一、获取当前工作目录
在shell中我们可以直接输入命令pwd 来显示当前的工作目录,在C程序中调用getcwd函数可以获取当前的工作目录。函数声明:
char *getcwd(char * buf,size_t size);
需要头文件: #include<unistd.h>
getcwd函数把当前工作目录存入buf中,如果目录名超出了参数size长度,函数返回NULL,如果成功,返回buf。例如:
char strpwd[512]; memset(strpwd,0,sizeof(strpwd)); getcwd(strpwd,sizeof(strpwd)-1); printf("当前工作路径是:%s ",strpwd); printf("%d ",getcwd(strpwd,sizeof(strpwd)-1)); printf("%d ",sizeof(strpwd)-1);
二、切换工作目录
函数声明:
int chdir(const char *path);
就像我们在shell中使用cd命令切换目录一样,在C程序中使用chdir函数来改变工作目录。
返回值:0-切换成功;非0-失败。
三、目录的创建和删除
在shell中可以通过mkdir/rmdir命令来创建/删除目录,C程序中用mkdir/rmdir函数来创建/删除目录。
创建目录函数的声明:
int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
mode的含义将按open系统调用的O_CREAT选项中的有关定义设置,当然,它还要服从umask的设置况,是不是看不明白?那先固定填0755,注意,0不要省略哦,它表示八进制。 例如:
mkdir("/tmp/aaa",0755); // 创建/tmp/aaa目录
删除目录函数的声明:
int rmdir(const char *pathname);
四、获取目录中的文件列表
在实际开发中,文件是存放在目录中的,在处理文件之前,必须先知道目录中有哪些文件,所以要获取目录中的文件列表。涉及到的库函数如下:
1、包含头文件
#include <dirent.h>
2、相关的库函数
打开目录的函数opendir的声明:
DIR *opendir(const char *pathname);
读取目录的函数readdir的声明:
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
关闭目录的函数closedir的声明:
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
3、数据结构
1)目录指针DIR
DIR *目录指针名;
2)struct dirent结构体
每调用一次readdir函数会返回一个struct dirent的地址,存放了本次读取到的内容,它的原理与fgets函数读取文件相同。
struct dirent { long d_ino; // inode number 索引节点号 off_t d_off; // offset to this dirent 在目录文件中的偏移 unsigned short d_reclen; // length of this d_name 文件名长 unsigned char d_type; // the type of d_name 文件类型 char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; // file name文件名,最长255字符 };
我们只需要关注结构体的d_type和d_name成员,其它的不必关心。
d_name文件名或目录名。
d_type描述了文件的类型,有多种取值,最重要的是8和4,8-常规文件(A regular file);4-目录(A directory),其它的暂时不关心。
4、读取目录
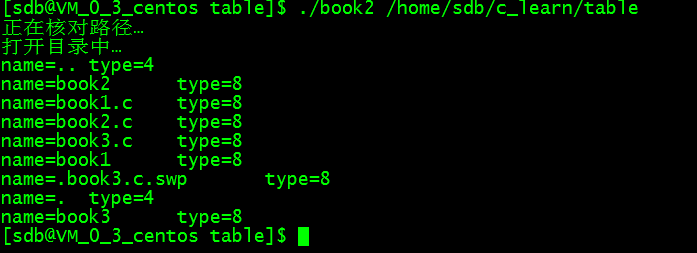
/* * 程序名:book123.c,此程序用于演示读取目录下的文件名信息 * 作者:C语言技术网(www.freecplus.net) 日期:20190525 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <dirent.h> int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { printf("请指定目录名。 "); return -1; } DIR *dir; // 定义目录指针 // 打开目录 if ( (dir=opendir(argv[1])) == 0 ) return -1; // 用于存放从目录中读取到的文件和目录信息 struct dirent *stdinfo; while (1) { // 读取一条记录并显示到屏幕 if ((stdinfo=readdir(dir)) == 0) break; printf("name=%s,type=%d ",stdinfo->d_name,stdinfo->d_type); } closedir(dir); // 关闭目录指针 }
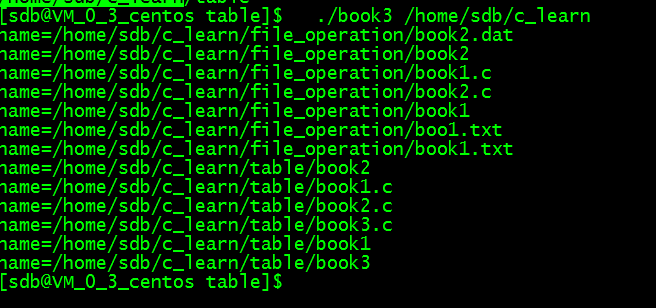
运行效果

五、应用经验
在实际开发中,对目录的操作并不会像book123.c那样简单。
实际需求是这样的,文件存放在某目录中,该目录下还会有多级子目录,程序员想要的是列出该目录及其子目录下全部的文件名。
例如存在/home/wucz/tmp目录,其子目录结构和文件如下:

/* * 程序名:book124.c,此程序用于演示读取目录及其子目录下全部的文件信息 * 作者:C语言技术网(www.freecplus.net) 日期:20190525 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <dirent.h> // 列出目录及子目录下的文件 int ReadDir(const char *strpathname); int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { printf("请指定目录名。 "); return -1; } // 列出目录及子目录下的文件 ReadDir(argv[1]); } // 列出目录及子目录下的文件 int ReadDir(const char *strpathname) { DIR *dir; // 定义目录指针 char strchdpath[256]; // 子目录的全路径 if ( (dir=opendir(strpathname)) == 0 ) return -1; // 打开目录 struct dirent *stdinfo; // 用于存放从目录读取到的文件和目录信息 while (1) { if ((stdinfo=readdir(dir)) == 0) break; // 读取一记录 if (strncmp(stdinfo->d_name,".",1)==0) continue; // 以.开始的文件不读 if (stdinfo->d_type==8) // 如果是文件,显示出来 printf("name=%s/%s ",strpathname,stdinfo->d_name); if (stdinfo->d_type==4) // 如果是目录,再调用一次ReadDir { sprintf(strchdpath,"%s/%s",strpathname,stdinfo->d_name); ReadDir(strchdpath); } } closedir(dir); // 关闭目录指针 }
运行效果