在Linux驱动中使用notifier通知链
背景
在驱动分析中经常看到fb_notifier_callback,现在趁有空学习一下。
介绍
linux中的观察者模式是最显然的就是“通知链”模型。
在linux中,如果你想让自己的行为被别人注意到,那么你就要申请一条通知链,然后让所有关注你自己的实体注册到这条通知链上。
最终的效果就是一旦发生一件值得关注的事情,所有的注册者都可以得到通知。
内核中通知链的基础文件就两个:
- 头文件:
include/linux/notifier.h - 源文件:
kernel/notifier.c
头文件和源文件所有代码加起来不超过1000行,总体来说还是比较好懂。
参考:
- https://blog.csdn.net/Wuhzossibility/article/details/8079025
- https://www.cnblogs.com/armlinux/archive/2011/11/11/2396781.html
我自己花了点时间写了一条类似的通知链,但是跨平台(应用程序、Linux内核、单片机)上都可以使用:
介绍
大多数内核子系统都是相互独立的,因此某个子系统可能对其它子系统产生的事件感兴趣。
为了满足这个需求,也即是让某个子系统在发生某个事件时通知其它的子系统,Linux内核提供了通知链的机制。通知链表只能够在内核的子系统之间使用,而不能够在内核与用户空间之间进行事件的通知。
通知链表是一个函数链表,链表上的每一个节点都注册了一个函数。当某个事情发生时,链表上所有节点对应的函数就会被执行。
所以对于通知链表来说有一个通知方与一个接收方。在通知这个事件时所运行的函数由被通知方决定,实际上也即是被通知方注册了某个函数,在发生某个事件时这些函数就得到执行。
图例
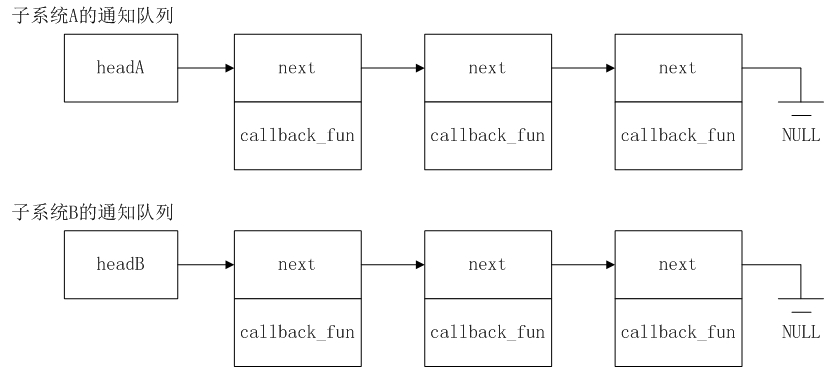
对系统A来说,它自己的通知队列上被被人注册了n个回调函数,那么当系统A的某个事件发生时,它必须去遍历自己的事件队列headA,然后依次去尝试执行队列里每个回调函数。
实际上,通知链上的注册的函数不一定都会执行。
对子系统B来说,情况是一样的。
原型定义
核心数据结构
#include <linux/notifier.h>
typedef int (*notifier_fn_t)(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long action, void *data);
struct notifier_block {
int (*notifier_call)(struct notifier_block *, unsigned long, void *);
struct notifier_block *next;
int priority;
};
解析:
notifier_call:当相应事件发生时应该调用的函数,由被通知方提供;notifier_block *next:用于链接成链表的指针;priority:回调函数的优先级,一般默认为0。
拓展
内核代码中一般把通知链命名为xxx_chain, xxx_nofitier_chain这种形式。
围绕核心数据结构notifier_block,内核定义了四种通知链类型。
原子通知链
struct atomic_notifier_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct notifier_block *head;
};
通知链元素的回调函数(当事件发生时要执行的函数)在中断或原子操作上下文中运行,不允许阻塞。
可阻塞通知链
struct blocking_notifier_head {
struct rw_semaphore rwsem;
struct notifier_block *head;
};
通知链元素的回调函数在进程上下文中运行,允许阻塞。
SRCU 通知链
struct srcu_notifier_head {
struct mutex mutex;
struct srcu_struct srcu;
struct notifier_block *head;
};a
可阻塞通知链的一种变体。
原始通知链
struct raw_notifier_head {
struct notifier_block *head;
};
对通知链元素的回调函数没有任何限制,所有锁和保护机制都由调用者维护。
网络子系统使用的通知链就是此类型。
API
实际上,除了基本通知链以外,还有其他有3种通知链:原子通知链、可阻塞通知链和原始通知链。
显然,实际上这3种也只是对基本通知链的操作函数进行了封装的。
声明与初始化
在定义自己的通知链的时候,心里必须明确,自己需要一个什么样类型的通知链,是原子的、可阻塞的还是一个原始通知链。
内核中用于定义并初始化不同类通知链的函数分别是:
// 定义并初始化一个名为name的原子通知链
#define ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
struct atomic_notifier_head name =
ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
// 定义并初始化一个名为name的阻塞通知链
#define BLOCKING_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
struct blocking_notifier_head name =
BLOCKING_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
//定义并初始化一个名为name的原始通知链
#define RAW_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
struct raw_notifier_head name =
RAW_NOTIFIER_INIT(name)
如果我们已经有一个通知链的对象(不通过上述的宏定义来声音通知链),Linux还提供了一组用于初始化一个通知链对象的API
// 分别用于初始化 对应类型的 通知链
ATOMIC_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
RAW_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(name)
/* srcu_notifier_heads must be initialized and cleaned up dynamically */
extern void srcu_init_notifier_head(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh);
下面的声明以及初始化更加常见(以原子通知链为例):
static struct atomic_notifier_head dock_notifier_list;
ATOMIC_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&dock_notifier_list);
或者
struct aw9523_kpad_platform_data {
// ...
