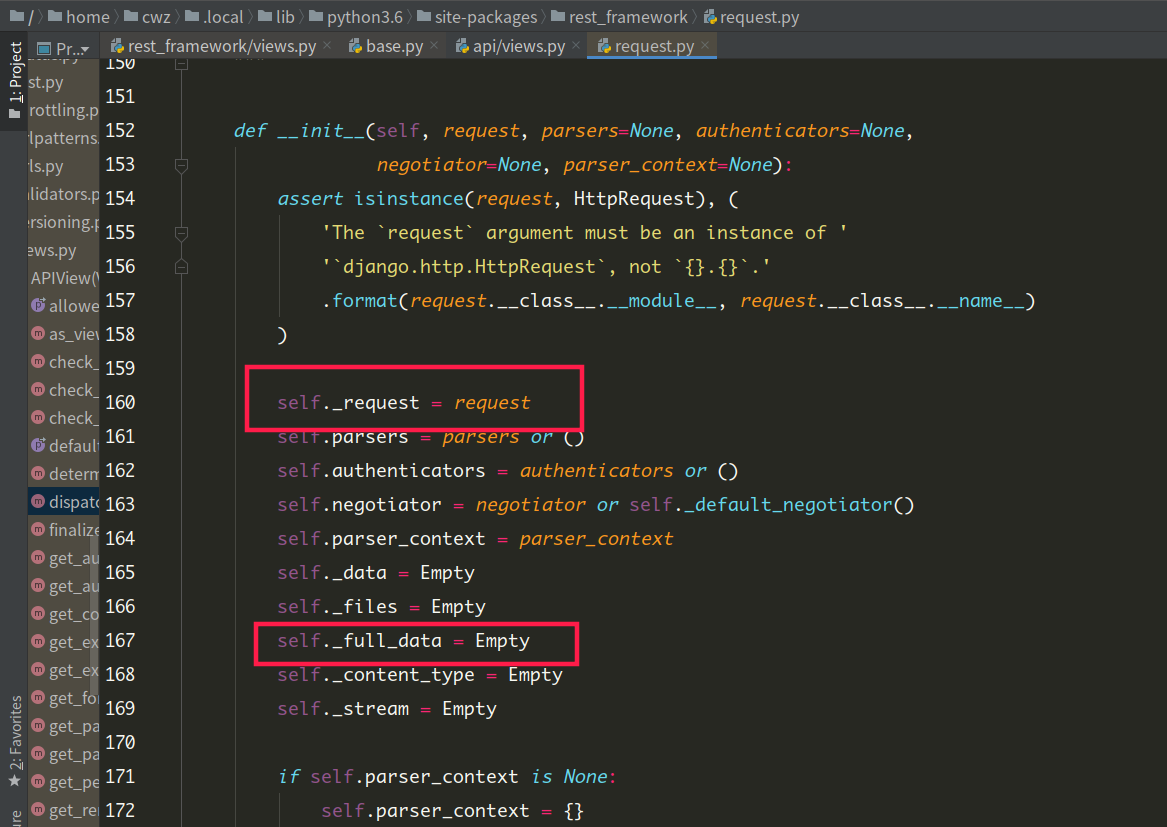
封装后的request对象完全兼容wsgi的request对象,并且将原request保存在新的
request._request中 -
重写了方法,将请求数据的存放位置进行了优化
- 拼接参数放在了:
request.query_params - 数据包参数放在了:
request.data
- 拼接参数放在了:
进入APIView的dispach方法的request=self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) 分析请求模块的源码
class BookView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
print(request.method) # 就是通过__getattr__ 走的是request.method
print(request._request.method) # 在内部将wsgi的request赋值给request._request
print(request.query_params) #走的是方法属性,就是给request._request.GET重新命名
print(request.data) # 走的是方法属性,值依赖于request._full_data
return Response({
'msg': 'view get ok'
})
解析模块
解析模块只处理数据包参数:form-data、x-www-form-urlencoded、json
-
全局配置所有视图类的解析方式,解析配置可以配置三种
REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser' ], } -
局部配置:
from rest_framework.parsers import JSONParser, FormParser,MultiPartParser class BookView(APIView): PARSER_CLASSES = [JSONParser, FormParser, MultiPartParser] def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print(request.method) print(request._request.method) print(request.query_params) print(request.data) return Response({ 'msg': 'view get ok' }) -
配置的查找顺序:局部(视图类的类属性) => 全局(settings文件的drf配置) => 默认(drf的默认配置)
响应模块
- data: 响应数据
- status: 响应的网络状态码
- template_name:drf完成前后端不分离返回页面,但是就不可以返回data
- headers:响应头,一般不规定,走默认的
- exception:一般异常响应,会将其设置成True,默认False,不设置也没事
- content_type:默认就是application / json,不需要处理
渲染模块
Postman请求结果是json,浏览器请求结果是页面
-
全局配置:可以用于所有视图类
REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer', # 上线后尽量关闭 ], } -
局部配置:只是适用于当前视图类
from rest_framework.renderers import JSONRenderer, BrowsableAPIRenderer class BookAPIView(APIView): RENDERER_CLASSES = [BrowsableAPIRenderer, JSONRenderer] def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print(request.method) print(request._request.method) print(request.query_params) print(request.data) return Response({ 'msg': 'view get ok' })
异常模块
通过异常模块的源码分析,知道exception_handler函数只处理客户端异常,不处理服务端异常,所以要自己重写exception_handler方法:
在settings文件中配置自定义的异常模块
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'api.exception.exception_handler'
}
在django项目 应用下新建一个文件exception.py:
from rest_framework.views import exception_handler as drf_exception_handler
from rest_framework.response import Response
def exception_handler(exc, context):
# 先给drf处理客户端异常,如果response为None,代表服务端异常,需要自己处理
response = drf_exception_handler(exc, context)
detail = '%s - %s -%s' % (context.get('view'), context.get('request').method, exc)
if not response: # 服务端错误
response = Response({
'detail': detail
})
else:
response.data = {'detail': detail}
# 核心: 要将response.data.get('detail')信息记录到日志文件中
return response