1. 首先安装
npm install d3 --save-dev
或者cnpm install d3 --save-dev (需要先安装cnpm,本人喜欢用这个国内镜像比较快)以防万一,然后看package.json
2. 引入:main.js
import * as d3 from "d3"; Vue.prototype.$d3 = d3; window.d3 = d3; //暂时设置为全局变量
3. demo代码: demo源码参考地址
<template>
<div style=" 100%;height: 100%;">
<svg version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" xml:space="preserve"
width="960" height="500"> </svg>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
var svg = d3.select("svg"),
width = +svg.attr("width"),
height = +svg.attr("height"),
color = d3.scaleOrdinal(d3.schemeCategory10);
var a = {
id: "a"
},
b = {
id: "b"
},
c = {
id: "c"
},
nodes = [a, b, c],
links = [];
var simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes)
.force("charge", d3.forceManyBody().strength(-1000))
.force("link", d3.forceLink(links).distance(200))
.force("x", d3.forceX())
.force("y", d3.forceY())
.alphaTarget(1)
.on("tick", ticked);
var g = svg.append("g").attr("transform", "translate(" + width / 2 + "," + height / 2 + ")"),
link = g.append("g").attr("stroke", "#000").attr("stroke-width", 1.5).selectAll(".link"),
node = g.append("g").attr("stroke", "#fff").attr("stroke-width", 1.5).selectAll(".node");
restart();
d3.timeout(function() {
links.push({
source: a,
target: b
}); // Add a-b.
links.push({
source: b,
target: c
}); // Add b-c.
links.push({
source: c,
target: a
}); // Add c-a.
restart();
}, 1000);
d3.interval(function() {
nodes.pop(); // Remove c.
links.pop(); // Remove c-a.
links.pop(); // Remove b-c.
restart();
}, 2000, d3.now());
d3.interval(function() {
nodes.push(c); // Re-add c.
links.push({
source: b,
target: c
}); // Re-add b-c.
links.push({
source: c,
target: a
}); // Re-add c-a.
restart();
}, 2000, d3.now() + 1000);
function restart() {
// Apply the general update pattern to the nodes.
node = node.data(nodes, function(d) {
return d.id;
});
node.exit().transition()
.attr("r", 0)
.remove();
node = node.enter().append("circle")
.attr("fill", function(d) {
return color(d.id);
})
.call(function(node) {
node.transition().attr("r", 8);
})
.merge(node);
// Apply the general update pattern to the links.
link = link.data(links, function(d) {
return d.source.id + "-" + d.target.id;
});
// Keep the exiting links connected to the moving remaining nodes.
link.exit().transition()
.attr("stroke-opacity", 0)
.attrTween("x1", function(d) {
return function() {
return d.source.x;
};
})
.attrTween("x2", function(d) {
return function() {
return d.target.x;
};
})
.attrTween("y1", function(d) {
return function() {
return d.source.y;
};
})
.attrTween("y2", function(d) {
return function() {
return d.target.y;
};
})
.remove();
link = link.enter().append("line")
.call(function(link) {
link.transition().attr("stroke-opacity", 1);
})
.merge(link);
// Update and restart the simulation.
simulation.nodes(nodes);
simulation.force("link").links(links);
simulation.alpha(1).restart();
}
function ticked() {
node.attr("cx", function(d) {
return d.x;
})
.attr("cy", function(d) {
return d.y;
})
link.attr("x1", function(d) {
return d.source.x;
})
.attr("y1", function(d) {
return d.source.y;
})
.attr("x2", function(d) {
return d.target.x;
})
.attr("y2", function(d) {
return d.target.y;
});
}
},
}
</script>
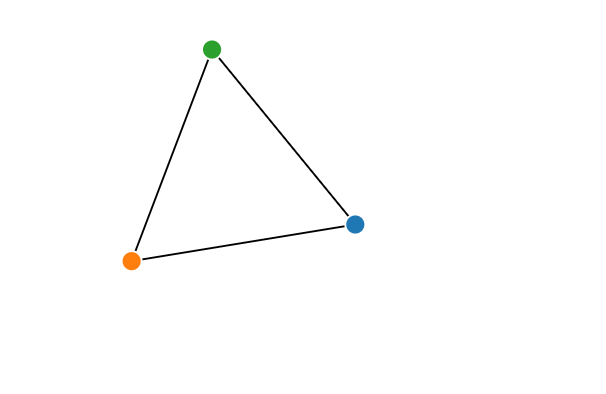
4. demo效果图
案例2: 渲染一个Vue组件,它使用常规的D3 DOM操作呈现一个简单的折线图:
<template>
<svg width="500" height="270">
<g style="transform: translate(0, 10px)">
<path :d="line" />
</g>
</svg>
</template>
<script>
import * as d3 from 'd3';
export default {
name: 'vue-line-chart',
data() {
return {
data: [99, 71, 78, 25, 36, 92],
line: '',
};
},
mounted() {
this.calculatePath();
},
methods: {
getScales() {
const x = d3.scaleTime().range([0, 430]);
const y = d3.scaleLinear().range([210, 0]);
d3.axisLeft().scale(x);
d3.axisBottom().scale(y);
x.domain(d3.extent(this.data, (d, i) => i));
y.domain([0, d3.max(this.data, d => d)]);
return { x, y };
},
calculatePath() {
const scale = this.getScales();
const path = d3.line()
.x((d, i) => scale.x(i))
.y(d => scale.y(d));
this.line = path(this.data);
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="sass" scoped>
svg
margin: 25px;
path
fill: none
stroke: #76BF8A
stroke- 3px
</style>非常酷,即使它没有公开任何属性并且数据是硬编码的,它很好地将视图从逻辑中分离出来,并且使用Vue钩子,方法和data对象,现象和上图一样的