#if defined(CONFIG_FB)
struct notifier_block fb_notif;
#endif
};
// ...
pdata->fb_notif.notifier_call = fb_notifier_callback;
操作
我们以最普通的通知链来介绍,其他都是类似的。
static int notifier_chain_register(struct notifier_block **nl, struct notifier_block *n);
static int notifier_chain_unregister(struct notifier_block **nl, struct notifier_block *n);
static int __kprobes notifier_call_chain(struct notifier_block **nl, unsigned long val, void *v, int nr_to_call, int *nr_calls);
这最基本的三个接口分别实现了对通知链上通知块的注册、卸载和遍历操作。
注册
static int notifier_chain_register(struct notifier_block **nl, struct notifier_block *n);
描述:被通知一方(other_subsys_x)通过notifier_chain_register向特定的chain注册回调函数
参数解析:
卸载
static int notifier_chain_unregister(struct notifier_block **nl, struct notifier_block *n);
描述:被通知一方(other_subsys_x)通过notifier_chain_unregister取消chain通知
通知事件发生
static int __kprobes notifier_call_chain(struct notifier_block **nl, unsigned long val, void *v, int nr_to_call, int *nr_calls);
描述: 通知者通过notifier_call_chain来通知其他的子系统(other_subsys_x)。
notifier_call_chain会按照通知链上各成员的优先级顺序执行回调函数(notifier_call_x);回调函数的执行现场在notifier_call_chain进程地址空间。
参数解析:
返回值:
把最后一个被调用的回调函数的返回值作为它的返回值。
NOTIFY_XXX的形式:
// include/linux/notifier.h
/* 对事件视而不见 */
#define NOTIFY_DONE 0x0000
/* 事件正确处理 */
#define NOTIFY_OK 0x0001
/*由notifier_call_chain检查,看继续调用回调函数,还是停止,_BAD和_STOP中包含该标志 */
#define NOTIFY_STOP_MASK 0x8000
/*事件处理出错,不再继续调用回调函数 */
#define NOTIFY_BAD (NOTIFY_STOP_MASK|0x0002)
/* 回调出错,不再继续调用该事件回调函数 */
#define NOTIFY_STOP (NOTIFY_OK|NOTIFY_STOP_MASK)
其他通知链对应的操作
其他类型的通知链的操作也是类似的:
// 原子通知链
int atomic_notifier_chain_register(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int atomic_notifier_chain_unregister(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int atomic_notifier_call_chain(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh, unsigned long val, void *v);
// 可阻塞通知链、SRCU通知链
int blocking_notifier_chain_register(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int blocking_notifier_chain_cond_register(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int srcu_notifier_chain_register(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int blocking_notifier_call_chain(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh,unsigned long val, void *v);
int srcu_notifier_call_chain(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh, unsigned long val, void *v);
int blocking_notifier_chain_unregister(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int srcu_notifier_chain_unregister(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
//原始通知链
int raw_notifier_chain_register(struct raw_notifier_head *nh, struct notifier_block *nb);
int raw_notifier_chain_unregister(struct raw_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb);
int raw_notifier_call_chain(struct raw_notifier_head *nh, unsigned long val, void *v);
上述这三类通知链的基本API又构成了内核中其他子系统定义、操作自己通知链的基础。
例如,Netlink定义了一个原子通知链,所以,它对原子通知链的基本API又封装了一层。
可阻塞通知链里的SRCU通知链,由于使用条件较苛刻,限制条件较多,所以使用的机会不是很多,在2.6.32的内核里只有cpufreq.c在用这种类型的通知链。
使用步骤
步骤很简单:
1、申明struct notifier_block结构
2、编写notifier_call函数
3、调用特定的事件通知链的注册函数,将notifier_block注册到通知链中
如果内核组件需要处理够某个事件通知链上发出的事件通知,其就该在初始化时在该通知链上注册回调函数。
例子
notifier_chain机制只能在内核个子系统间使用,因此,这里使用3个模块:test_notifier_chain_0、test_notifier_chain_1、test_notifier_chain_2;
当 test_notifier_chain_2通过module_init初始化模块时发出事件TESTCHAIN_2_INIT;
然后 test_notifier_chain_1作出相应的处理:打印 test_notifier_chain_2正在初始化。
test_chain_0.c
通知、被通知者的功能实现。
申明一个通知链;
1、 向内核注册通知链;
2、 定义事件;
3、 导出符号,(因而必须最先安装、最后退出)
#include <linux/notifier.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything() */
#define TESTCHAIN_INIT 0x52U
static RAW_NOTIFIER_HEAD(test_chain);
/* define our own notifier_call_chain */
static int call_test_notifiers(unsigned long val, void *v)
{
