每天学习一点点 编程PDF电子书、视频教程免费下载:
http://www.shitanlife.com/code
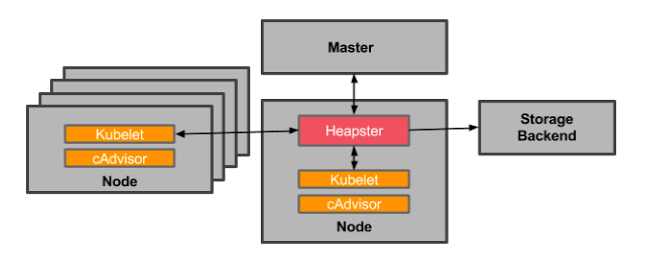
1、浅析整个监控流程
heapster是一个监控计算、存储、网络等集群资源的工具,以k8s内置的cAdvisor作为数据源收集集群信息,并汇总出有价值的性能数据(Metrics):cpu、内存、网络流量等,然后将这些数据输出到外部存储,如InfluxDB,最后就可以通过相应的UI界面显示出来,如grafana。 另外heapster的数据源和外部存储都是可插拔的,所以可以很灵活的组建出很多监控方案,如:Heapster+ElasticSearch+Kibana等等。
2、创建k8s资源对象
使用官方提供的yml文件有一些小问题,请参考以下改动和说明:
2.1、创建InfluxDB资源对象
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: influxdb
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: influxdb
spec:
containers:
- name: influxdb
image: k8s.gcr.io/heapster-influxdb-amd64:v1.3.3
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: influxdb-storage
volumes:
- name: influxdb-storage
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: monitoring-influxdb
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- nodePort: 31001
port: 8086
targetPort: 8086
selector:
k8s-app: influxdb注意:这里我们使用NotePort暴露monitoring-influxdb服务在主机的31001端口上,那么InfluxDB服务端的地址:http://[host-ip]:31001 ,记下这个地址,以便创建heapster和为grafana配置数据源时,可以直接使用。
2.1、创建Grafana资源对象
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: monitoring-grafana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: grafana
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: grafana
spec:
containers:
- name: grafana
image: k8s.gcr.io/heapster-grafana-amd64:v4.4.3
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs
name: ca-certificates
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /var
name: grafana-storage
env:
- name: INFLUXDB_HOST
value: monitoring-influxdb
- name: GF_SERVER_HTTP_PORT
value: "3000"
# The following env variables are required to make Grafana accessible via
# the kubernetes api-server proxy. On production clusters, we recommend
# removing these env variables, setup auth for grafana, and expose the grafana
# service using a LoadBalancer or a public IP.
- name: GF_AUTH_BASIC_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED
value: "true"
- name: GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_ROLE
value: Admin
- name: GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL
# If you're only using the API Server proxy, set this value instead:
# value: /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/monitoring-grafana/proxy
value: /
volumes:
- name: ca-certificates
hostPath:
path: /etc/ssl/certs
- name: grafana-storage
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
# For use as a Cluster add-on (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cluster/addons)
# If you are NOT using this as an addon, you should comment out this line.
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: monitoring-grafana
name: monitoring-grafana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
# In a production setup, we recommend accessing Grafana through an external Loadbalancer
# or through a public IP.
# type: LoadBalancer
# You could also use NodePort to expose the service at a randomly-generated port
type: NodePort
ports:
- nodePort: 30108
port: 80
targetPort: 3000
selector:
k8s-app: grafana注意:这里我们使用NotePort暴露monitoring-grafana服务在主机的30108上,那么Grafana服务端的地址:http://registry.wuling.com:30108 ,通过浏览器访问,为Grafana修改数据源,如下: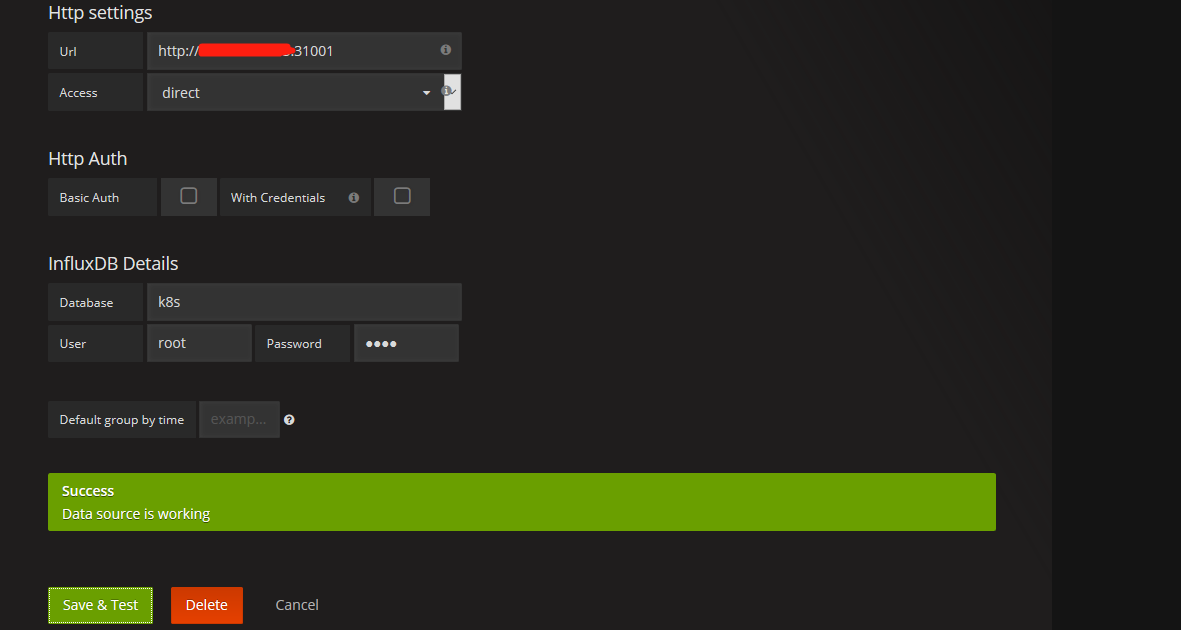
标红的地方,为上一步记录下的InfluxDB服务端的地址。
2.2、创建Heapster资源对象
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: heapster
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: heapster
spec:
serviceAccountName: heapster
containers:
- name: heapster
image: k8s.gcr.io/heapster-amd64:v1.4.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- /heapster
- --source=kubernetes:https://kubernetes.default