return raw_notifier_call_chain(&test_chain, val, v);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(call_test_notifiers);
/* define our own notifier_chain_register func */
static int register_test_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb)
{
int err;
err = raw_notifier_chain_register(&test_chain, nb);
if(err)
goto out;
out:
return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(register_test_notifier);
static int __init test_chain_0_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "I'm in test_chain_0
");
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_chain_0_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "Goodbye to test_chain_0
");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("fishOnFly");
module_init(test_chain_0_init);
module_exit(test_chain_0_exit);
test_chain_1.c
被通知者。
1、定义回调函数;
2、 定义notifier_block;
3、 向chain_0注册notifier_block;
#include <linux/notifier.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything() */
extern int register_test_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb);
#define TESTCHAIN_INIT 0x52U
/* realize the notifier_call func */
int test_init_event(struct notifier_block *nb, unsigned long event,
void *v)
{
switch(event){
case TESTCHAIN_INIT:
printk(KERN_DEBUG "I got the chain event: test_chain_2 is on the way of init
");
break;
default:
break;
}
return NOTIFY_DONE;
}
/* define a notifier_block */
static struct notifier_block test_init_notifier = {
.notifier_call = test_init_event,
};
static int __init test_chain_1_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "I'm in test_chain_1
");
register_test_notifier(&test_init_notifier); // 由chain_0提供的设施
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_chain_1_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "Goodbye to test_clain_l
");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("fishOnFly");
module_init(test_chain_1_init);
module_exit(test_chain_1_exit);
test_chain_2.c
通知者。
发出通知链事件
#include <linux/notifier.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything() */
extern int call_test_notifiers(unsigned long val, void *v);
#define TESTCHAIN_INIT 0x52U
static int __init test_chain_2_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "I'm in test_chain_2
");
call_test_notifiers(TESTCHAIN_INIT, "no_use");
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_chain_2_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_DEBUG "Goodbye to test_chain_2
");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("fishOnFly");
module_init(test_chain_2_init);
module_exit(test_chain_2_exit);
Makefile
# Comment/uncomment the following line to disable/enable debugging
# DEBUG = y
# Add your debugging flag (or not) to CFLAGS
ifeq ($(DEBUG),y)
DEBFLAGS = -O -g -DSCULL_DEBUG # "-O" is needed to expand inlines
else
DEBFLAGS = -O2
endif
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
# call from kernel build system
obj-m := test_chain_0.o test_chain_1.o test_chain_2.o
else
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
endif
clean:
rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions
depend .depend dep:
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -M *.c > .depend
ifeq (.depend,$(wildcard .depend))
include .depend
endif
测试
$ sudo dmesg -c > /dev/null
$ sudo insmod. /test_chain_0.ko
$ sudo insmod. /test_chain_1.ko
$ sudo insmod. /test_chain_2.ko
$ dmesg
[3215807.747547] I'm in test_chain_0
[3215809.759092] I'm in test_chain_1
[3215811.225148] I'm in test_chain_2
[3215811.225150] I got the chain event: test_chain_2 is on the way of init
$ sudo rmmod. /test_chain_2.ko
$ sudo rmmod. /test_chain_1.ko
$ sudo rmmod. /test_chain_0.ko
$ dmesg
[3215850.606570] Goodbye to test_chain_2
[3215853.346589] Goodbye to test_clain_l
[3215855.510567] Goodbye to test_chain_0