- --sink=influxdb:http://150.109.39.33:31001 # 这里填写刚刚记录下的InfluxDB服务端的地址。
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
# For use as a Cluster add-on (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cluster/addons)
# If you are NOT using this as an addon, you should comment out this line.
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: Heapster
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8082
selector:
k8s-app: heapster--source 为heapster指定获取集群信息的数据源。参考:https://github.com/kubernetes/heapster/blob/master/docs/source-configuration.md
--sink 为heaster指定后端存储,这里我们使用InfluxDB,其他的,请参考:https://github.com/kubernetes/heapster/blob/master/docs/sink-owners.md
这里heapster留下了一个的坑,请继续往下看,当我部署完heapster,查看Heapster容器组的标准输出: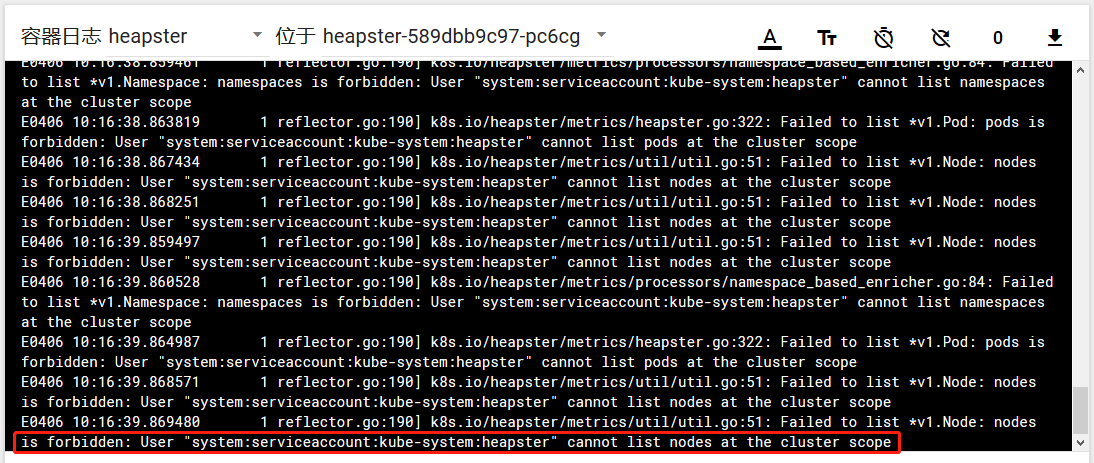
很多人都以为是https或者k8s配置的问题,于是去就慌忙的去配置InSecure http方式,导致坑越来越深,透明度越来越低,更是无从下手,我也是这样弄了很久,都较上劲了,此处省略一万字。。。,当这些路子都走遍了,再次品读下面的原文:
才发现是权限的问题,heaster默认使用一个令牌(Token)与ApiServer进行认证,通过查看heapster.yml发现 serviceAccountName: heapster ,现在明白了吧,就是heaster没有权限,那么如何授权呢-----给heaster绑定一个有权限的角色就行了,如下:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: heapster
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system当创建heapster资源的时候,直接把这段代码加上,就行了。
3、从不同维度查看应用程序性能指标
在k8s集群,应用程序的性能指标,需要从不同的维度(containers, pods, services, and whole clusters)进行统计。以便于使用户深入了解他们的应用程序是如何执行的以及可能出现的应用程序瓶颈。
3.1、通过dashboard查看集群概况
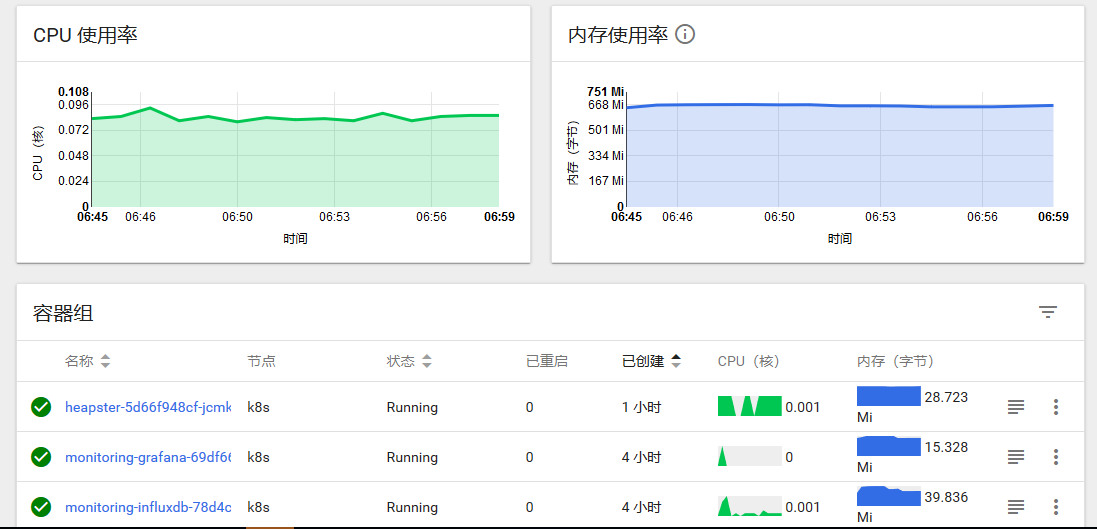
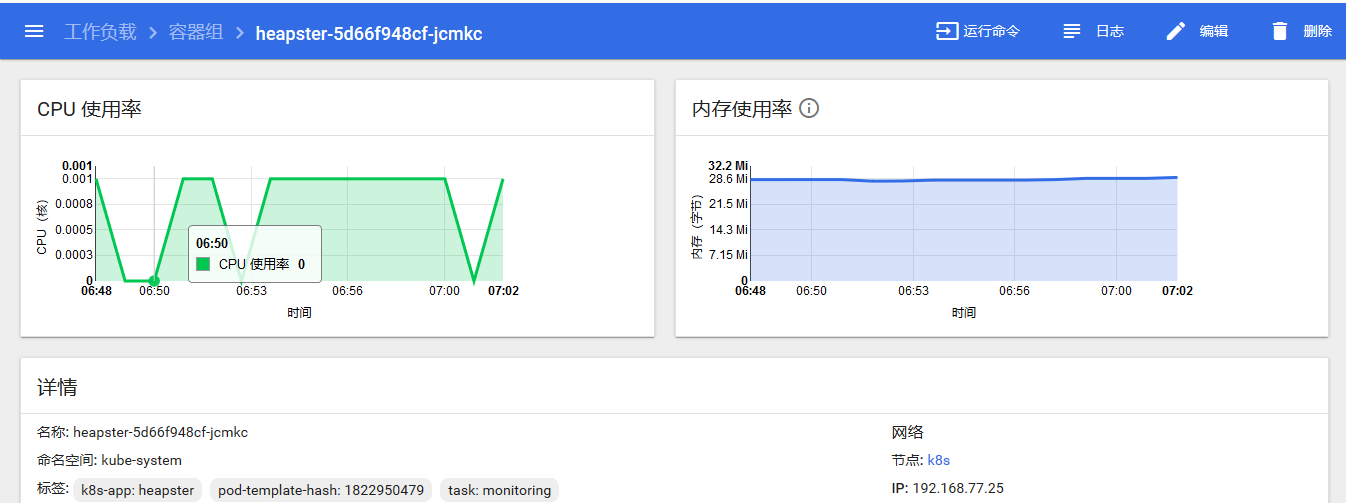
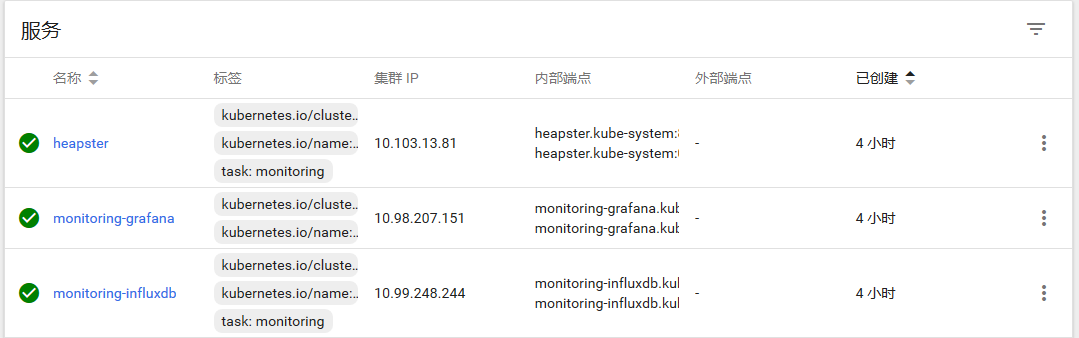
整个监控方案部署成功后,从上图可以看到,在不同粒度/维度下,dashboard上可以呈现对象的具体CPU和内存使用率。
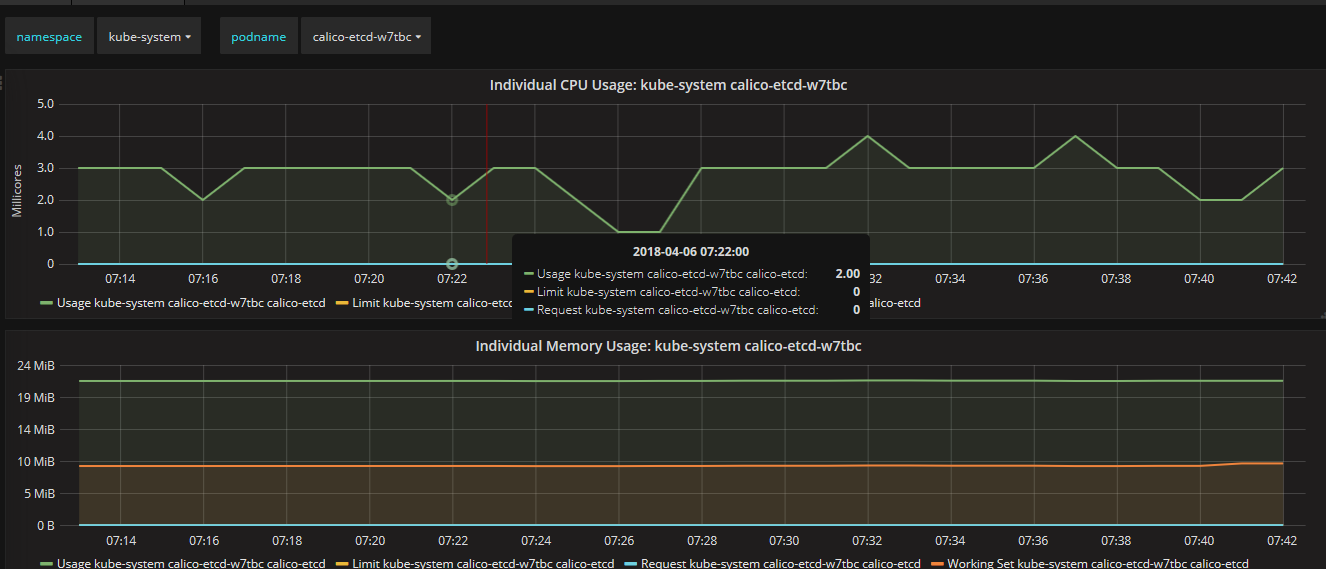
3.2、通过Grafana查看集群详情(cpu、memory、filesystem、network)
通过Grafana可以查看某个Node或Pod的所有资源使用率,一部分截图如下所示: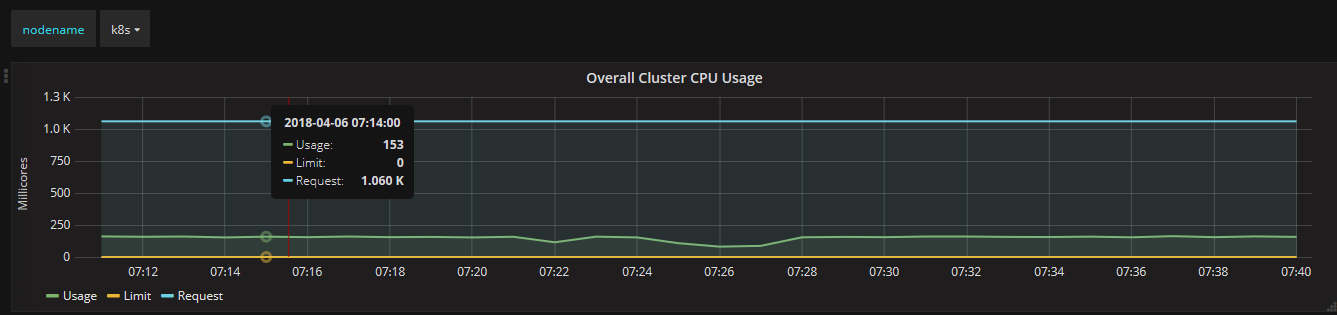
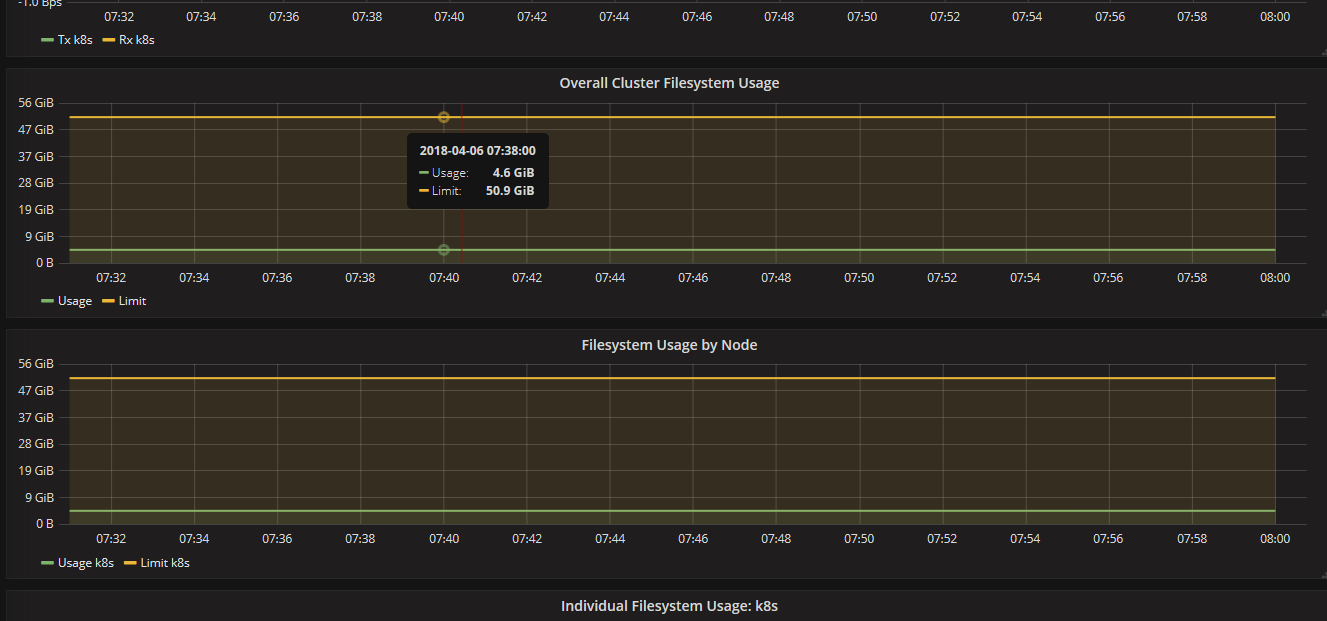
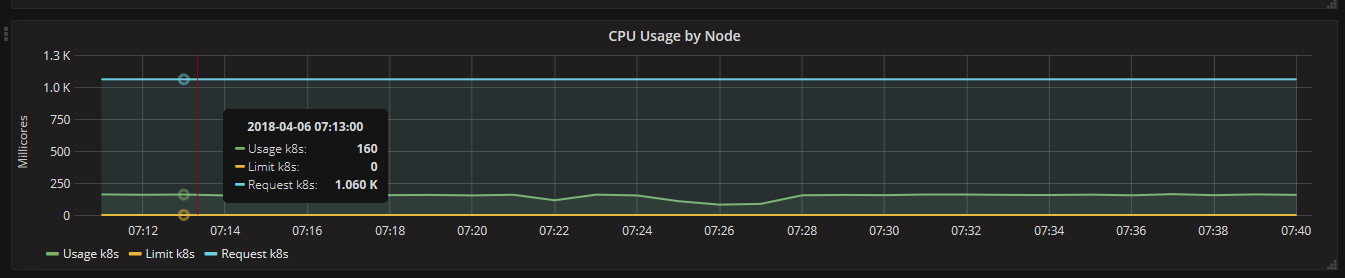
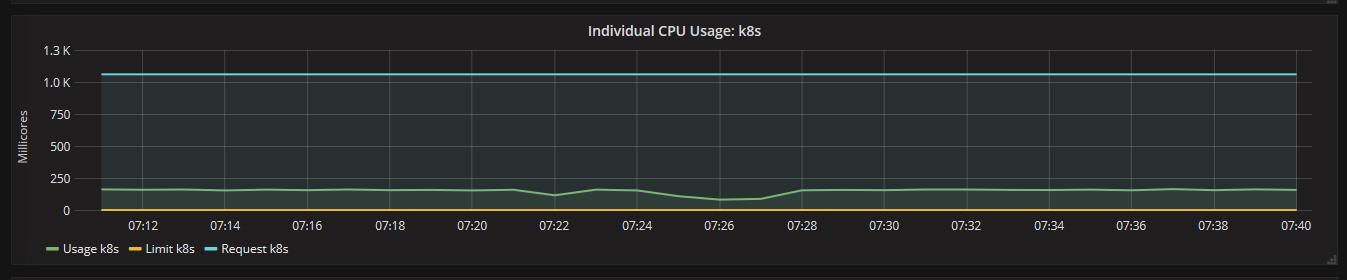
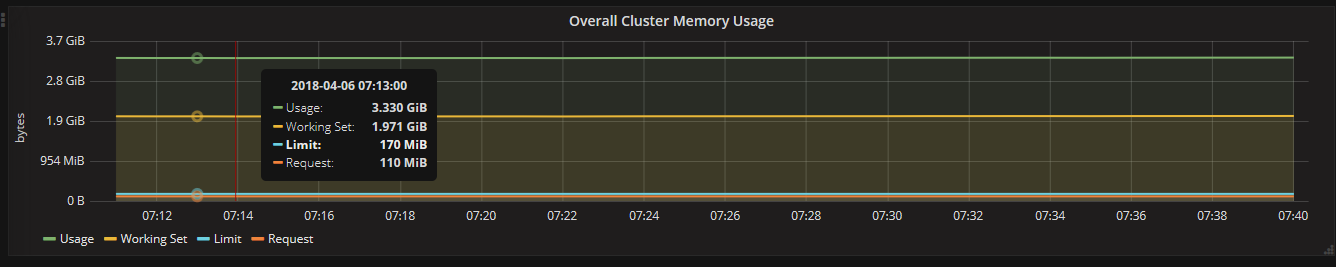
4、总结
监控是一个非常大的话题,监控的目的是为预警,预警的目的是为了指导系统自愈。只有把 监控=》预警 =》自愈 三个环节都完成了,才算的上是一个真正意义的监控系统,所以这个系列会一直朝着这个目标努力下去,请大家继续关注。如果有什么好的想法,欢迎评论区交流。